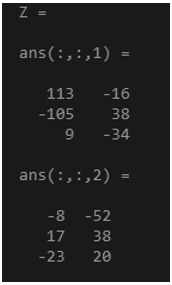Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Cross Product
In this article, we will learn about Matlab Cross Product. Vectors are defined as the quantity that has both magnitude and direction. They are mainly used in the field of mathematics and physics to demonstrate or define any mathematical quantity. There are various operations that can be performed using vectors, one such function is the multiplication of different vectors. There are two ways in which we can multiply vectors with other vectors, which are known as Cross Product and Dot Product. While dealing with the dot product, the resultant is always scalar whereas in Cross Product the resultant quantity is a vector.
How does Cross Product Work in Matlab?
The Following are the Working with Cross Product in Matlab with Syntax and Examples:
Cross product is defined as the quantity, where if we multiply both the vectors (x and y) the resultant is a vector(z) and it is perpendicular to both the vectors which are defined by any right-hand rule method and the magnitude is defined as the parallelogram area and is given by in which respective vector spans. In Matlab, the cross product is defined by using the cross () function and serves the same purpose as the normal cross product in mathematics.
Please find the below syntax which is used in Matlab to define the cross product:
- Z=cross (x, y): This returns the cross product of x and y which is Z, where x and y are vectors and they should have a length of three. If x and y are multidimensional arrays or matrices, then they should be of the same size.
- Z=cross (x, y, dimension): This returns the cross product of x and y along the defined dimension which is given by “dimension” in the syntax. It should be noted that the size of x and y should be the same, where size (x, dimension) and size (y, dimension) must have a length of three.
The input x and y can be input arrays which are generally numeric in nature. The data types that are supported are single and double. It also supports complex numbers. Another input i.e.dimension, it’s valued should be a positive value. If there is no value given to it, then by default it considers the dimension of the first array. If we mention the function as a cross (x, y,1) then it gives the cross product of x and y across the columns, where the inputs are treated as vectors. If we mention the function as a cross (x, y,2) then it gives the cross product of x and y across the rows, where the inputs are treated as vectors.
Examples to Implement in Matlab Cross Product
Below are the examples to implement in Matlab Cross Product:
Example #1
a. To find the cross product of the two vectors and check whether the resultant is perpendicular to the inputs using the dot product:
Code:
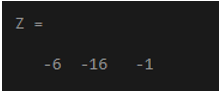
x = [5 -2 2];
y = [2 -1 4];
Z = cross(x,y)
Output:
b. To check whether the resultant is perpendicular to the inputs i.e. x and y, we have used the dot product.
Code:
p=dot(Z,x)==0 & dot(Z,y)==0
Output:
In the above example, Z is the cross product of the two input arrays x and y. p=1, which means that the output is perpendicular to the inputs x and y. If it is not perpendicular, then p will be 0.
Example #2
To find the cross product of the two matrices where integers are arranged randomly:
Code:
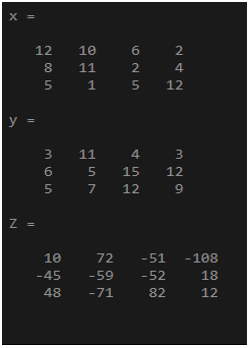
x = randi(12,3,4)
y = randi(15,3,4)
Z= cross(x,y)
Output:
There are various properties associated with the cross product, some of them are described below:
- Cross product of two vectors length is defined as ||x*y||=|x||y|sin α, where α is the angle of the defined vectors. The cross product is given by the length of each vector x and y and the angle between them. If the two vectors x and y are parallel to each other, then the result of the cross product is zero.
- It follows the property of anticommutativity, which means the result is the negative of the input. It is given by ||x*y||= -x*y.
- If we multiply any scalar quantity to the vectors, then it is in the below format: (cx)*y=c(x*y) =x*(cy), where c is the scalar quantity, x and y are the vectors.
- It follows the property of Distributivity, which is one of the most important properties in Mathematics. It follows the format as: x*(y+z) =x*y+x*z
- If x, y, and z are the vectors, then the scalar triple product of these vectors will be in the form of x+(y*z) =(x*y) +z
- If x, y, and z are the vectors, then the vector triple product of these vectors will be in the form of x*(y*z) =(x+z) y –(x+y) z
Example #3
a. To find the cross product of the multi-dimensional arrays which contain the random integers. Random Integers in Matlab can be defined by the “randi” function which generates the random numbers within a given range.
Code:
x = randi(15,3,2,2);
y = randi(10,3,2,2);
Z= cross(x,y)
Output:
b. If we consider the cross product along the rows, then we have to specify “2”, which is meant for rows in the command. Here resultant will be an accumulation of all the row vectors.
Code:
x = randi(15,3,3,2);
y = randi(10,3,3,2);
Z= cross(x,y,2)>/code>
Output:
c. If we want to find the cross product along the third dimension of the matrix, then we can mention it in the command.
Code:
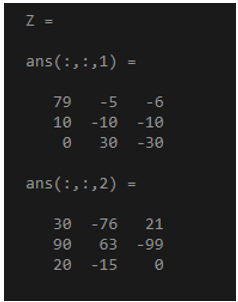
x = randi(15,3,3,3);
y = randi(10,3,3,3);
Z= cross(x,y,3)
Output:
Conclusion
Cross Product is an important aspect while dealing with vector quantities. They are mainly used in mathematical sectors to determine the cross product of the vectors. They are also used to find whether the two vectors are orthogonal in nature. So, learning the use of cross products is important if we are dealing with any vector related work.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Cross Product. Here we discuss basic concept, how does it works and examples to implement in Matlab Cross Product. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –