Updated June 8, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Full Text Search
The following article provides an outline for MySQL Full Text Search. We can define Full-Text Search as a procedure that performs a search operation for documents that effortlessly is not equal to the search standards. The documents are database entities comprising textual data such as blog posts, articles, product details, etc. Let us see its features; we use search engines such as Google and Bing regularly to implement the full-text search or FTS to allow search based on keywords. These engines first assemble the content info from different websites into the databases.
MySQL supports partial text searching through the regular expression and LIKE operator. This means FTS produces results that may include the searched words distinctly or consists of words in a separate order, like using either and, or conjunctions or, sentence type. Since the text column can be large and using these two factors may slow down the performance, it can influence flexible search and relevance ranking.
Complete Text Search Methodologies in MySQL
- In MySQL, the server maintenances full-text searching and indexing. Here, the full-text index denotes an index of MySQL Data type FULLTEXT. This type of index related to full-text is applicable only in MyISAM or InnoDB tables and can be used for TEXT, CHAR, or VARCHAR database columns. You can define this index during table creation using a CREATE TABLE query or add it later using CREATE INDEX or ALTER TABLE statements.
- We need to index columns in a table before applying a full-text search to its data so that lookups on these indexes using a classy algorithm can help search queries to match rows. Sometimes, when the table column values get modified, MySQL will restructure the full-text index for search-facilitated table columns MySQL routinely maintenances indexing and re-indexing data processes.
We will implement the basic syntax for MySQL Full-Text Search written as follows:
MATCH (ColumnName1, ColumnName2, ...) AGAINST (Expression[SearchModifier])Here, the terms are given below:
- ColumnName1, ColumnName2,… denotes the list of table columns separated by commas to be searched.
- AGAINST () accepts a string that is to be searched. It also includes a modifier specifying the kind of search to execute, an optional type.
- The search is case-insensitive by default. We must apply a binary collation for those indexed columns if we require a case-sensitive search based on a full-text index.
Remember that certain words are excluded or avoided during full-text searches.
The word to be searched should have a minimum length of:
- 3 characters for search indexes in InnoDB
- 4 characters for search indexes in MyISAM
Some words, like stop words that are exactly mutual as we can say – as, the, or it, displays in almost every document and are neglected during the search operation.
The full-text search can be categorized into three types described as follows:
1. Natural Language Full-Text Search
In this Natural Language Full Text Search, the searching process understands the search string defined as a free text with no exceptional operators needed further. This free text is Natural Human Language. If the modifier named “IN NATURAL LANGUAGE MODE” is provided, this type of full-text search becomes a natural language search technique.
Based on the text collection, the function MATCH() finds a string, resulting in a valid value for every table row. This shows the similarity between the search string provided in the function AGAINST() as an argument and the text, which denotes the columns in the table displayed as a MATCH() list.
We have an elementary format for this natural language-type mode of search as follows:
Code:
SELECT * FROM TableName WHERE MATCH(ColumnName1, ColumnName2) AGAINST ('Searching_Terms' IN NATURAL LANGUAGE MODE);To demonstrate, let us create a table and insert some records into it using queries:
Code:
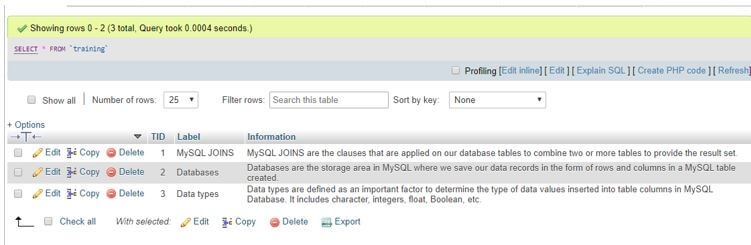
CREATE TABLE Training(TID INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL, Label VARCHAR(255), Information TEXT, FULLTEXT (Label, Information)) ENGINE=InnoDB;INSERT INTO Training (Label, Information) VALUES ('MySQL JOINS', 'MySQL JOINS are the clauses that are applied on our database tables to combine two or more tables to provide the result set.'), ('Databases', 'Databases are the storage area where we save our data records in the form of rows and columns in a MySQL table created.'), ('Data types', 'Data types are defined as an important factor to determine the type of data values inserted into table columns in MySQL Database. It includes character, integers, float, Boolean, etc.');View the table:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Training;Output:
Now, suppose we will search the string using ‘left right’ in the information field:
Code:
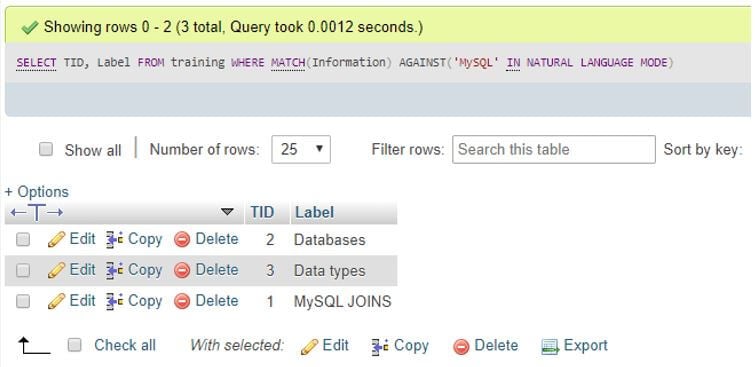
SELECT TID,Label FROM training WHERE MATCH(Information) AGAINST('MySQL'IN NATURAL LANGUAGE MODE);Output:
In this search, we query the term “MySQL” in MySQL, and the system displays the count based on the row contents in a case-insensitive manner.
2. Boolean Full-Text Search
In this search method, MySQL utilizes Boolean operators in the search queries to execute complex search processes. In the Boolean approach, MySQL searches for related words instead of concepts used in the natural language search.
Here, we will implement the modifier as IN BOOLEAN MODE in the AGAINST function as an argument option.
Example:
Code:
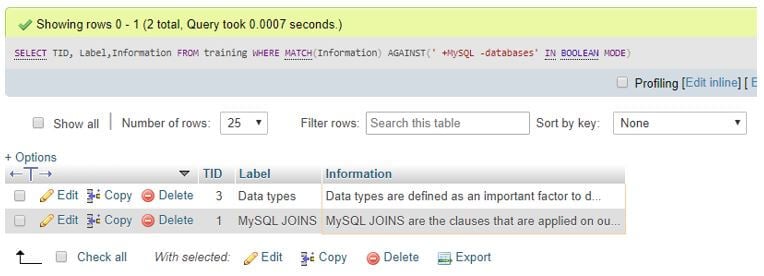
SELECT TID, Label,Information FROM training WHERE MATCH(Information) AGAINST(' +MySQL -databases' IN BOOLEAN MODE);Output:
The query searches for rows that include MySQL but not database using Boolean operators + and – i.e. include or exclude, and more operators can be used similarly.
3. Query Expansion Search
This full-text search is based on programmed relevance response that helps to broaden the search results queries. Here, users search for data according to their knowledge and experience by typing too short keywords. Thus, MySQL’s full-text search technique has introduced this query expansion methodology to allow users to perform a better search.
In this case, the search engine finds all the relevant words from all the rows that might match the keyword and displays the related results the users are looking for.
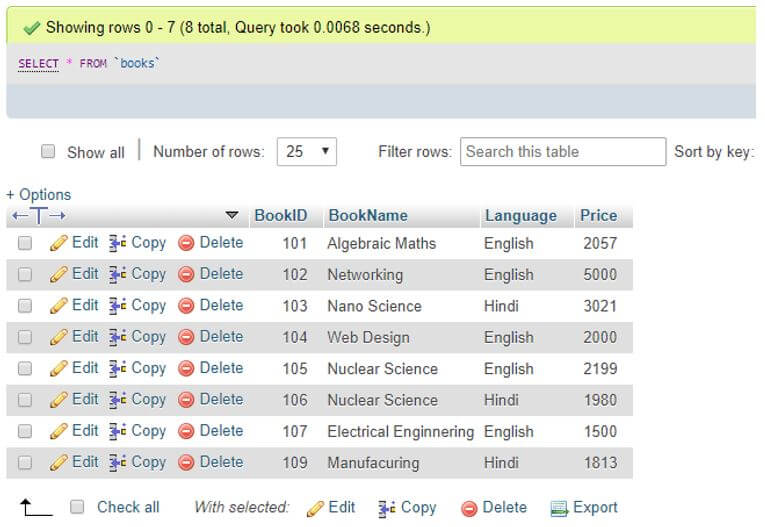
Suppose we have the following Books table:
Code:
Select * from Books;Output:
We will use the modifier WITH QUERY EXPANSION as an argument in AGAINST() in the search query as shown below:
Code:
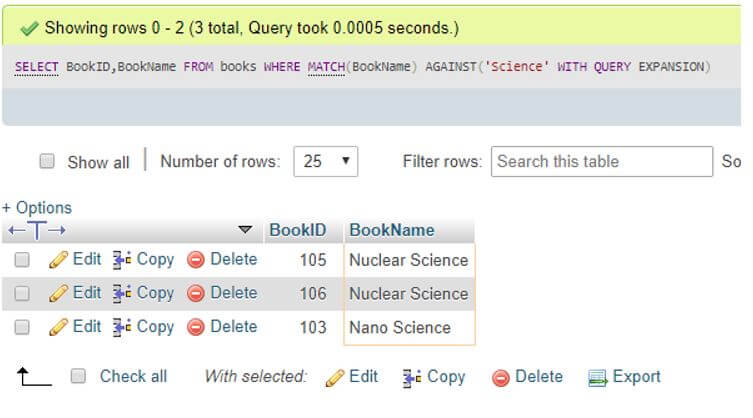
SELECT BookID,BookName FROM books WHERE MATCH(BookName) AGAINST('Science' WITH QUERY EXPANSION);Output:
Rows containing only the term “Science” appear in the output, and these rows are searched along with other identical rows using query expansion.
Conclusion
In MySQL server, Full-Text Search permits users to execute full-text commands against data in database tables that are character based. MySQL Full-text search shows essential features like a Natural SQL-like interface, Completely dynamic index, Speed, and Reasonable index size. The MySQL Full-text search also powers the search results on different websites like News, Blogs, E-commerce, Travel, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Full Text Search” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.