Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Timezone
The timezones and different settings to manage and manipulate the date and time-related fields to store and retrieve zone-related times are supported by MySQL. By default, whenever MySQL is installed on the machine, the timezone variables are set such that the timezone set in the system that is the machine’s operating system is referred to. We can further change and manipulate these variables as per our convenience and necessity to store and use date and time values in MySQL. We can change the timezone values by adding or subtracting the required time in hours and minutes from UTC or by specifying the timezone in the named format per region and zone.
This article delves into the workings of time zones in MySQL, explores pertinent variables, and explains how to retrieve and modify their values for manipulating time zones. Additionally, it demonstrates the manual loading of timezone-related tables in MySQL and provides examples relevant to time zones.
Functions of MySQL Timezone
- MySQL searches for the system’s set timezone and assigns the retrieved timezone value from the host machine to the system variable named system_time_zone when it starts. After completing this process during server startup, the value of this variable remains unchanged.
- To change the system’s time zone during server startup, you can set the value of the environment variable TZ before executing the mysqld command.
- Besides that, one more method exists to set the system time zone. If you use mysqld_safe mode for your server, you can select the value for the –timezone option.
- The allowed values that can be set to the TZ variable or –timezone option depend on your operating system. Refer to your operating system’s documentation for acceptable timezone values.
- The current and global values of the time_zone system variable determine the time zone used by the MySQL server. By default, the value at the beginning of the time_zone variable is SYSTEM, meaning MySQL uses the time zone of the host machine’s operating system.
- We can set the value of the time_zone global variable only if we have SUPER privileges assigned or SYSTEM_VARIABLE_ADMIN privilege using the SET GLOBAL time_zone command.
- The SET time_zone command allows the session variable for each client session to override the time zone value set to SYSTEM or global time zone, setting it to the required time zone value for that specific session.
- The time zone set at the session level affects all the zone-sensitive values. The values displayed by the Now() and CURTIME() functions and the columns that have TIMESTAMP as the datatype are affected when storing and retrieving such values.
- The values stored and retrieved in the columns with datatype DATE, TIME, or DATETIME are unaffected by the session time zone settings. Along with that, functions such as UTC_TIMESTAMP() also remain unchanged.
- The time zone can be set at the global level or session level in either of the two formats that define the offset from the UTC in string format in hours and minutes format hh: mm by adding like ‘-5:30’, ‘+5:30’, etc. or subtracting that value or named time zones like America or New_York for America or Asia/Kolkata for Indian Standard Time, i.e., UTC+05:30.
- The second format requires loading and populating the information tables related to time zones in your MySQL server to specify time zones in the named format.
Populating Information Tables Related to the Timezone
Installing MySQL on your machine creates various tables to store time zone-related information inside the MySQL schema. However, the installation only creates these tables, while loading and populating them is necessary for using the named time zones and other similar functionalities.
We can load the time zone tables manually. Some operating systems, such as macOS, Solaris, Linux, and FreeBSD, have a database that stores the zone information. We can use this file to keep the same information in our MySQL schema’s zone tables. The path where you will most often find this file is /usr/share/zoneinfo directory. We can use the mysql_tzinfo_to_sql program for populating zone tables from the system zone information database using the following command:
mysql_tzinfo_to_sql /usr/share/zoneinfo | mysql -u username -p passwordWhich considers that you are using the account with username as the name and password as the password for that account and have to write privileges on MySQL schema. For operating systems that do not have such zonal information, you can use downloadable packages.
Examples of MySQL Timezone
The following query statement can be used to get the global time zone value.
SELECT @@GLOBAL.time_zone;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output with SYSTEM as the value specifying that the MySQL global time zone is the same as the operating system’s time zone.
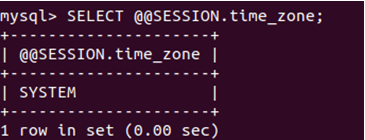
The following query statement can be used to get the session time zone value.
SELECT @@SESSION.time_zone;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output with SYSTEM as the value specifying that the MySQL time zone is the same as the operating system’s time zone.
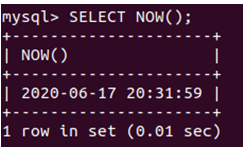
Let us retrieve the current date and time using the NOW() function that gives the following output:
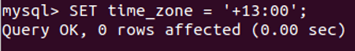
SELECT NOW();Let us change the time zone for the current session using the following command:
SET time_zone = '+13:00';That gives the following output:
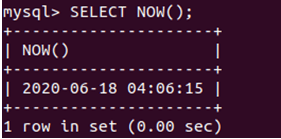
Let us again execute the same command to retrieve the current date and time:
SELECT NOW();That gives the following output:
Conclusion
MySQL provides various variables that help us maintain and manage time zone-related information in MySQL. We can get and set the values of the time zone by changing its value on the global or session level or inside the configuration file.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Timezone” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.