Definition of Merger
A merger is an agreement between two entities to combine to form a new entity. In other words, it is the amalgamation of two separate entities into one legal entity.
In the corporate world, several types have different intentions. Thus, companies can merge to venture into new segments, expand their reach, or gain market share.
Key Takeaways
- Mergers are a voluntary union of two entities into a new legal entity under similar conditions. Usually, both parties are identical in size concerning the scope of operations.
- It can also help companies broaden their customer base, enter new market categories, or increase their market share.
- Its execution can happen either in cash, stocks, or its combination.
- The five main types are conglomerate, product extension, market extension, horizontal, and vertical.
- An acquisition means taking over a firm, while a merger occurs when businesses come together to establish a new entity.
How Does it Work?
Mergers happen when two businesses voluntarily combine to become one legal entity. Typically, entities entering an agreement are approximately equal in size. It is sometimes known as the merger of equals.
Companies pursue these to expand their business, increase market share, cut back operating costs, boost profitability, etc. Post-merger, the new entity issues its shares to the existing shareholders. Thus, this process involves transactions in cash, stock, or both. Usually, the acquiring company can purchase stocks of the target entity in money or exchange stocks.
Types of Merger
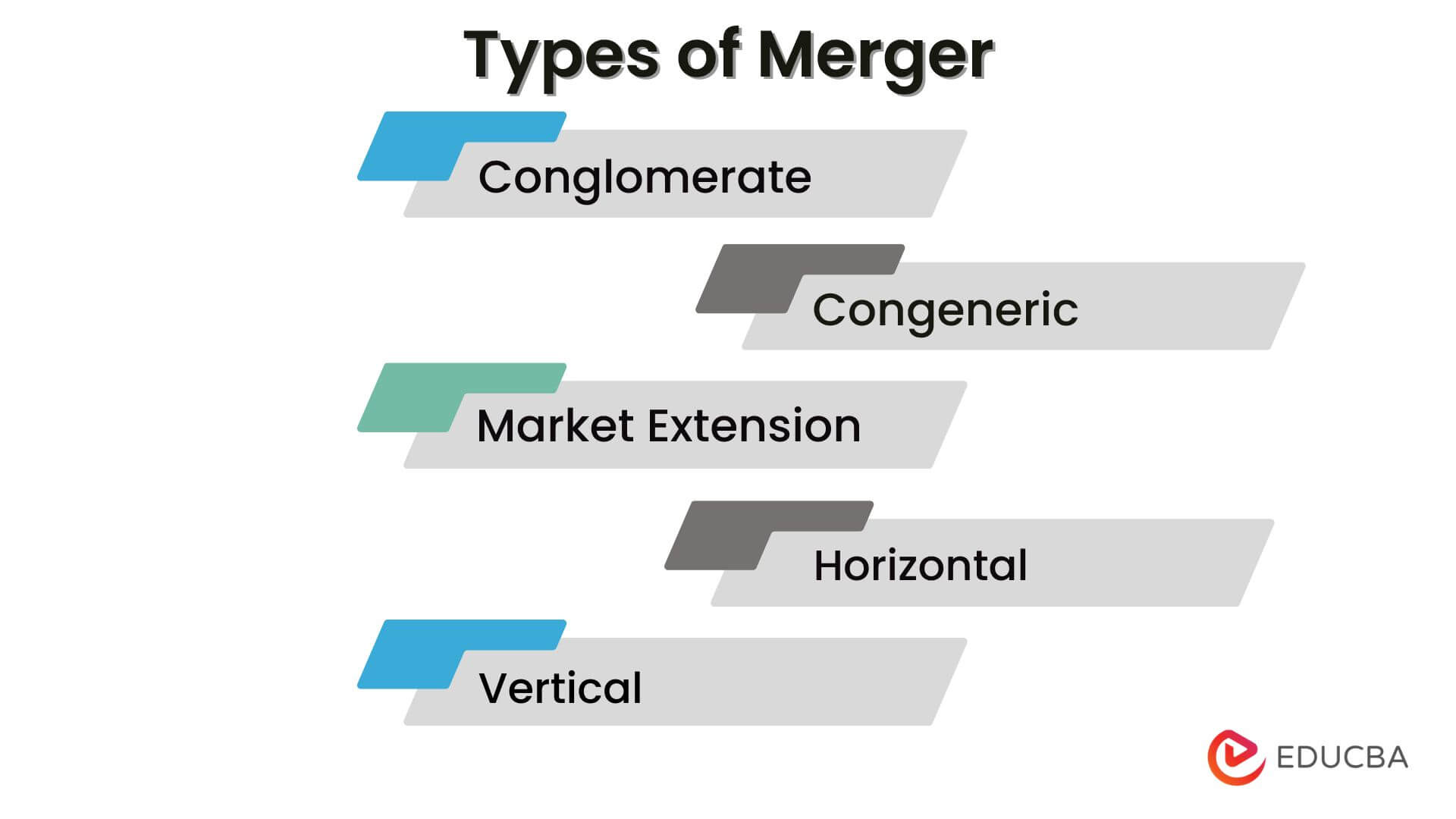
1. Conglomerate
- The merging companies are not from the same line of business.
- A pure conglomerate consists of two distinct companies. In contrast, a mixed conglomerate involves businesses with unrelated commercial endeavors.
- Therefore, a business mostly does this to diversify. Such a variety strategy helps the firm grow its clientele and scale.
2. Product Extension
- The companies have the same line of business and operate in a similar market with overlapping technologies.
- Such companies intend to leverage by adding one’s product line to another’s.
- Therefore, the new entity can build a more extensive customer base and reap the benefits of transferring technical knowledge.
3. Market Extension
- Both companies engage in the sales of similar products but in different geography.
- Hence, it enables the companies to expand their product’s reach to other geographies to enhance market reach.
4. Horizontal
- These companies belong to a similar industry and sell the same products.
- To prosper, a company must steadily grow its market share and eliminate the competition. Therefore, it must either acquire the rival or provide higher-quality products.
- Therefore, it results in a more significant market share, reduced operating costs, and economies of scale.
5. Vertical
- Both companies operate at different levels in the same industry.
- It affects the production and distribution of the product/service.
- Therefore, companies do this to impose more control over the supply chain.
- It is either backward integration or forward integration. It usually results in a reduction in operating costs.
Examples
- The Merger of ABC Inc. and Walt Disney Co. in 1995 is an example of a conglomerate. ABC Inc. was in the broadcast television network, while Walt Disney belonged to the entertainment industry.
- The Merger of Broadcom and Mobilink Telecom Inc. in 2002 exemplifies product extension. Both entities were from the electronics industry, allowing them to combine their technical know-how.
- The Merger of RBC Centura and Eagle Bancshares Inc. in 2002 is an example of market extension. It allowed RBC to expand its operations in the North American market.
- The Merger of Hewlett-Packard (HP) and Compaq in 2001 is an example of a horizontal merger. It created a global technology leader valued at over $87 billion.
- The Merger of Time Warner and AOL in 2000 is an example of a vertical merger. Time Warner was in the information industry through CNN and Time Magazine, while AOL distributed information over the internet.
Difference Between Merger and Acquisition
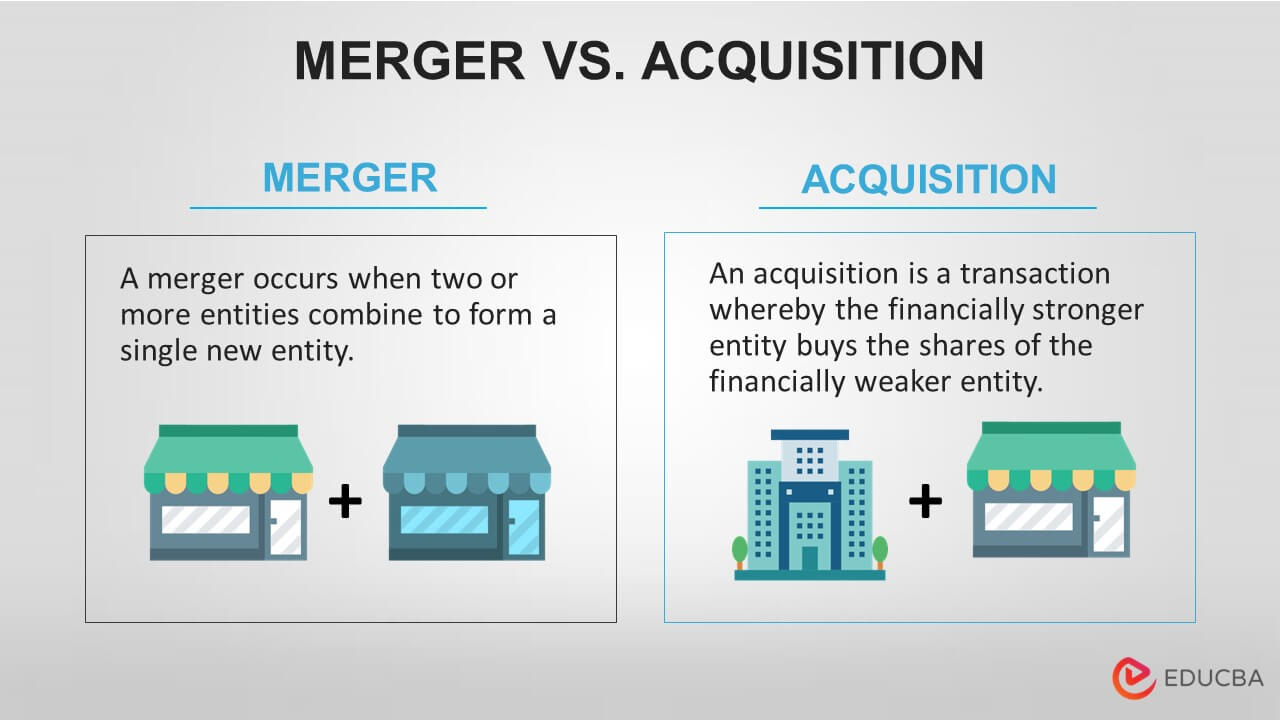
Mergers
- It is the process of combining two or more entities to form a new one.
- It results in an amicable situation as the companies decide after discussions and agreements between the combining entities.
- Usually, the companies are of equal stature. Hence they can draw the benefits of synergy.
Acquisition
- It is a process in which the financially stronger entity takes over the weaker one.
- It can result in a chaotic situation as, in most cases, the decision is not mutual.
- Therefore, the acquiring company often imposes its will on the target company resulting in a power gradient.
Post Merger Integration (PMI)
- It merges two or more entities to optimize synergies to guarantee that the transaction delivers the estimated return.
- Planning in the initial PMI step is closely related to value creation.
- The entity should clarify the governance of its operations in a meeting following the integration.
- Before the process ends, a comprehensive plan must be in place to prevent typical risks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
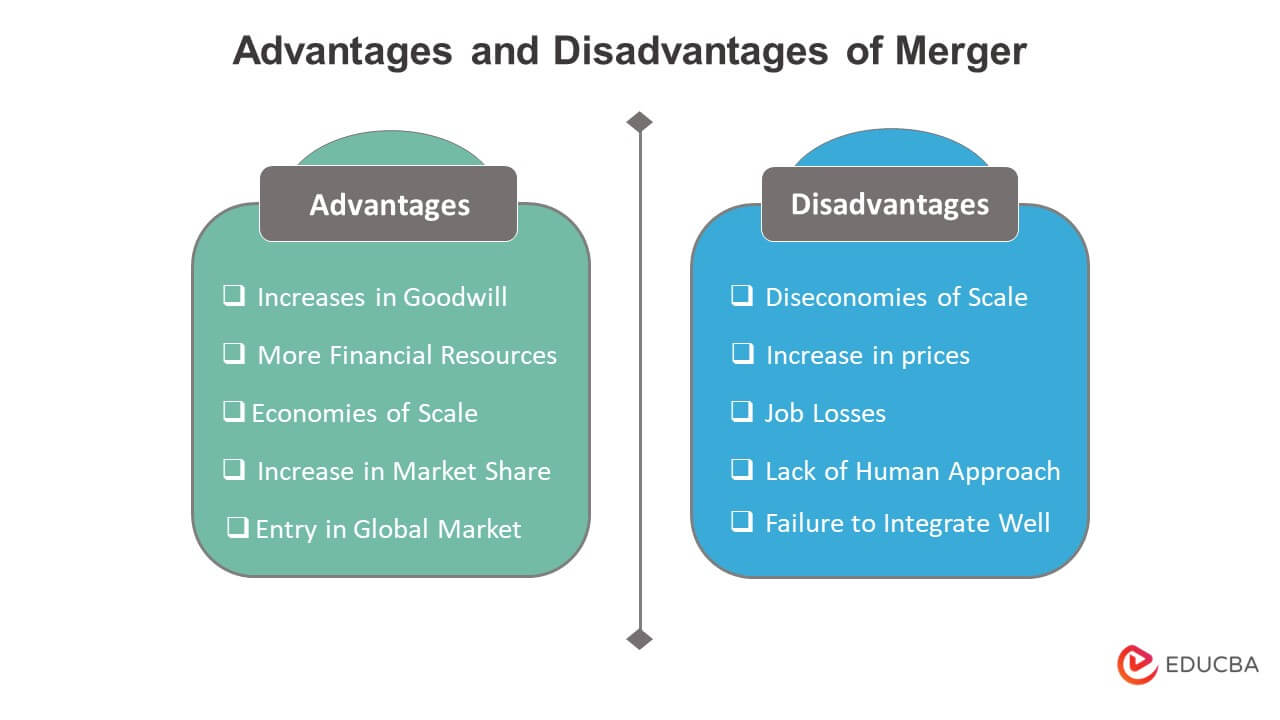
Advantages
- It helps gain a larger market share for entities competing in the same market.
- It also offers the benefit of economies of scale that reduces the cost of operations.
- Companies wanting to venture to other geographies can expand their operations without the hassles of setting themselves up.
- It results in organic and inorganic revenue growth.
- It can also save a corporation from bankruptcy and keep an unprofitable enterprise from closing.
Disadvantages
- In some cases, the growth rate of the new entity can be lower than before.
- Communication and coordination among employees can be challenging.
- It can result in a larger entity potentially engaging in a monopoly.
- A firm can also get rid of the underperforming resources of the other corporation, which might lead to workers losing their jobs.
- For companies with few similar attributes, gaining synergies can be challenging.
Conclusion
A merger is an essential business strategy as it is imperative to grow a business. It promotes sustainability in evolving markets by providing both organic and inorganic growth. It is different from acquisition and has its benefits. Therefore, companies can align their businesses with conglomerate, horizontal, vertical, product, or market extensions.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is a merger? What are its types?
Answer: A merger establishes a new entity by combining two independent businesses. In other words, it combines two distinct legal entities into one. Therefore, the five types are conglomerate, horizontal, vertical, product extension, and market extension.
Q2. What does a reverse merger mean?
Answer: A reverse merger is when a private corporation buys a publicly listed corporation. It is also called a reverse takeover (RTO) or reverse IPO. Thus, it simplifies the process of a private company going public.
Q3. Why do companies use mergers?
Answer: A merger can occur for a variety of reasons. Some reasons can be to acquire more resources and expand the scope of operations. Companies can also use it to diversify their products to boost earnings or lower the cost of product advertising.
Q4. Are mergers and acquisitions the same?
Answer: A merger occurs when two independent organizations unite to form a new organization. On the other hand, an acquisition is the taking over of one organization by another.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Merger. Here we discuss how a merger works, its examples, types, and advantages & disadvantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more,


