Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Offset
We use MySQL Offset to specify the row from which we want to retrieve the data. To be precise, determine which row to start retrieving from. Offset is used along with the LIMIT. Here, LIMIT is nothing but to restrict the number of rows from the output. In combination, when you use LIMIT with the offset, it means that we are trying to retrieve data from the given offset to the limit value. We can use this with the SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE command.
Syntax:
select * from <table_name> limit [row_count] offset [offset_value];or
select * from <table_name> limit [offset_value,] [row_count];In this syntax:
- The [offset_value] specifies the offset of the first row to return. The offset of the first row is 0, not 1.
- The [row_count] specifies the maximum number of rows to return.
How Does MySQL Offset Work?
Now let us see how the LIMIT and OFFSET work in MySQL along with the example:
create table Test(id integer, message varchar(100));
insert into Test(id, message) values(1, "Hello, Hi I am Fred");
insert into Test(id, message) values(4, "Fred received message");
insert into Test(id, message) values(3, "Articles has been checked");
insert into Test(id, message) values(2, "Offset example");
insert into Test(id, message) values(7, "limit example");
insert into Test(id, message) values(8, "Example");
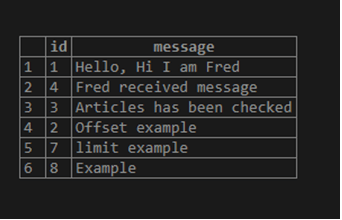
select * from Test;Output:
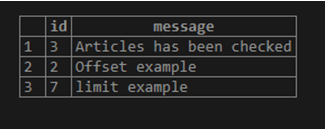
select * from Test limit 3 offset 2;The above query is to get data from the offset value “2” and restrict the data to the specified “2” rows value of LIMIT. Output for the above query can be seen in the diagram:
Examples of MySQL Offset
Now let us see real-time examples and apply the LIMIT and OFFSET. Create the table below:
CREATE TABLE BANK_CUST_DATA
(
CUST_ID INT,
BANK_ID VARCHAR(10),
BANK_NAME VARCHAR(10),
BANK_IFSC VARCHAR(20),
ACCOUNT_AMT INT,
CREDIT_CARD_AVAILABILITY VARCHAR(2),
CREDIT_LIMIT INT
);Insert data into the table:
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (343,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 900000,'Y',1200000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (263,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 120000,'Y',987600 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (113,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 876543,'Y',765000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (893,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 987654,'Y',890000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (983,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 789654,'Y',900000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (583,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 589654,'Y',900000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (783,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 889654,'Y',900000 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (383,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 389654,'N',0 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (183,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 289654,'N',0 );
INSERT INTO BANK_CUST_DATA VALUES (883,'SBI_12','SBI','UTX1000546', 189654,'N',0 );
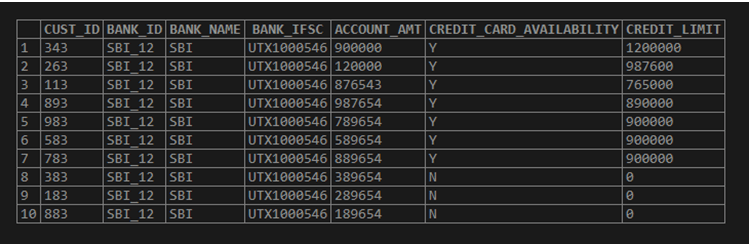
select * from BANK_CUST_DATA;Output:
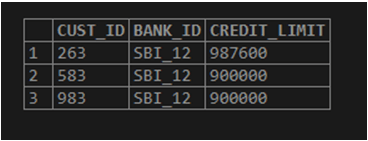
Now let us find the top 3 customer IDs with the highest credit_limit using the limit and offset.
SELECT
CUST_ID,
BANK_ID,
CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM
BANK_CUST_DATA
ORDER BY CREDIT_LIMIT DESC
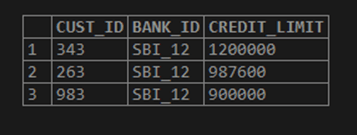
LIMIT 0, 3;Output:
The example shows that the third value is the “900000” credit limit for more than one “cust_id”. We get only three rows as we have set the limit to 3. Row for “900000” can be randomized for each execution of the query to restrict. We can apply the RANK function here for the table and get the data.
Now let us find the 3 customer IDs that start from the second-highest “credit_limit” using the limit and offset.
SELECT
CUST_ID,
BANK_ID,
CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM
BANK_CUST_DATA
ORDER BY CREDIT_LIMIT DESC
LIMIT 1, 3;Output:
Here we are getting the second-highest “credit_limit” with limit 3;
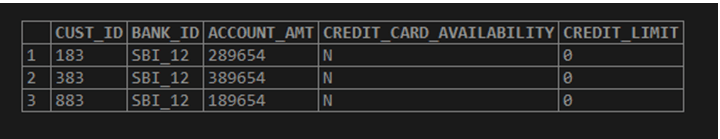
Now let us find the 3 customer id with the lowest “credit_limit” using the limit and offset.
SELECT
CUST_ID,
BANK_ID,
ACCOUNT_AMT,
CREDIT_CARD_AVAILABILITY,
CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM
BANK_CUST_DATA
ORDER BY CREDIT_LIMIT ASC
LIMIT 0, 3;Output:
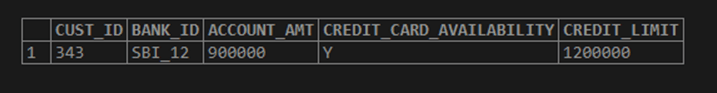
Now let us find only the first customer id with the highest “credit_limit” using the limit and offset.
SELECT
CUST_ID,
BANK_ID,
ACCOUNT_AMT,
CREDIT_CARD_AVAILABILITY,
CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM
BANK_CUST_DATA
ORDER BY CREDIT_LIMIT DESC
LIMIT 0, 1;Output:
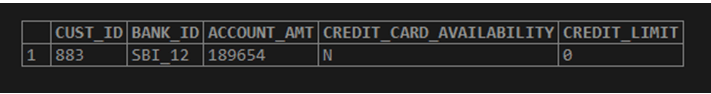
Now let us find only the first customer id with the lowest “credit_limit” using the limit and offset.
SELECT
CUST_ID,
BANK_ID,
ACCOUNT_AMT,
CREDIT_CARD_AVAILABILITY,
CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM
BANK_CUST_DATA
ORDER BY CREDIT_LIMIT ASC
LIMIT 0, 1;Output:
Conclusion
MySQL Offset is used to specify from which row we want the data to retrieve. To be precise, specify which row to start retrieving from. Offset is used along with the LIMIT. Here, LIMIT is nothing but to restrict the number of rows from the output. In combination, when you use LIMIT with the offset, it means that we are trying to retrieve data from the given offset to the limit value. We can use this with the SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE commands. OFFSET value starts from 0 (start value).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Offset” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.