Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Multidimensional Array in C
This article focuses on the multidimensional array in c which is predominantly used in computer and research analysis. Generally, an array linearly focuses a piece of information which is said to be one-dimensional. Single dimensional stores data only single information like regno of the students. In some situations, it is necessary to store data in a table format that comprises rows and columns or to handle complex data. To visualize it we need a matrix format which we called as two-dimensional arrays in where the arrangements require pixels of the image, graphics. The data are stored in a tabular fashion. Array manipulations are performed by rearranging an element by using functions like reshape, squeeze.
How to declare a multidimensional array in C?
Syntax:
The general declaration of Multidimensional array is given as:
type name [ size] [size]……. N;- Here, data type name – It denotes the type of elements (integer, float).
- Array name – Denotes name assigned to the dimensional array.
- Row-size – No. of row elements ex. row-size = 8 , then array has 8 rows.
- Column- size – No. of column elements.
How to Initialize the Multidimensional Array in C?
The size of the multidimensional arrays is predicted by multiplying the size of various dimensions. And they store values in the form of two ways like row-major and column-major. And the memory allocation validates both length and rank properties.
In C, Multidimensional array has three types:
- Two-dimensional array
- Three-dimensional Array
- Four-dimensional Array
1. Two-Dimensional Array
Two-dimensional Array is structured as matrices and implemented using rows and columns, also known as an array of arrays. The memory allocation is done either in row-major and column-major. And the default format is Row-Major. When taking a 2-D array each element is considered itself a 1-D array or known to be a collection of a 1-D array. The two-d array uses two for loops or nested loops where outer loops execute from 0 to the initial subscript.
Syntax:
type array name [ no. of rows] [ no. of Columns];Example:
int td [4][3];here 4 is the no. of rows and 3 is the no. of columns.
Initialization of Two-Dimensional Array
Initialization in the 2-D array is done in multiple ways, it is shown here.
int m [3][2] = {{10,3} {4,2} {6,4} {5,4} {3,4}};
int di [2][4] = {10,5,8,12,45,13,11,61};Here, we have mentioned the no. of rows and columns in the box It is mandatory to assign the second index to make understand compiler about the ending and start of the row. The below table shows the memory allocation of the 2-D array.
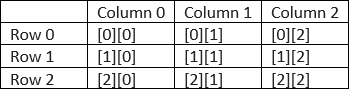
The number of elements is determined by manipulating a number of rows and columns and multiplying no. of rows and columns respectively. for Instance, the no. of elements an array holds B [-2…4, -3.6]. It is calculated by Lower bound and upper bound.
No. of rows= UB-LB +1
=4-(-2) +1 = 4+2+1= 7
No. of columns = UB-LB +1
= 6-(-3) + 1= 11
No. of elements = Rows * columns = 7 * 11 =77 elementsImplementation
It is done using Row major and column-major Implementations
Row-Major:
The formula for address manipulation is given as:
= B +W [ n(I-1) +[J-1]]Where b- is the base address and n- No. of columns for W bytes.
Column Major:
= B +W [ r(j-1) +[i-1]]where r – is the no. of rows.
Examples of Two-Dimensional Array
Examples of Two-Dimensional Array are :
Example #1
Each element of an array A [-10.10, 20…35] needs 1 byte of memory. And the array fits in Column major at the address 400, Find the location of A [0,30].
Solution
BA =400, W=1
R = no. of rows -> 10-(-10) +1 = 21
I= -10; J= 20
Address A [0,30] = 400 + 1[(0-(-10) +21(30-20))]
=400 +(10+21*10)
=400 +(10+210) = 620A familiar operation performed in the 2-d array is Algebra of matrices with m * n Matrix of B. The mathematical concept of the matrix is implemented the same as in programming.
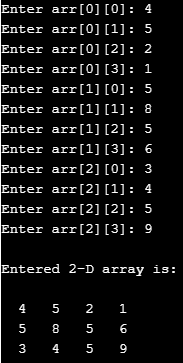
The below example stores an element in the matrix format and prints the same.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int a[3][4], i, j;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
printf("Enter arr[%d][%d]: ", i, j);
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\nEntered 2-D array is: \n\n");
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
printf("%3d ", a[i][j] );
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
C program performing the sum of two matrices.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int mat[20][20];
int i,j,r,c;
int s;
printf("Enter number of Rows :");
scanf("%d",&r);
printf("Enter number of Cols :");
scanf("%d",&c);
printf("\nEnter matrix elements :\n");
for(i=0;i< r;i++)
{ for(j=0;j< c;j++)
{
printf("Enter the number of inputs [%d,%d] : ",i+1,j+1);
scanf("%d",&mat[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i< r;i++)
{
s=0;
for(j=0;j< c;j++)
{
printf("%d\t",mat[i][j]);
s+=mat[i][j];
}
printf("\tSUM : %d",s);
printf("\n");
}
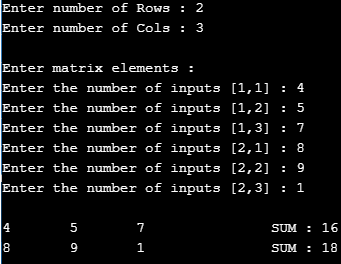
}The above program calculates the sum of two matrices A[20,20] B[20,20] provided they have two identical matrices. Through for loop, it takes two input matrix and loops to accept matrix.
Output:
Example #3
Transpose of a Matrix
Interchanging rows and columns to form a new matrix which is known as the transpose of a matrix.
Example:
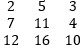
Then Transpose give,

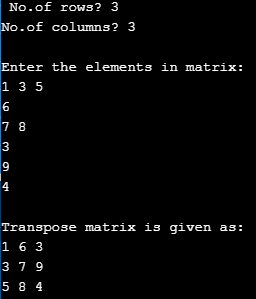
Matrix Transpose Using C program
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int T[5][5],i,j,a,b;
printf(" No.of rows?");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("No.of columns?");
scanf("%d",&b);
printf("\nEnter the elements in matrix:\n");
for(i=0;i<b;++i)
for(j=0;j<a;++j)
scanf("%d",&T[i][j]);
printf("\nTranspose matrix is given as:\n");
for(i=0;i<b;++i)
{
for(j=0;j<a;++j)
printf("%d ",T[j][i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}In the above program To read a matrix we had used two for loops and to print its transpose the nested for loop is used to display the output. Here we have used 3* 3 matrix.
Output:
2. Three-Dimensional Array
It is Called an Array of Array Elements or An Array of Matrices. It’s Quite a Buzzy One but Once You Get Practice Towards the Logic It Makes Easier to Implement. and This 3-D Array Requires More than Three Dimensions and Requires the Bulk of Memory to Store.
It can be declared as:
data_type array_name [table name] [ no. of row] [ no. of column]
int L[m][n] [p];int L [3][4][2]; Here the array L can hold 24 elements. And all these can be initialized during the compilation process, but when uninitialized there are put into a garbage value.
Initialization can be done in the same way as a two-dimensional array. Here is a sample,
int L [2][3][4] = {{{2,2,1,3},{1,6,5,11},{22,11,13,5}},{{13,5,77,8},{6,8,2,4},{3,2,7,8}}};Examples of Three-Dimensional Array
Here are some examples of the three-dimensional array which are given below:
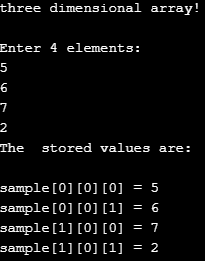
Example #1
Below comes a simple example in C programming illustrating three-dimensional Array. It is done using for a loop by considering 3 for loops for 3d elements.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf("three dimensional array!\n\n");
int i, j, k, s[2][1][2], siz;
siz=2*1*2;
printf("Enter %d elements: \n",siz);
for(i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < 1; ++j)
{
for(k = 0; k < 2; ++k )
{
scanf("%d", &s[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
printf("The stored values are:\n\n");
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 1; j++)
{
for(k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
printf("sample[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n", i, j, k, s[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
}Output:
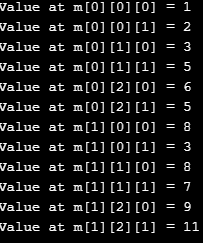
Example #2
Another example of a 3-D array to print elements automatically.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int m[2][3][2] =
{
{ {1,2}, {3,5}, {6,5} },
{ {8,3}, {8,7}, {9,11} }
};
for (int i = 0; i <2; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j <3; ++j)
{
for (int k = 0; k <2; ++k)
printf("Value at m[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n", i, j, k, m[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}Output:
3. Four-Dimensional Array
It is an array of three-dimensional array and it is very difficult in managing the dimensions. It is viewed as a bunch of cubes together and applicable for space vectors.
Declaration of 4-D Array:
Type array name [1][2][3][4] ……. [n] where 1,2 denotes the dimensions and n implies nth dimensions.
Example:
int state [5][6][7][8];Example of Four-dimensional array
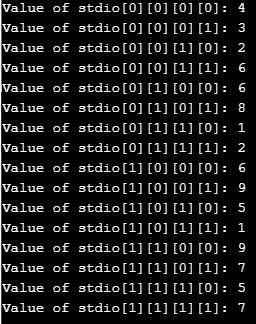
C program to implement 4- D array.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, j, k, l, s;
int d[2][2][2][2];
s = 2;
d[0][0][0][0] = 4;
d[0][0][0][1] = 3;
d[0][0][1][0] = 2;
d[0][0][1][1] = 6;
d[0][1][0][0] = 6;
d[0][1][0][1] = 8;
d[0][1][1][0] = 1;
d[0][1][1][1] = 2;
d[1][0][0][0] = 6;
d[1][0][0][1] = 9;
d[1][0][1][0] = 5;
d[1][0][1][1] = 1;
d[1][1][0][0] = 9;
d[1][1][0][1] = 7;
d[1][1][1][0] = 5;
d[1][1][1][1] = 7;
for (i = 0; i < s; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < s; j++) {
for (k = 0; k < s; k++) {
for (l = 0; l < s; l++) {
printf("Value of stdio[%d][%d][%d][%d]: %d ", i, j, k, l, d[i][j][k][l]);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
To the end, in this article, we discussed multidimensional arrays and their subtypes in C programming. And also, their declaration and accessing the elements in a matrix format. These techniques are applied in the concept like binary searching and sorting implementation. Here an index plays a key role in as they specify an element in the array structure.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in C. Here we discuss how to initialize the multidimensional array in C along with examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-


