Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Multidimensional Array
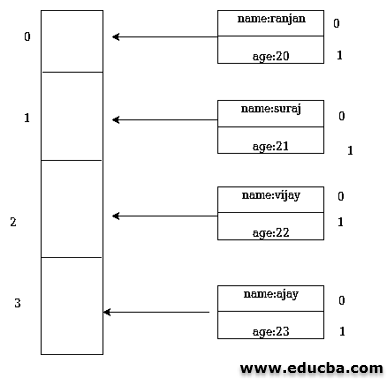
Before I start explaining to you how multi-dimensional arrays works, let us understand what is an array. By default PowerShell mixed type, This means that you can mix different data types inside an array—that is, you can combine numerical values, dates, or strings in a single variable. PowerShell Multidimensional Array in this article, the data elements of a PowerShell array need not be of the same type unless the data type is declared (explicitly). However, if you want a similar data type into an array then you can strictly define it. Now an array inside another array is called Multidimensional array. For example, an array containing employee details and every employee can have their own details.
In the above image there are two arrays one is the main array and it’s each index holds another array that contains user name and age.
Syntax of PowerShell Multidimensional Array
In PowerShell, we can have two types of array, normal array, and jagged array. In below syntax we can see, we can strictly define the data type for an array or it can be without any data type. So we should take care of these things, if we need mixed data array or we need similar data arrays. So for example, if we need an array of numbers than we can define int32, in the same way, if we need an array with string then we can define with string.
$array = @( @(“data2”), @(“data3”), @(“data4”) …….)
Above one is the syntax of Without type of array it can have any type of data like numeric or string combined together like 23,” Ranjan”,” Vijay”,”xyx”,”45.4” etc.
[int32[]]$array = @( @(“data2”), @(“data3”), @(“data4”) …….)
Above is the syntax of strictly type for int value, which means the only numeric value will be allowed like 1,3,412,33,45,34 etc. If we defined array as strictly type and we are trying to assign different data types of then it will throw an error.
[string[]]$array = @( @(“data2”), @(“data3”), @(“data4”) …….)
Above is the syntax of strictly type for a string value, which means only string value will be allowed. like “Ajay”,” Vijay”,” Rakesh” etc . And if we try to assign values like 1,56,7 than it will throw an error as we have defined it as a string and we are trying to assign integers value.
So in a similar way, we can also strictly defined for decimal(Decimal values only), boolean, double data type, etc.
All these syntaxes are mainly to create a 2-dimensional array, but if wanted to create a three-dimensional array we need to use command New-Object ‘object[,]’ i,j.
below are given syntax for 3-dimensional array creation. this is a true way to create a multidimensional array.
$array = New-Object 'object[,]' i,j
Here i,j represent the dimension of the matrix we can write it according to our requirements .for example we can write it New-Object ‘object[,]’ 3,3. Here 3,3 represent 3*3 matrix.
How to declare a Multidimensional Array in PowerShell?
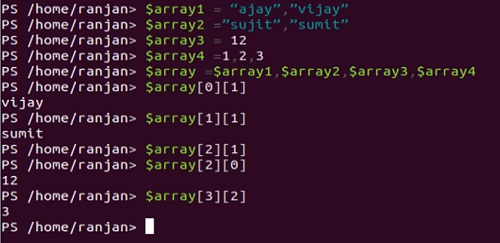
$array1 = “ajay”,”vijay”
$array1[0]
$array1 = “ajay”,”vijay”
$array2 =”sujit”,”sumit”
$array3 = 12
$array4 =1,2,3
$array =$array1,$array2,$array3,$array4
$array[0][1]
$array[1][1]
$array[2][1]
$array[2][0]
$array[3][2]
In the below screenshots declaration and accessing both are defined.
To access any element of multidimensional arrays we can simply access by using the array[i][j]. So suppose we want to access “sumit” than we can $array[1][1]. Remember here we are not defining data type. Here Size of the array is flexible, that’s mean whatever we assign to it, it will automatically be converted to that size.
In the same way, it can do for a strictly defined type also.
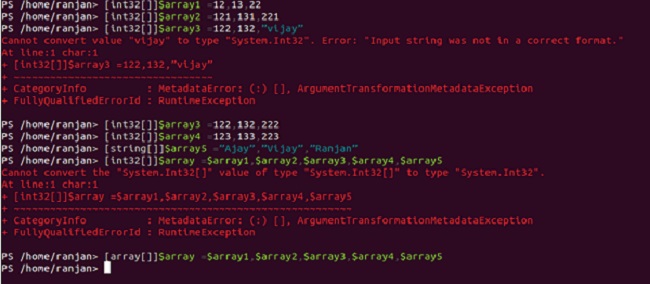
[int32[]]$array1 =12,13,22//Integer type
[int32[]]$array2 =121,131,221//Integer Type
[int32[]]$array3 =122,132,”Vijay”//Wrong way
[int32[]]$array3 =122,132,222//right way as Integer type
[int32[]]$array4 =123,133,223//Integer type
[string[]]$array5 =”Ajay”,”Vijay”,”Ranjan”//String type
[int32[]]$array =$array1,$array2,$array3,$array4,$array5//Wrong as it is array type
[array[]]$array =$array1,$array2,$array3,$array4,$array5//right way
Is it the combination of array type so we should define an array, not int32.
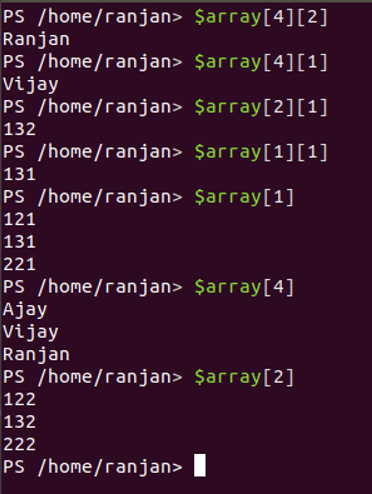
Output:
Accessing values
[int32[]]$array1 =12,13,22
[int32[]]$array2 =121,131,221
[int32[]]$array3 =122,132,”vijay”
[int32[]]$array3 =122,132,222
[int32[]]$array4 =123,133,223
[string[]]$array5 =”Ajay”,”Vijay”,”Ranjan”
[array[]]$array =$array1,$array2,$array3,$array4,$array5
$array[4][2]
$array[4][1]
$array[2][1]
$array[1][1]
$array[1]
$array[4]
$array[2]
Output:
So here we learned how to declare a multidimensional array and accessing its attribute.
How to initialize the Multidimensional Array in PowerShell?
We can also check length of $array by $array.count.
$array = (“ranjan”,”vijay”,”sujit”,”ajit”),(1,2,3),(‘lion’,'tiger','dog','fox')
$array.count
Output:
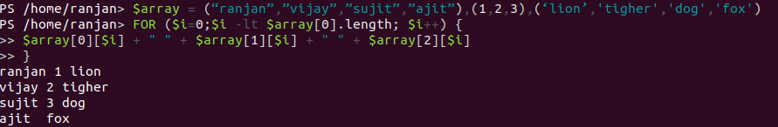
We can run a for loop to check all attributes in our array, like this:
$array = (“ranjan”,”vijay”,”sujit”,”ajit”),(1,2,3),(‘lion’,'tiger','dog','fox')
FOR ($i=0;$i -lt $array[0].length; $i++) {
$array[0][$i] + " " + $array[1][$i] + " " + $array[2][$i]
}
Output:
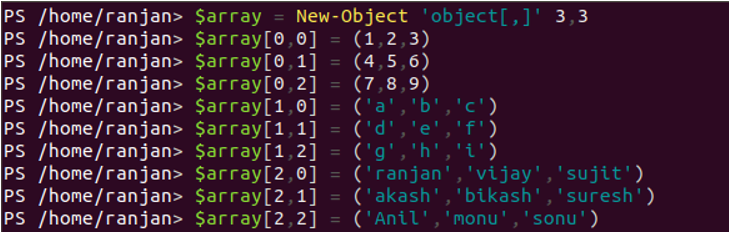
Till now we talk about the 2-dimensional array, So if we wanted to create a 3-dimensional array we need to use command “New-Object ‘object[,]’3,3’” and we can start creating our 3-dimensional array. You can use a FOR loop to see the contents of the multidimensional array:
$array = New-Object 'object[,]' 3,3
$array[0,0] = (1,2,3)
$array[0,1] = (4,5,6)
$array[0,2] = (7,8,9)
$array[1,0] = ('a','b','c')
$array[1,1] = ('d','e','f')
$array[1,2] = ('g','h','i')
$array[2,0] = ('ranjan','vijay','sujit')
$array[2,1] = ('akash','bikash','suresh')
$array[2,2] = ('Anil','monu','sonu')
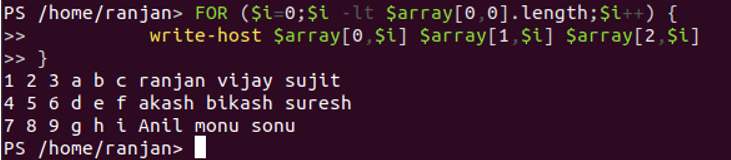
FOR ($i=0;$i -lt $array[0,0].length;$i++) {
write-host $array[0,$i] $array[1,$i] $array[2,$i]
}
The output is given below for the above for loop to access its attributes:
Types of Multidimensional Array in PowerShell
In the above we have already seen how to create a 3-dimensional array in PowerShell, Now we are going to understand the types of Multi-Dimensional array into PowerShell. There are mainly two types of multidimensional arrays in PowerShell, Jagged array and Strictly Data type defined array.
1. Jagged Array
In Jagged array, we are free to use any type of data type, which means we can place string along with the numeric or decimal with an integer type. In real-world people mostly needed mixed data types of the array because most of the data contain different types of attributes like age(integer), Name(String), Height(Decimal), So to handle all these kinds of attributes it’s important to use Jagged array. Here a good thing about Jagged array in PowerShell is Jagged array by default. These types of arrays are very cost-effective because you can have any size of data inside it. Syntax of Jagged array.
In the below example, we are not defining data type of array, so In PowerShell by default, the array type is Jagged array.
Below is an example of a Jagged array.
$array = @(("Ranjan","Vijay","Ajay"),(31,50,60))
2. Array(Strictly Defined data type)
In the above, we discussed Jagged array and it’s importance, but in some cases, we need to have a strictly defined data type for array. For example, suppose we have some large amount of data for employee id(numeric) only, so we are sure that this array will always hold only integer values.
So we can define it strictly with int/decimal/boolean etc according to our requirements.
Below is the example of strictly defining an array.
$array = @(("ranjan","vijay","ajay"),(31,50,60))
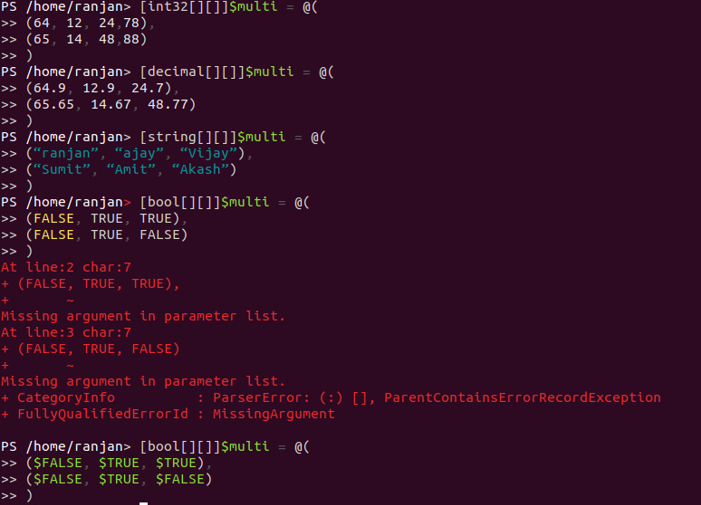
[int32[][]]$multi = @(
(64, 12, 24,78),
(65, 14, 48,88)
)
[decimal[][]]$multi = @(
(64.9, 12.9, 24.7),
(65.65, 14.67, 48.77)
)
[string[][]]$multi = @(
(“ranjan”, “ajay”, “Vijay”),
(“Sumit”, “Amit”, “Akash”)
)
[bool[][]]$multi = @(
($FALSE, $TRUE, $TRUE),
($FALSE, $TRUE, $FALSE)
) //Right way
[bool[][]]$multi = @(
(FALSE, TRUE, TRUE),
(FALSE, TRUE, FALSE)
) //Wrong way
Output:
Conclusion
To conclude, multidimensional arrays allow us to handle similar and different types of data types. Multidimensional arrays are very powerful to handle large and related data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Multidimensional Array. Here we discuss syntax and example of PowerShell Multidimensional Array, along with initialization and types with respective examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –