Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Window Functions
Windows function in MySQL helps to solve a query problem. The operation is performed on a set of query rows while keeping the number of rows intact. Windows function is easily understood when explained in comparison with aggregate functions. On a broader note, both operate on a subset of the result set. But the significant difference between these two functions is that when the aggregate function reduces the number of rows in the result, the windows function returns the same number of rows.
Syntax
General syntax:
window_function (expression)
OVER ( [partition_definition]
[order_defenition]
)Where,
- window_funtion -the name of the window function
- expression – field on which function is performed
- partition_definition – constraint for partition
- order_definition – order of result set
The part detailed within the OVER() clause is not mandatory, though the use of it will help in easier results.
How do Window Functions work in MySQL?
The window functions work closely to aggregate functions. Let’s compare the operations of both functions.
Scenario: segregate the total marks of each student in the class
Code:
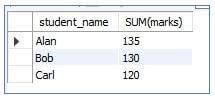
SELECT student_name, SUM (marks)
from students
GROUP BY student_name;Output:
Here we used the aggregate function SUM () to get the total, and we saw the number of rows was reduced.
Code:
Using window function:
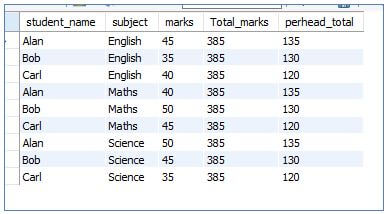
SELECT student_name, subject, marks,
SUM (marks) OVER () AS Total_marks,
SUM (marks) OVER (PARTITION BY student_name) AS perhead_total
From students
ORDER BY subject;Analyzing the query: The total_marks column is derived as a sum of marks of all students in all subjects, whereas the column perhead_total is, to sum up, the marks per student for all three subjects.
Output:
A window function can be used only within a SELECT query, and an OVER() clause is mandatory. The OVER() clause can be left blank or hold clauses like PARTITION BY, ORDER BY, etc. Almost all aggregate functions that allow an OVER() clause and certain non-aggressive functions can be used as window functions, with the OVER() clause mandatory.
Window Functions in MySQL
More window functions as below:
1. ROW NUMBER ( )
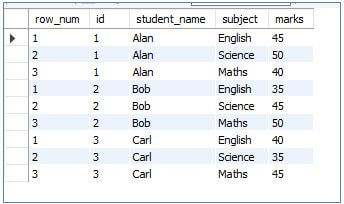
This function is used to insert row numbers into each row. As a window function, it will add rows to the small groups of result sets and will have the following syntax:
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY student_name) AS row_num,
id,
student_name,
subject,
marks
FROM students
ORDER BY student_name;Output:
2. RANK()
This function will provide every row with rank, but it is not always a consecutive number like Row_number().
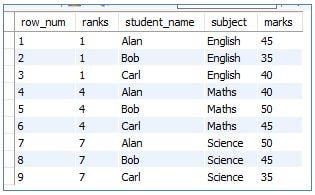
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by subject) as row_num,
RANK () OVER (ORDER BY subject) as ranks,
student_name,
subject,
marks
FROM students;Output:
3. DENSE RANK ()
This function is similar to the RANK() function except that even when divided into smaller groups of the total result set, the DENSE_RANK() function will assign consecutive rank numbers for each group.
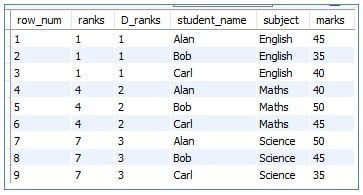
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by subject) as row_num,
RANK () OVER (ORDER BY subject) as ranks,
DENSE_RANK () OVER (ORDER BY subject) as D_ranks,
student_name,
subject,
marks
FROM students;Output:
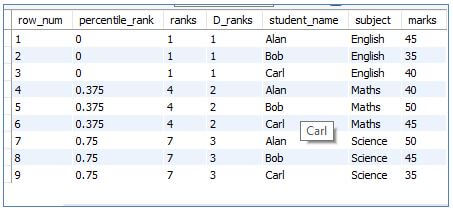
4. PERCENT_RANK()
This function calculates the percentile of a row within the small result set and will return a value ranging from 0 to 1 for every row. Also, note that the function will return 0 for the first-row set.
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by subject) as row_num,
PERCENT_RANK () over (order by subject) as percentile_rank,
RANK () OVER (ORDER BY subject) as ranks,
DENSE_RANK () OVER (ORDER BY subject) as D_ranks,
student_name,
subject,
marks
FROM students;Output:
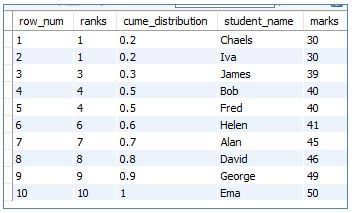
5. CUME_DIST()
This will return the Cumulative Distribution of a value over a set of values in the result set. The value returned will be within 0 to 1, and any repetition in the column value will end up in the same cumulative distribution.
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by marks) as row_num,
RANK () OVER (ORDER BY marks) as ranks,
CUME_DIST () over (order by marks) as cume_distribution,
student_name,
marks
FROM marklist;Output:
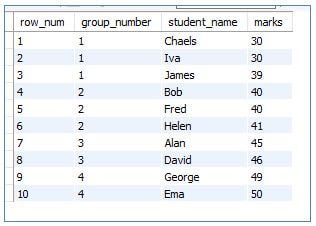
6. NTILE()
This helps to split the result set rows into a specified number of groups based on the partition_by and order_by clauses provided.
Code:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by marks) as row_num,
NTILE (4) over (order by marks) as group_number,
student_name,
marks
FROM marklist;Output:
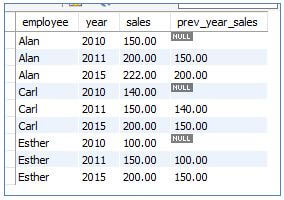
7. LAG()
LAG() is a window function that returns the value to the previous rows in a sorted and partitioned result set.
Code:
SELECT
employee,
year,
sales,
LAG (sales, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY employee ORDER BY year) prev_year_sales
FROM sales;Output:
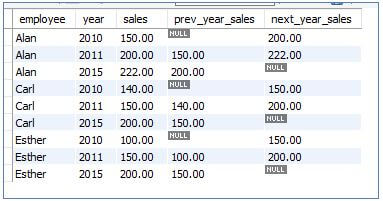
8. LEAD()
This function does the exact opposite operation of the lag() function. The Lead() function will return the values ahead in the partitioned and sorted result set.
Code:
SELECT
employee,
year,
sales,
LAG (sales, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY employee ORDER BY year) prev_year_sales,
LEAD (sales, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY employee ORDER BY year) next_year_sales
FROM sales;Output:
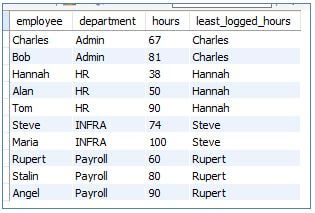
9. FIRST VALUE()
This window function returns the first row among a partitioned sorted result set.
Code:
SELECT
employee,
department,
hours,
FIRST_VALUE (employee) OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY hours) AS least_logged_hours
FROMloggedhours;Output:
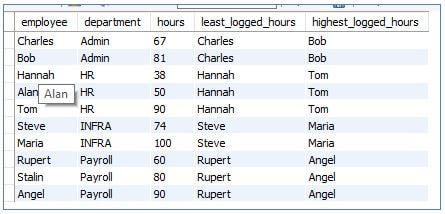
10. LAST VALUE()
This window function returns the first row among a partitioned sorted result set. The syntax is as follows:
Code:
SELECT
employee,
department,
hours,
FIRST_VALUE (employee) OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY hours) AS least_logged_hours,
LAST_VALUE (employee) OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY hours
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING) AS highest_logged_hours
FROM loggedhours;Output:
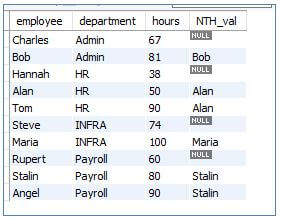
11. NTH VALUE ()
The window function NTH_VALUE returns the Nth row among a partitioned sorted result set.
Code:
SELECT
employee,
department,
hours,
NTH_VALUE (employee, 2)
FROM FIRST
OVER ( PARTITION BY department ORDER BY hours) as NTH_val
FROM loggedhours;Output:
Conclusion
The window function operates upon a window of a table from the database. The operation of a window function is very much close to an aggregate function. Many aggregate and non-aggregate functions can be termed respective window functions by using the OVER() clause. The OVER() clause can have values or be left blank, and we also discussed the difference in outcomes.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Window Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.