Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Binlog
MySQL Binlog is a binary log, which consists of all the modifications that happen in the database. All the details are written in the server in binary format. To read the contents in the file, we use the “mysqlbinlog” utility. The Binary log is helpful in MySQL replication, where the main server will send data from binary logs to the remote servers. When we perform operations like creating the table or updating the data from the existing table, these event details are stored in the binary logs.
In this session, let us see in detail the binary log and how it works in MySQL.
Syntax:
We use below the syntax to see all the binary logs: –
SHOW BINARY LOGS;/* - - here we are updating the row - - */
Below is the syntax we use to read the contents of the binary logs.
mysqlbinlog [options] <log_file_name>
MySQL Binary Log
Below are a few options:
- Debug: This option is used to write a debugging log.
- Debug-Check: This option prints the debugging information when the program exits.
- Start-DateTime: This option is used to read binary logs. Get data when the timestamp is equal to or later than the DateTime argument specified in the command.
- Start-Position: This option is used to decode the binary log. Decode from the first event with a position equal to or greater than the argument specified in the command.
- Stop-DateTime: This option is used to stop reading binary logs. Stop reading from the first event with a timestamp equal to or greater than the datetime argument specified in the command.
- Stop-Never: This option is used to stay connected to the server after reading the last binary log file.
- Stop-Never-Slave-Server-Id: This option makes the slave server ID report when connecting to the server.
- Stop-Position: This option stops decoding binary logs at the first event with a position equal to or greater than the argument specified in the command.
- To-Last-Log: This option is used when you want to not stop at the end of the requested binary log from a MySQL server and continue printing to the end of the last binary log.
- User: This option checks the MySQL user name for connecting to the server.
- Verbose: Reconstruct row events as SQL statements
- Verify-Binlog-Checksum: This option is used to verify checksum from the binary log.
- Version: This option is used to display version information and exit.
How Does MySQL Binary Log Work?
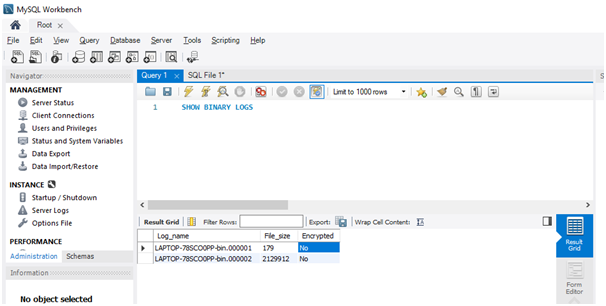
Let us see the existing log files present in the server using the below syntax:
Query:
Show BINARY LOGS
Output:
Now let us create a table and perform an update on the table and see the binary log creation in the server.
Query:
create table Data_034
(
id int,
name varchar(20),
location varchar(20)
);
Insert data into the table:
Query:
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (1, 'Rose', 'United Kingdom' );
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (2, 'Jack', 'United states') ;
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (3, 'Will', 'Britain');
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (4, 'Bentley', ‘USA’);
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (5, 'Sam', 'Rome');
INSERT INTO DATA_034 VALUES (6, 'Hammington', 'Italy');
Update the table row as below:
Query:
update data_034 set location='Rome' where id=6;/* - - here we are updating the row - - */
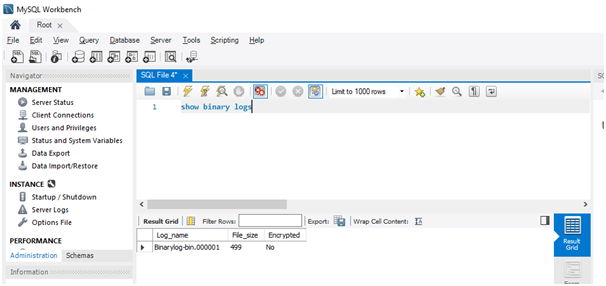
Now we have changed the binary log name, which is available in the
“c:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.ini” to “Binarylog-bin.000001”
Query:
SHOW BINARY LOGS; /* - - to show all the binary logs files - - */
Output:
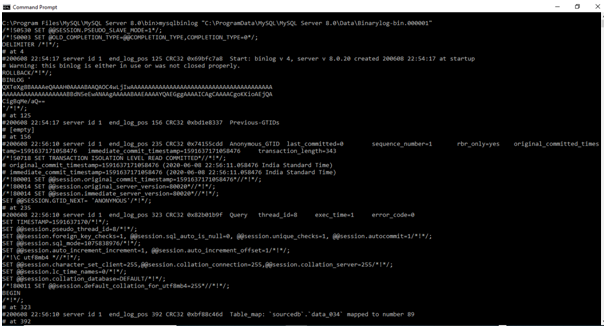
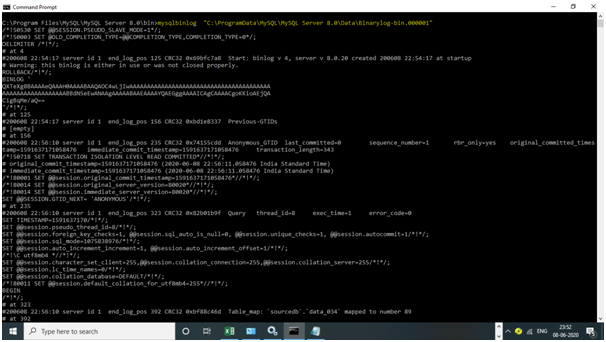
Let us read the binary log and see the output: –
To read, we use the mysqlbinlog utility: –
Open command prompt ->go to the path of the “mysqlbinlog” bin as “C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin”.
Input:
mysqlbinlog "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin>mysqlbinlog "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
Output:
Example:
The table consists of the following rows in it: –
| id | Name | Location |
| 1 | Rose | United Kingdom |
| 2 | Jack | India |
| 3 | Will | Britain |
| 4 | Bentley | USA |
| 5 | Sam | Rome |
| 67 | Hammington | Rome |
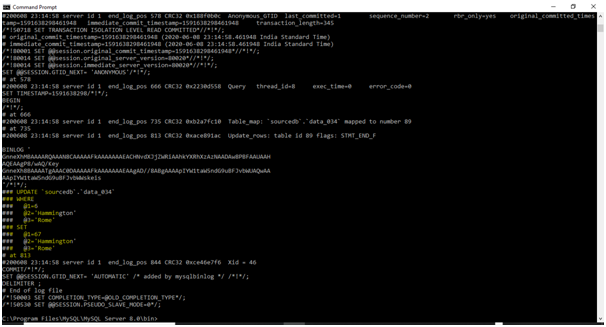
Here update the table below: –
Query:
update data_034 set id=67 where id=6; /* - - here we are updating the row - - */
Below let us get the last log that performed as in the above we are not able to read the binary log: –
Input:
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin>mysqlbinlog -v "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
/* - - to view the logs in the readable format - - */
Output:
Below is the data present in the table after the update: –
| id | Name | Location |
| 1 | Rose | United Kingdom |
| 2 | Jack | India |
| 3 | Will | Britain |
| 4 | Bentley | USA |
| 5 | Sam | Rome |
| 6 | Hammington | Rome |
Display content in a user-friendly manner:
Query:
mysqlbinlog <binary_log_file_name>
Example
mysqlbinlog “C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001”
Screenshot for the same:
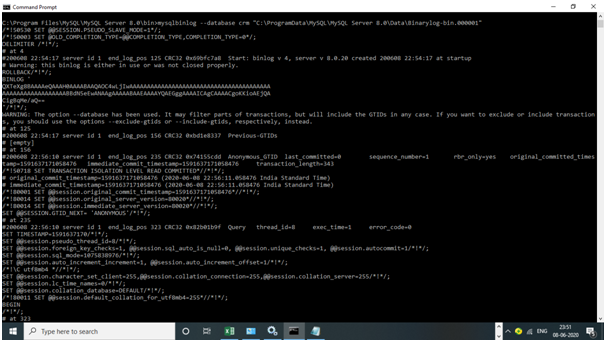
To display the Events that Happened in a Particular Database:
Query:
mysqlbinlog -d crm<binary_log_file_name>
or
mysqlbinlog --databasecrm<binary_log_file_name>
Example
mysqlbinlog-d crm“C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001”
or
mysqlbinlog -databasecrm“C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001”
Screenshot for the Same:
To Control the Binlog Output:
The output can be controlled based on the possible values provided. They are: –
- Never
- Always
- Decode-rows
- Auto (default)
Never:
This will work when there is no event occurring in “row_level”.
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=never "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
Always:
This will display only the BINLOG entries whenever possible.
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=always "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
Decode-rows:
This option will decode the row-based events into commented SQL statements.
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows "C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
Auto:
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=auto"C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data\Binarylog-bin.000001"
Conclusion – MySQL Binlog
MySQL Binlog is a binary log, which consists of all the modifications that happen in the database. All the details are written in the server in binary format. To read the contents in the file, we use the “mysqlbinlog” utility. The Binary log is helpful in MySQL replication, where the main server will send data from binary logs to the remote servers. When we perform operations like creating the table or updating the data from the existing table, these event details are stored in the binary logs.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Binlog” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.