Difference Between MongoDB vs DynamoDB
MongoDB is a cross-platform, free, open-source document and oriented NoSQL database which is written in C++. MongoDB is very much useful for high volume data storage which provides high performance, high availability, and also automatic scaling. A MongoDB database stores the data in an area which is known as collections and not in tables. Those are the rough which is equivalent of RDBMS tables. DynamoDB provides support for key-value and document data structures which makes a fast and predictable performance with smooth, continuous scalability. DynamoDB uses the Dynamo model in the principle of its design which improves its features.
MongoDB
- MongoDB is designed and developed by MongoDB Inc (it is an American Software Company). And it is published with a combination and coordination of the GNU Affero General Public License and the Apache License. MongoDB is released in the year February 2009 and the latest stable release was on June 2018.
- Typically, a single MongoDB server has multiple databases in it. MongoDB document does not support the SQL and it supports high, rich and ad-hoc query language.
- A MongoDB is written in C++, C, and JavaScript programming language. MongoDB conveniently operates in the following Operating systems: Windows Vista and later, Linux, OS X 10.7 and later, Solaris, and FreeBSD.
DynamoDB
- DynamoDB is a fully managed proprietary and hosted NoSQL database service, this database service is provided by Amazon as a part of Amazon Web Services (AWS). Amazon DynamoDB is also known by other names – i.e., Dynamo Database or DDB.
- DynamoDB is designed and developed by Amazon.com and its initial release was made in the year January 2012. It runs on the Cross-platform operating system.
- DynamoDB allows its users to create databases that are capable of storing and retrieval of a huge amount of data from it and also manages any amount of traffic. Managing data traffic happens automatically by distributing data and manages each customer’s requests traffic over servers to dynamically, and also it helps to maintain and improve performance.
- DynamoDB initially began to manage the website’s scalability challenges that are presented by the holiday season loads. DynamoDB is mainly known for its low latencies and scalability.
Head to Head Comparison between MongoDB and DynamoDB
Below is the top 5 difference between MongoDB and DynamoDB:
Key Difference Between MongoDB and DynamoDB
Let us discuss some of the major differences between MongoDB and DynamoDB:
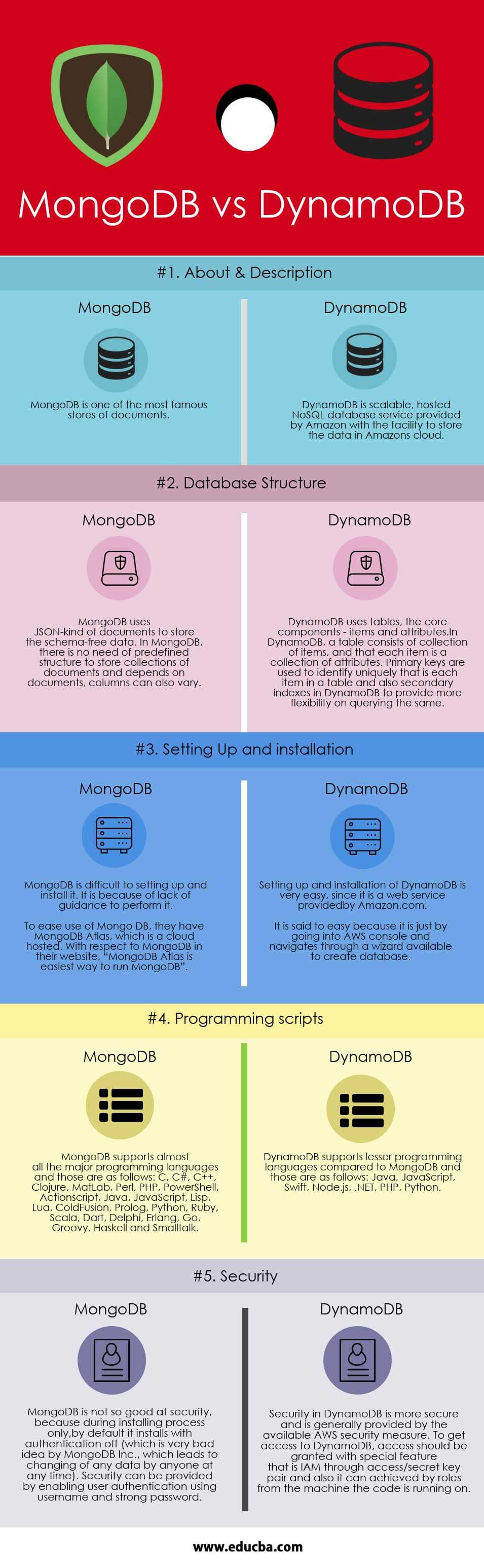
- MongoDB is one of the most famous documents oriented database whereas DynamoDB is scalable, hosted NoSQL database service provided by Amazon with the facility to store the data in Amazon’s cloud.
- In MongoDB, setting up and installation process is difficult compared to DynamoDB. The process is said to easy because it is just by going into AWS console and navigates through a wizard available to create a database.
- Mongo database offers some API for user-defined Map/Reduce methods, whereas Map Reduce is not supported in Dynamo database.
- Server-side scripts (i.e., stored procedure) can be achieved by using JavaScript in MongoDB but it is not allowed in DynamoDB.
- Linux, OS X, Solaris, and Windows are the Server operating systems that support to MongoDB whereas for DynamoDB it is hosted NoSQL database service.
- In MongoDB, by default data is strongly consistent as all read/writes go to the primary in a MongoDB replica set whereas data in DynamoDB is eventually consistent by default. Again DynamoDB users can configure read operations, but this will be an additional charge (which almost doubles the cost of the read and also it adds latency to it.
- There is native document validation feature is included in MongoDB but there is no data validation feature made available in DynamoDB.
- MongoDB Atlas in MongoDB includes continuous, queryable backups with point-in-time recovery is available for the backup process. But in DynamoDB it is different since it is web service they provide backups with an additional charge based on On-demand and continuous backups.
- Pricing for MongoDB Atlas is completely depended on the selection of RAM, I/O, and storage. But for DynamoDB, it is based on Throughput means a price will be affected based on a wide range of inputs.
- MongoDB can be used where organizations that are looking to support a large number of use cases in their database with more deployment flexibility and no platform lock-in. Whereas DynamoDB can be used where organizations which are looking for a database that support simple key-value workloads and also who has invested heavily in AWS with there are plans to change their deployment environment in the future.
MongoDB vs DynamoDB Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between MongoDB vs DynamoDB
| Basis of Comparison between MongoDB vs DynamoDB | MongoDB | DynamoDB |
| About & Description | MongoDB is one of the most famous stores of documents. | DynamoDB is a scalable, hosted NoSQL database service provided by Amazon with the facility to store the data in Amazon’s cloud. |
| Database Structure | MongoDB uses JSON-kind of documents to store the schema-free data. In MongoDB, there is no need of predefined structure to store collections of documents and depends on documents, columns can also vary. |
DynamoDB uses tables, the core components – items and attributes. In DynamoDB, a table consists of a collection of items, and that each item is a collection of attributes. Primary keys are used to identify uniquely that is each item in a table and also secondary indexes in DynamoDB to provide more flexibility on querying the same. |
| Setting up and Installation | MongoDB is difficult to set up and install it. It is because of a lack of guidance to perform it. To ease the use of Mongo DB, they have MongoDB Atlas, which is a cloud hosted. With respect to MongoDB in their website, “MongoDB Atlas is the easiest way to run MongoDB”. |
Setting up and installation of DynamoDB is very easy since it is a web service provided by Amazon.com. It is said to easy because it is just by going into AWS console and navigates through a wizard available to create a database. |
| Programming Scripts | MongoDB supports almost all the major programming languages and those are as follows: C, C#, C++, Clojure, MatLab, Perl, PHP, PowerShell, Actionscript, Java, JavaScript, Lisp, Lua, ColdFusion, Prolog, Python, Ruby, Scala, Dart, Delphi, Erlang, Go, Groovy, Haskell and Smalltalk. |
DynamoDB supports lesser programming languages compared to MongoDB and those are as follows: Java, JavaScript, Swift, Node.js, .NET, PHP, Python. |
| Security | MongoDB is not so good at security, because during installing process only, by default it installs with authentication off (which is a very bad idea by MongoDB Inc., which leads to changing of any data by anyone at any time). Security can be provided by enabling user authentication using a username and a strong password. |
Security in DynamoDB is more secure and is generally provided by the available AWS security measure. To get access to DynamoDB, access should be granted with a special feature that is IAM through access/secret key pair and also it can be achieved by roles from the machine the code is running on. |
Conclusion
In the race between MongoDB vs DynamoDB, both are very competitive solid database solutions with respect to each of it, because both MongoDB vs DynamoDB databases have pros and cons in a few of the fields. Below are some of the points which can be considered to choose from MongoDB vs DynamoDB databases:
- All sizes of organizations can adopt MongoDB because it handles highly diverse data types, and also it manages those applications more efficiently. But in DynamoDB, it is very limited data types support in this.
- Considering the security feature, DynamoDB is recommended compared to MongoDB.
Below are some of the companies uses the MongoDB vs DynamoDB databases:
Dynamo database: HTC, Samsung, Amazon, Netflix, Snapchat, the New York Times, Electronic Arts, AdRoll, Dropcam, Twiitch, Clubhouse, Shazam, Twilio, Localytics and many other companies.
MongoDB: Cisco, Adobe, SAP Google, UPS, eBay, BOSCH, Facebook, Forbes, and many other companies.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top differences between MongoDB vs DynamoDB. Here we have discussed MongoDB vs DynamoDB head to head comparison, key differences along with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –