Updated March 1, 2023
Differences Between MongoDB and SQL Server
There are basically two types of databases present: SQL and NoSQL. The example of the SQL database is MySQL and NoSQL is MongoDB. MongoDB stores the data in JSON like documents that can vary in structure offerings a dynamic, flexible schema. MongoDB was also designed for high availability and scalability with auto-sharding. SQL Server is a database management and analysis system for e-commerce and data warehousing solutions. MongoDB is one of the several databases that rise under the NoSQL database which is used for high volume data storage. Instead of using tables rows as Relational Database, MongoDB is based on the architecture of collections and documents. In MongoDB, the rows (or documents as called in MongoDB) don’t need to have a schema defined beforehand. Instead, the fields can be created on the fly. The data model available within MongoDB allows you to represent hierarchical relationships, to store arrays, and other more complex structures more easily.
History of MongoDB
- MongoDB is developed by Inc and it was released by GNU Affero General Public License and the Apache License.
- 10gen software organization started developing MongoDB as a component of a planned platform as a service product.
- The company opted open source development model in 2009 and in 2013 it’s become MongoDB.Inc.
MongoDB
“MongoDB is Open-Source, cross-platform, NoSQL document database written in C++ that provides high performance, high availability and high scalability.”
Let us discuss what does each term signifies in this definition
- High Performance-It means it provides faster read and writes scan.
- High Availability-Many replicated servers are used to provide high availability of data without delay
- Scalability-Automatic SHARDING distributes collection data across machines and eventually, consistent read scan can be distributed over replicated servers.
Why is it the NoSQL Database?
It is a type of NoSQL database Document Stored Database.
MongoDB avoids the traditional table-based Relational database structure in favor of JSON like documents with dynamic schemas, making the integration of data in certain types of applications easier and faster.
Features of MongoDB
There basically three main important features of MongoDB that makes it unique
- Flexibility
- Scalability
- Performance
- Flexibility- You can enforce any type of data in MongoDB. Data in MongoDB has a flexible schema. Collections do not enforce document structure. This flexibility gives you data modeling choices to match your application and its performance requirements dynamically (pdf, audio, video). Therefore, it can dynamically modify the schema without downtime.
- Scalability- IT means that you should able to meet the consumption of data growth. It can be defined as the ‘ability of the systems to handle a growing amount of workload capable manner’. As the size of the data increases in MongoDB, a process Sharding solves the problem by doing Horizontal Scaling.
- Performance- MongoDB performs well. As the number of queries increases SQL takes more time to execute those queries but the performance of MongoDB is better in such a scenario. There are various factors that are responsible for the high performance of MongoDB IT provides the embedding of documents. It avoids the concept of joins and provides indexing of data.
What is SQL Server?
SQL Server is a Microsoft relational database management system(RDBMS). The competitors are Oracle DB and MySQL. It supports a 32-bit and 64-bit environment. It also is known as MSSQL and Microsoft SQL Server. Some more details regarding SQL Server are given below:
- Its first version was released in 1989 by Microsoft.
- It supports XML data type support, dynamic management views and database mirroring.
- It supports e-commerce and data warehousing.
- It has several editions: Enterprise, Standard, Web, Business Intelligence, Express.
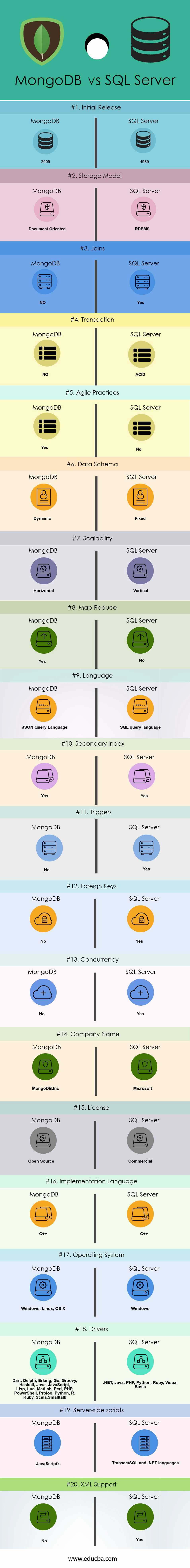
Head to Head Differences Between MongoDB and SQL Server (Infographics)
Below are the top 20 differences between MongoDB and SQL Server:
Key Differences Between MongoDB and SQL Server
Both MongoDB vs SQL Server performance are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major difference between MongoDB and SQL Server:
- MongoDB is more fast and scalable in comparison to the SQL server.
- MongoDB doesn’t support JOIN and Global transactions but the SQL server supports it.
- MongoDB supports a big amount of data but the MS SQL server doesn’t.
- MongoDB support Agile practices but MS SQL server doesn’t support it.
- MongoDB schema is dynamic but MS SQL server schema is fixed.
- Ms. SQL server provides XML support but MongoDB doesn’t.
MongoDB and SQL Server Comparision Table
Below is the comparison table between MongoDB and SQL Server.
| Base of Comparison | MS SQL Server | MongoDB |
| Initial Release | 1989 | 2009 |
| Storage Model | RDBMS | Document-Oriented |
| Joins | Yes | No |
| Transaction | ACID | NO |
| Agile practices | No | Yes |
| Data Schema | Fixed | Dynamic |
| Scalability | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Map Reduce | No | Yes |
| Language | SQL query language | JSON Query Language |
| Secondary index | Yes | Yes |
| Triggers | Yes | No |
| Foreign Keys | Yes | No |
| Concurrency | Yes | No |
| Company Name | Microsoft | MongoDB.Inc |
| License | Commercial | Open Source |
| Implementation Language | C++ | C++ |
| Operating System | Windows | Windows, Linux, OS X |
| Drivers | .NET, Java, PHP, Python, Ruby, Visual Basic
|
Dart, Delphi, Erlang, Go, Groovy, Haskell, Java, JavaScript, Lisp, Lua, MatLab, Perl, PHP, PowerShell, Prolog, Python, R, Ruby, Scala, Smalltalk
|
| Server-side scripts | Transact SQL and .NET languages | JavaScript’s |
| XML Support | Yes | No |
Conclusion
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that is more advanced and capable of handling more data. SQL Server is a database management system that is used to manage the relational database system.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between MongoDB vs SQL Server. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following MongoDB vs SQL Server articles to learn more –