Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Create users
The following article provides an outline for MySQL create users. MySQL user is a row in the table named user in the database of the MySQL server, which gives us the information for attributes like login, account permissions, and MySQL user account. Making a user in the table for various purposes, like accessing and managing the databases, is crucial. We create user statements in MySQL to create new users in the database. It is used to validate the resource limit, user’s role, and password management of the new user.
It also controls the initially blocked or unblocked accounts. Mandatory to have overall permissions to create a user in the table or to have the insert permissions for the schema if make user statement is used. If we try to create a user already existing in the table, it gives us a technical error message; however, if we add an if not exist clause in the create user statement, it will provide us with a warning message for each existing user instead of an error message.
Syntax to create a user:
Create user [if not exists] account_name identified by 'password';The account_name in the create statement has two portions. Both parts are separated by @. The part before @ is the name given to the new user, and the part after @ is the hostname through which the created user will connect with the server, which is my local host.
username@hostnameThe hostname in the account_name is optional. It means the user will get connected to any host from the various options present on the server. Account name lacking hostname can also be written as username@%.
Example of MySQL Create User Statement
Given below is the example mentioned:
Steps to create a user in MySQL server:
Step 1: Login into the MySQL server from the command line as the root user.
mysql -u root –p‘ u’ is the root username, and ‘p’ is the root password.
Step 2: Check for all existing users in the present working server.
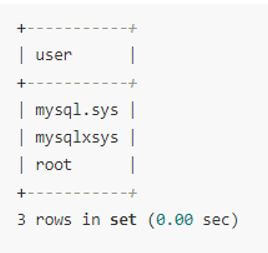
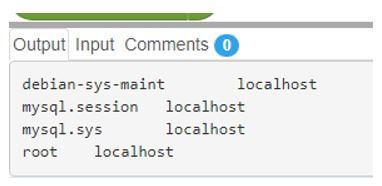
SELECT user from mysql.user;MySQL is the database’s name, and the user is the table’s name.
We can also write the above statement as:
Step 1:
use mysql;Step 2:
select user from user;The output of a list of users:
Step 3: Create a new user.
CREATE USER abc@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'abc123';Step 4: We will use the IF NOT EXISTS clause with the CREATE USER statement.
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS abc@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'abc123';List of Privileges provided by Server
Given below is the list of privileges provided by the server:
- ALL PRIVILEGES: It gives all privileges to a new user.
- CREATE: It gives the user privilege to create databases and tables.
- DROP: It gives the user privilege to drop databases and tables.
- DELETE: It gives the user privilege to delete rows from a specific table.
- INSERT: It allows the user to insert rows into a table.
- SELECT: It provides the user with the privilege to read a database.
- UPDATE: It gives the user the right to update table rows.
Syntax of Grant Privileges to the User
Given below is the syntax for granting privileges to the user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'newuser'@'localhost';- Below is the query if we want to share all privileges with a user.
Code:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO abc@localhost;‘*’ allows the user to read, edit, execute, and perform all tasks in all the databases and tables.
- If you want to give specific privileges to a newly created user, execute the following command.
Code:
GRANT CREATE, SELECT, INSERT ON * . * TO abc@localhost;- Given below is the query to flush all the privileges of a user.
Code:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;- If we want to see the existing privileges for the user, execute the following command.
Code:
SHOW GRANTS for username;- Given below is the query to list fields of the user table.
Code:
desc mysql.user;Output:
Code:
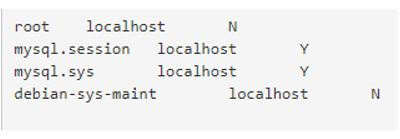
select user,host,account_locked from mysql.user;Output:
- Given below is the query to see the current user.
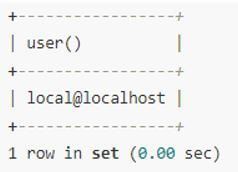
Code:
SELECT user();Output:
Or
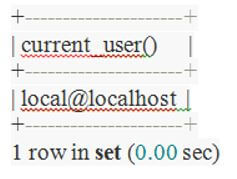
Code:
SELECT current_user();Output:
Code:
SELECT User, host FROM mysql.user;Output:
- If you want to display unique usernames.
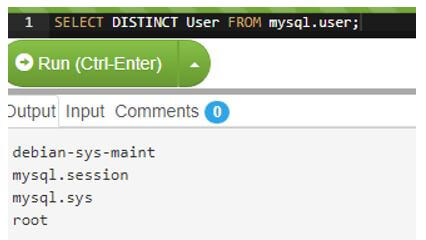
Code:
SELECT DISTINCT User FROM mysql.user;Output:
- Given below is the query to Delete a user.
Code:
Drop user 'user'@'localhost';- Given below is the query to Revoke privileges from the user.
Code:
Revoke all privileges on database_name from 'user'@'localhost';- Given below is the query to view a list of all users.
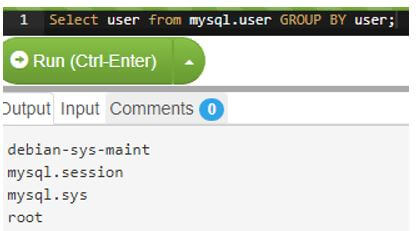
Code:
select user from mysql.user GROUP BY user;Output:
- Given below is the query to delete a specific user.
Code:
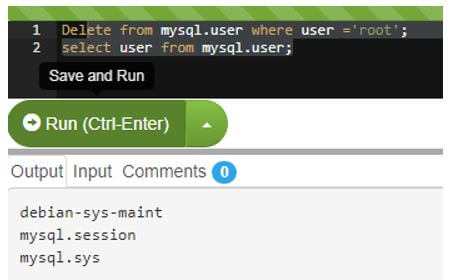
Delete from mysql.user where user ='username';Where username is the name of the user which we want to delete.
Output:
So, after the deletion of the root user, we are left with only three users.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how to create and delete new users. We have also seen how to grant privileges to users and revoke privileges and different types of privileges granted to the users in a MySQL database. We have also seen how to list users in the present server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Users” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.