Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to MySQL MOD()
MySQL MOD() function allows us to divide a literal number with another numeric expression to return the remainder of it. The MOD() takes numeric values as arguments for the function to execute and produce the result. The arguments can be said as dividend and divisor as in Maths which works on the fractional numeric values to output the special remainder. If the divisor or, say, the second parameter of the MySQL MOD() function is set to 0 (zero), the result will be NULL. This function can be used safely with BIGINT data type values, but mainly it is used for fractional parts to perform the division and show the remainder after calculating logically.
Syntax
The following syntax code introduces the structure to apply the Math function MOD() in MySQL:
MOD(a,b)a MOD ba % bWe have the above three syntaxes to use the MOD() function within the queries in MySQL.
- Here, the ‘a’ and ‘b’ parameters are the required numeric values that can be either fractional part or BIGINT data type values with the help of the MOD() function’s division process. After the completion of the command query then, the return value is the remainder balanced within numbers as in Maths calculation problems.
- Also, we can define the first argument value (a) as dividends and the other one-second argument (b) as the divisor for the MOD() calculation to produce the result of the division.
- Thus, with the literal numbers, the MOD() function returns the remains of the division, and if the divisor is zero like MOD(dividend,0), the result will be NULL.
How does MySQL MOD() Function work?
As per the syntax above, dividing a numeric expression by another literal number will result in the remainder of this MOD() function in MySQL.
This performs the same work as Modulus calculation is calculated in Maths that we do manually using logic and basic concepts. In addition, we also use SELECT query statement to supplement the MOD() function used in MySQL, so we use the MOD() function as:
SELECT MOD(a,b);The working of the MOD() function can be explained in detail with the help of some examples demonstrated below:
Code: Let us take a query using the MOD() function for MySQL to illustrate the function syntaxes that can be executed in three forms-
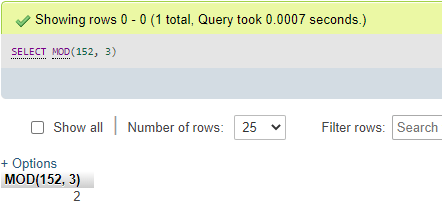
SELECT MOD(152, 3);Or,
SELECT 152 % 3;Or,
SELECT 152 MOD 3;Output:
Explanation: As you can see that the results show the remainder of each query form that is executed on the server. So, like this, the Math function implements the logic to produce the modulus process result.
Examples of implementing MOD() function in MySQL
Let us illustrate the MySQLMOD() function with the help of the following examples and show executions results generated simultaneously:
1. Some Simple Examples Using MySQL MOD() function
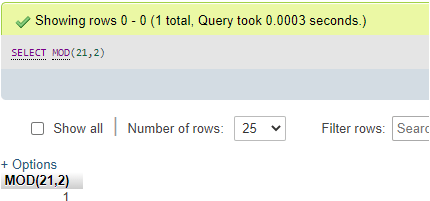
Code #1
SELECT MOD(21,2);Output:
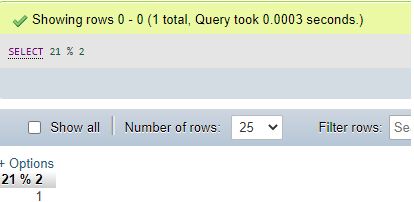
It can be noticed that MySQL permits to use of the modulus operator, i.e., %, which can be considered as the synonym for this MOD() function to give the result also like this:
Code #2
SELECT 21 % 2;Output:
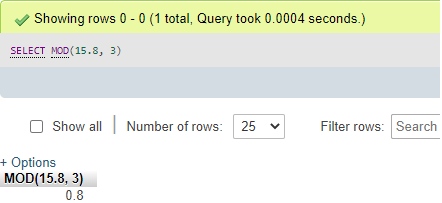
Also, look at the results gained using the MOD() function that accepts fractional elements to return the remainder of the division process. The query for this is as follows:
Code #3
SELECT MOD(15.8, 3);Output:
By utilizing both a dividend and divisor with fractional values, the following code demonstrates how to obtain the result:
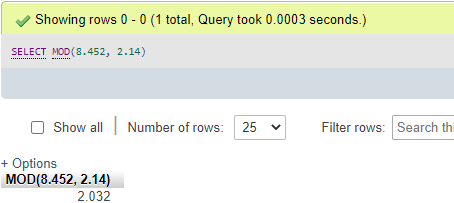
Code #4
SELECT MOD(8.452, 2.14);Output:
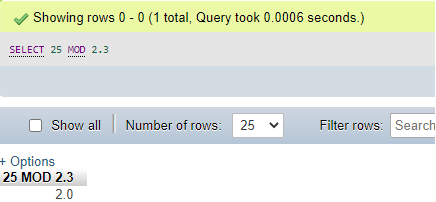
The result of the remainder is also with fractional values. Also, view the below query with a divisor in fractional value only:
Code #5
SELECT 25 MOD 2.3;Output:
2. Using MOD() function for zero divisor value
Suppose we have set the divisor as zero and dividend like any literal numeric expression; then the MOD() function applied to it will produce the following result as a reminder:
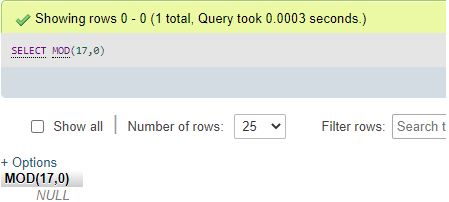
Code #1
SELECT MOD(17,0);Output:
You can view that the remainder of the above query with a 0 divisor value is NULL when executed on the MySQL server.
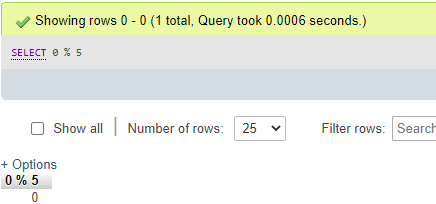
Let us try out the result of the MOD() function in MySQL when we set zero value for dividend and non-zero or, say, any literal number for divisor using the succeeding query:
Code #2
SELECT 0 % 5;Output:
So, do remember that if we divide the 0 value with any numeric expression, mathematically, it will give the result zero, just the opposite if we reverse the statement values when the divisor is zero. If the dividend is non-zero, then the output will be NULL.
3. Using MOD() function on Database Table fields
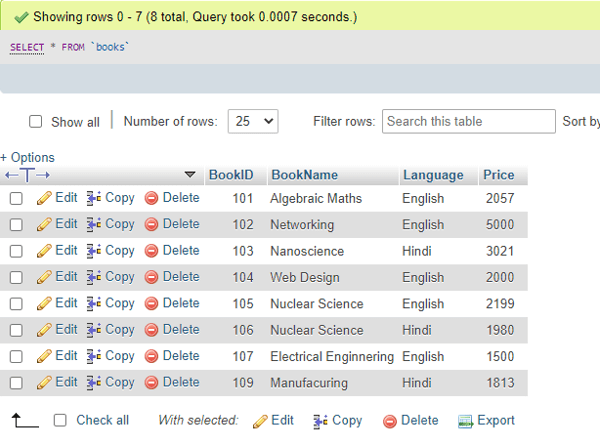
Supposing we have created a table named ‘Books’ where we will implement the MOD() function in MySQL. To accomplish this, you can utilize the following code for table creation, which includes the fields BookID, BookName, Language, and Price:
CREATE TABLE Orders(BookID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, BookNameVarchar(255) NOT NULL, LanguageVarchar(255) NOT NULL, Price INT NOT NULL);Let us enter some data records in the table Books with the following SQL query:
Code #1
INSERT INTO TABLE (BookID, BookName, Language, Price) VALUES('101','Algebraic Maths','English','2057');And so on.
Output: View the table here:
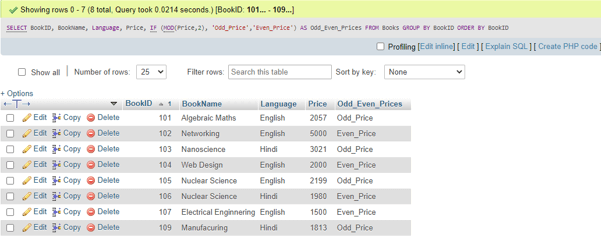
Now, we will use MySQLMOD() query on the table column ‘Price’ to check whether the values are even or odd:
Code #2
SELECT BookID, BookName, Language, Price,
IF (MOD(Price,2), 'Odd_Price','Even_Price') AS Odd_Even_Prices
FROM Books GROUP BY BookID ORDER BY BookID;Output:
In this illustration:
- In this case, we utilize the price column to fetch its values for performing the MOD() operation, specifically on numeric values.
- When we apply the MOD() function, the values in the Price column will undergo division by 2 as the divisor, resulting in the retrieval of the remainder. The query will evaluate odd or even according to the results produced in zero or one.
- At last, we have applied the IF() function that, when executed, will show Odd and Even prices string based on the result of the MOD() operation.
Conclusion
- MySQL provides the MOD() function, which actively evaluates the given values and generates the remainder after dividing the specified arguments.
- The MySQL MOD() thus implements a modulo operation on calling the function to provide the remainder of two numeric values passed in the function by the division method.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL MOD()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.