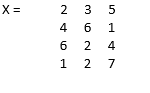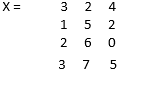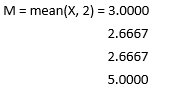Updated March 21, 2023
Overview of Mean Function in Matlab
MATLAB is a language used for technical computing. As most of us will agree, an easy to use environment is a must for integrating tasks of computing, visualizing and finally programming. MATLAB does the same by providing an environment that is not only easy to use but also, the solutions that we get are displayed in terms of mathematical notations which most of us are familiar with. In this article, we are going to discuss the mean function in detail in Matlab.
Uses of MATLAB include (but not limited to)
- Computation
- Development of Algorithms
- Modeling
- Simulation
- Prototyping
- Data analytics (Analysis and Visualization of data)
- Engineering & Scientific graphics
- Application development
MATLAB provides its user with a basket of functions, in this article we will understand a powerful function called the ‘Mean function’.
Syntax of Mean Function in Matlab
Let us understand the Syntax of mean function in MATLAB
- M = mean(X)
- M = mean(X,dim)
- M = mean(X,vecdim)
- M = mean(___,outtype)
- M = mean(___,nanflag)
Now let us understand all these one by one with the help of examples
But before that, please keep in mind that in MATLAB, matrices have the following dimensions:
1=rows, 2=columns, 3=depth
Description of Mean Function in Matlab
1. M = mean(X)
- This function will return the mean of all the elements of ‘X’, along the dimension of the array which is non-singleton i.e. the size is not equal to 1 (It will consider the first dimension which is non-singleton).
- mean(X) will return the mean of the elements, if X is a vector.
- mean(X) will return a row vector which will have mean of each column, if X is a matrix.
- If X is a multidimensional array, mean(X) will operate along the 1st array dimension whose size is non-singleton (not equal to 1) and will treat all the elements as vectors. This dimension will become 1 and the size of other dimensions will not be changed.
Example
X = [2 3 5; 4 6 1; 6 2 4; 1 2 7]
So,
Solution: M = mean(X) = 3.2500 3.2500 4.2500
Here, since the dimension is not mentioned, the mean is taken along the row elements {for the first set of row elements we will get (2 + 4 + 6 + 1) divided by 4, i.e. 3.2500 and so on}
2. M = mean(X, dim)
This function will result in the mean along the dimension dim. The dimension passed will be a scalar quantity.
Example
X = [3 2 4; 1 5 2; 2 6 0; 3 7 5]
So,
Solution
3. M = mean(X, vecdim)
This function will calculate the mean on the basis of the dimensions specified in the vecdim vector. For eg. if we have a matrix, then the mean(X,[1 2]) will be the mean of all the elements present in A, because every element of the matrix A will be contained in the slice of the array defined by the dimensions 1 & 2 (As already mentioned, please do Remember that dimension 1 is for Rows and 2 is for columns)
Example
Let’s first create an array:
X(:, :, 1) = [3 5; 2 6];
X(:, :, 2) = [2 7; 1 3];
We need to find M = mean(X, [1,2])
Solution: M1 =
M1(:, :, 1) = 4
M1(:, :, 2) = 3.2500
There is also a new feature introduced in MATLAB, starting in R2018b.
This helps us to calculate the mean over all the dimensions of the array. We can simply pass ‘all’ as the argument to our function.
So, if we again consider the above-mentioned example and use the function M = mean(X, ‘all’), we will get the output as 3.6250 (which is actually the mean of 4 and 3.25 obtained above )
4. M = mean(___,outtype)
It will use any of any input arguments of the previous syntax and return the mean with the specified data type(outtype)
Out type can be of following three types:
- Default
- Double
- Native
Let’s understand this under 2 scenarios:
- When an argument is native
- When the argument is “double”
Example 1 (Argument is native)
X = int32(1 : 5);
M = mean(A, ‘native’)
Solution:
M = int32
3
Where int32 is the native data type of the elements of X and 3 is mean of the elements from 1 to 5
Example 2 (Argument is “double”)
X = ones(5,1);
M = mean(X, ‘double)
Solution:
M = 1
Here, we can check the class of output by using: class(M), which will return ‘double’
5. M = mean(___,nanflag)
This function will define whether to exclude or include NaN values from the computation of any previous syntaxes.
It has the following 2 types:
- Mean(X,’omitNaN’): It will omit all NaN values from the calculation
- Mean(X,’includeNaN’): It will add all the NaN values in the calculation.
Example
Let’s define a vector X = [1 1 1 NaN 1 NaN];
M = mean(A,’omitnan’)
Solution: Here, the output that we will get is mean of all the values after removing NaN values, which is:‘1’
So, as we can see, MATLAB is a system whose basic data element is an array that does not require any dimensioning. This allows us to solve computing problems, especially the problems with matrix & vector formulations.
All this is done in a significantly less amount of time when compared to writing a program in a scalar and non-interactive language such as C.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Mean Function in Matlab. Here we discuss the uses of Matlab along with a description of Mean Function in Matlab with its syntax and various examples.