Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Struct
A structure is defined as the record-making process having various fields with different names. All fields can have different types of data whereas a single field should have some type of data. The keyword used for a structure in Matlab is “struct” Array of a structure is also possible in Matlab. A struct can have a single field, many fields, and even no field. It can be one dimensional or multi-dimensional. Value to the structure can be added using a structure name and filedname connected with the dot operator. Character values should be added using ‘ ‘ whereas numerical value can be added as it is.
Syntax:
str_name = struct('fieldname1', value1, 'fieldname2', value2, ...)
This creates a structure array with the specified fields and values. The type of value arrays i.e. value1, value2, etc., should be cell having the same size. The field name of the structure field is case-sensitive and should start with an alphabet. The remaining part of the field name can have alphabets, numbers, and special characters. Command “namelengthmax” can be used to find the maximum length of a field name.
Following are various methods to create a structure:
- str_name = struct(‘fieldname1’, {}, ‘fieldname2’, {}, …): Creates a structure which is empty with fields fieldname1, fieldname2, …
- struct([]): Creates a structure which is empty and has no fields.
- struct(o): Transforms the object o into its equivalent structure.
Example:
As an example, if we want to create a record of students in a class.
Using struct it can be done as follows:
str_stud=struct(‘rollno’,[1 2 3], ‘subjects’, char(‘physics’, ‘chemistry’, ‘maths’))
This example has a structure name as str_stud with field names rollno and subjects. Each having different values.
Working of Structure in Matlab
Given below is the working of structure in Matlab:
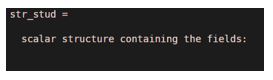
1. Structure with no field
str_stud=struct()
Output:
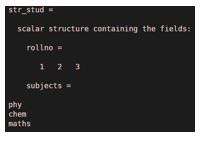
2. Structure with fields
str_stud=struct('rollno',[1 2 3],'subjects',char('phy', 'chem' ,'maths'))
Output:
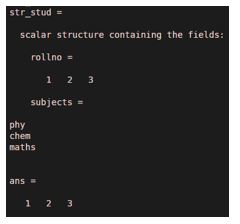
3. To display values of a particular field from structure
str_stud=struct('rollno',[1 2 3],'subjects',char('phy', 'chem' ,'maths'))
str_stud.rollno
Output:
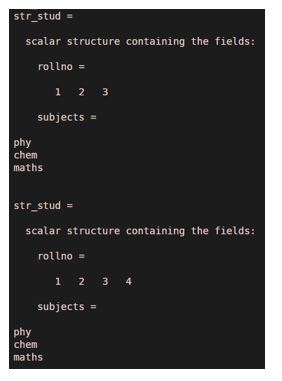
4. To add new value in the field
str_stud=struct('rollno',[1 2 3],'subjects',char('phy', 'chem' ,'maths'))
str_stud.rollno(4)=4
Output:
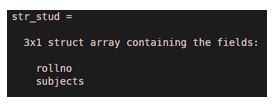
5. Example of structure array
str_stud=[struct(‘rollno’,[1 2 3], 'subjects',char('phy', 'chem' ,'maths'));
struct(‘rollno’,[4 5 6], 'subjects',char('phy', 'chem' ,'bio'));
struct(‘rollno’,[7 8 9], 'subjects',char('maths', 'comp' ,’sst'))];
str_stud
Output:
This will create a 3X1 structure array name str_stud.
Manipulating Structures
Structure manipulation is similar to the manipulation of arrays i.e by accessing elements of the structure using indexing and change the values of particular fields. The main difference is that all values of a field across a structure array cannot be assigned to a variable using a colon range specifier.
Example:
When str_stud is a 3X1 structure array, the following are the valid and non-valid operations in structures:
- Str_stud(1).subjects(2) is valid and gives the second element of subjects from the first record of str_stud
- Str_stud(1).subjects(:) gives all elements of subjects from Str_stud(1), same as Str_stud(1).subjects
- A=Str_stud(:).subjects is invalid, does not assign subjects from all records to A, though the command Str_stud(:).subjects or Str_stud.subjects displays subjects from all records.
To assign values to a variable, we have to use a loop construction:
- For i=1:3, all_subjects(i,:)= Str_stud(i).subjects; end.
The values cannot be assigned directly using a colon as the values of fields from various records are considered separate entities. The field contents can also be of different sizes. Hence, although the loop can be used for assignment, yet assignment should make sense. For example, in the for loop mention in the code above, Str_stud(2).subjects has only 2 entries, then the assignment will give an error. So, it is proved that indices can be used for structures and also fields for accessing data. Here, we have shown a small example. However, we can also have a structure inside structures in which the level of indexing will be a bit tough and confusing, and require extra effort in case of nested structures.
Conclusion – Matlab Struct
A structure is a record in which each record can have information or data about various things under different fields. Matlab uses a struct to implement this record-keeping technique. Structure in Matlab can be single dimensional as well as multi-dimensional which is also called a structure array.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Matlab Struct. Here we discuss the introduction, working of structure in Matlab, manipulating structures and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –