What is the McKinsey 7S Model?
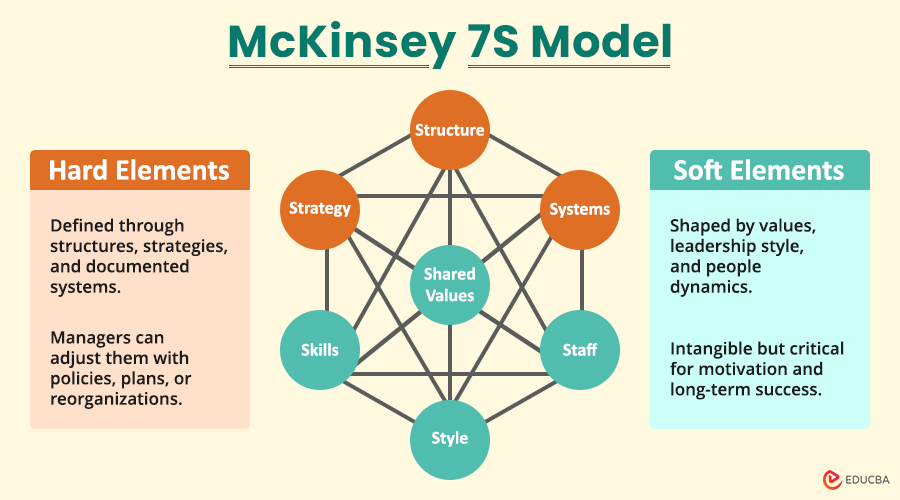
The McKinsey 7S Model is a management tool that examines seven key areas: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills, to help improve an organization’s performance. Unlike models that prioritize only strategy or structure, the 7S Model emphasizes that all seven elements are interdependent, and changes in one area affect the others.
The McKinsey 7S Model divides these seven elements into hard elements and soft elements, reflecting tangible operational components and intangible cultural and behavioral aspects, respectively. This dual focus allows managers and leaders to identify misalignments, optimize resource allocation, and enhance organizational performance.
The model can be applied across industries, including corporate enterprises, startups, educational institutions, and non-profit organizations, making it versatile for both strategic planning and operational execution.
Table of Contents
Seven Elements of the McKinsey 7S Model
The McKinsey 7S Model categorizes seven interrelated elements into hard elements and soft elements. Understanding these elements is key to analyzing an organization effectively.
Hard Elements
These are tangible, concrete aspects that can be directly influenced by management:
1. Strategy
Strategy refers to the long-term plan an organization adopts to achieve competitive advantage and meet objectives. It encompasses market positioning, product differentiation, growth plans, and resource allocation.
A well-defined strategy aligns all organizational efforts with corporate goals and enables the organization to respond effectively to market changes. Misalignment in strategy can lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and loss of market share.
2. Structure
Structure defines the organizational hierarchy, reporting lines, departmental divisions, and roles. It defines who performs each task and how employees communicate within the organization.
Structural alignment is critical because even the most effective strategies fail if the organizational framework does not support their implementation. Common structures include functional, divisional, matrix, and flat organizations.
3. Systems
Systems are the processes and routines, both formal and informal, that keep daily operations running smoothly. Examples include performance appraisal systems, IT systems, financial controls, and supply chain processes.
Efficient systems enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and support consistent execution of strategic objectives.
Soft Elements
These are intangible factors, often more difficult to measure, yet crucial for cultural and behavioral alignment:
1. Shared Values
Shared values represent the core beliefs, principles, and corporate culture that guide the behavior of an organization. They form the foundation of decision-making, ethical conduct, and organizational identity.
Organizations with strong, well-communicated shared values create cohesion among employees, improve engagement, and foster a sense of purpose.
2. Style
Style refers to the leadership approach and organizational culture that influence employee behavior and communication. Leadership style, whether autocratic, democratic, or transformational, affects motivation, productivity, and organizational climate.
Alignment of leadership style with strategy and shared values is critical for achieving organizational goals and managing change effectively.
3. Staff
Staff encompasses the workforce, including talent management, recruitment, retention, and professional development.
Ensuring the right people are in the right roles is essential for organizational efficiency. Investment in training and career development enhances employee competencies and aligns them with strategic objectives.
4. Skills
Skills are the capabilities, competencies, and expertise of employees. They determine whether the organization can effectively execute its strategy.
Organizations must continually assess skill gaps, provide targeted training programs, and capitalize on employee strengths to maintain a competitive edge.
How does the McKinsey 7S Model Work?
The 7S Model operates as a dynamic framework, where each element is interconnected. Changes in one area inevitably impact others. For instance, introducing a new strategy may require restructuring departments, reskilling staff, and adapting leadership styles to support it.
Step-by-Step Implementation:
1. Assess the Current State
Conduct a thorough evaluation of each of the seven elements to understand existing strengths, weaknesses, and misalignments.
2. Define the Desired Future State
Establish clear goals and targets for each element based on strategic objectives and market demands.
3. Identify Gaps and Misalignments
Identify inconsistencies or gaps between the current state and the desired state that may hinder performance.
4. Develop Action Plans
Formulate initiatives to address gaps, such as process improvements, leadership training, or cultural alignment programs.
5. Monitor Progress and Adapt
Continuously track progress, gather feedback, and adjust strategies to maintain alignment and achieve sustainable performance.
Benefits of the McKinsey 7S Model
The model provides numerous advantages to organizations that seek to align internal processes with strategic objectives:
- Enhanced organizational alignment: Ensures all elements of strategy, structure, systems, and culture work in harmony.
- Improved operational performance: Streamlines workflows and enhances productivity across departments.
- Effective change management: Facilitates smooth transitions during mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring.
- Insightful diagnostics: Helps identify gaps, weaknesses, and improvement opportunities.
- Employee engagement and retention: Aligns staff skills, leadership style, and shared values, fostering motivation and loyalty among employees.
- Strategic agility: Encourages organizations to respond effectively to market dynamics while maintaining internal cohesion.
Practical Applications of the 7S Model
The McKinsey 7S Model is widely applicable in various organizational contexts:
- Strategic planning: Ensures that strategy, resources, and culture align to achieve long-term goals.
- Organizational transformation: Assists in restructuring, digital transformation, and operational optimization.
- Mergers & acquisitions: Harmonizes processes, culture, and structures of merged or acquired entities.
- Performance improvement: Identifies skill gaps, optimizes talent deployment, and enhances operational efficiency.
- Change management initiatives: Aligns leadership, values, and processes to facilitate adoption of new practices.
Challenges and Limitations
While powerful, the McKinsey 7S Model is not without limitations:
- Complexity: Evaluating and aligning all seven elements can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Measurement challenges: Soft elements such as shared values, culture, and leadership style are subjective and difficult to quantify.
- Implementation requires leadership buy-in: Success depends on strong commitment from top management.
- Adaptation in rapidly changing environments: Frequent market changes require continuous reassessment to maintain alignment.
Final Thoughts
The McKinsey 7S Model remains an essential framework for organizations seeking to achieve internal alignment and strategic coherence. By systematically analyzing and aligning strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills, organizations can enhance performance, manage change effectively, and sustain competitive advantage.
By actively addressing every element, organizations foster a culture of continuous improvement and drive strategic agility. Organizations that adopt the 7S Model gain the insight and structure necessary to navigate complex business environments successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can the model be used for international or global organizations?
Answer: Yes. The 7S Model can guide global organizations in aligning their structures, strategies, and cultural values across multiple regions, ensuring coherence despite geographic and operational diversity.
Q2. Is there a software tool to implement the McKinsey 7S Model?
Answer: While there is no dedicated 7S software, project management, HR, and strategic planning tools can help track and implement changes in the seven elements effectively.
Q3. How does the McKinsey 7S Model differ from SWOT analysis?
Answer: Unlike SWOT analysis, which examines external opportunities and threats alongside internal strengths and weaknesses, the 7S Model focuses on aligning seven key internal organizational elements to enhance performance and execute strategy effectively.
Q4. How do organizations prioritize elements in the 7S Model?
Answer: Prioritization depends on organizational needs and challenges. For example, a startup may focus on strategy and skills, while a mature company may focus on culture, leadership style, or systems optimization.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide to the McKinsey 7S Model provided valuable insights into organizational alignment. Explore our related articles on strategic management frameworks, leadership development, and change management techniques to deepen your understanding and enhance business effectiveness.
