Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Matlab LineWidth
There are the various operations of lines in Matlab in which line width is one of the operations. Line width is used to adjust (increase) the width of any object. Line width operation mostly executes inside the plot operation. Plot operation is used to plot the input and output in a graphical way. We can increase the width of an object to any extent. By default, the line width size is ‘1’ in Matlab. Sometimes in complex figures or diagrams output gets disturbed or vanish, in such cases line width plays an important role. This command is represented as ‘LineWidth’. In this topic, we are going to learn about Matlab LineWidth.
Syntax –
Plot( x axis values, y axis values, ‘LineWidth’, value of width)
Example – plot(x,y,'LineWidth',1)
How does Matlab linewidth work?
Algorithm to implement LineWidth command in Matlab given below;
Step 1: Accept two inputs to plot graph
Step 2: Plot the graph
Step 3: Apply line width command
Step 4: Display the result
Examples
Here are the examples of Matlab LineWidth mention below
Example #1
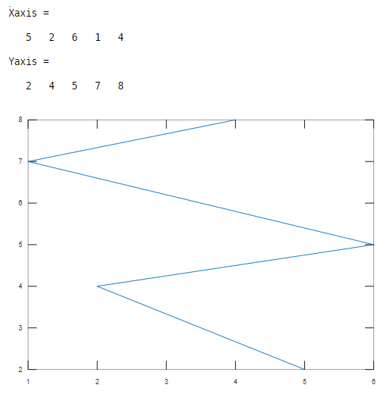
Let us consider two inputs as x-axis and y-axis. Here the values of first input are 5, 2, 6,1,4 and values of second input are 2,4,5,7,8. And the line width value is 1. This example illustrated in table 1.
Code:
Xaxis =[ 5 2 6 1 4]
Yaxis =[2 4 5 7 8 ]
plot(Xaxis , Yaxis ,'LineWidth', 1)
Output:
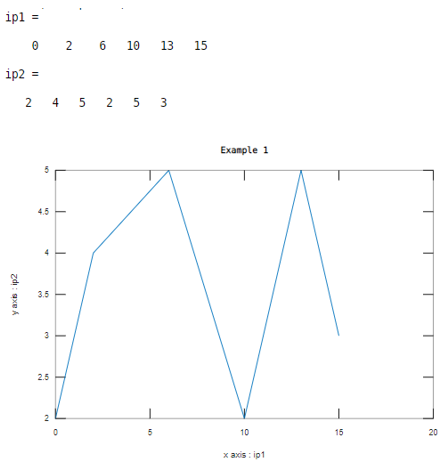
Let us consider two inputs as xaxis and yaxis. Here values of first input are 0, 2 , 6 , 1 0 , 1 3 , 1 5 and values of second input are 2 , 4 , 5 , 2 , 5 , 3 . And the line width value is 1. This example illustrated in table 2.
Code:
ip1=[ 0 2 6 10 13 15]
ip2=[2 4 5 2 5 3]
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1 ,ip2,'LineWidth',1)
title('Example 1')
Output:
Example #2
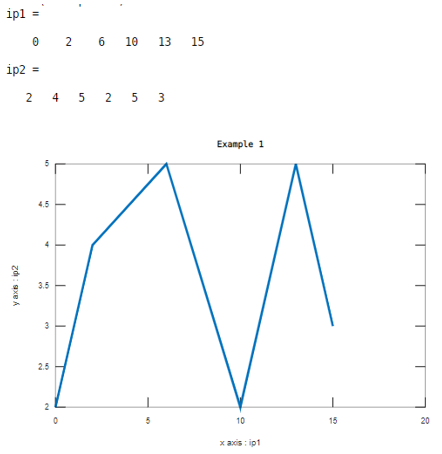
Let us consider two inputs as xaxis and yaxis. Here values of first input are 0, 2 , 6 , 1 0 , 1 3 , 1 5 and values of second input are 2 , 4 , 5 , 2 , 5 , 3 . And the line width value is 3. This example illustrated in table 3
Code:
ip1=[ 0 2 6 10 13 15]
ip2=[2 4 5 2 5 3]
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'LineWidth',3)
title('Example 1')
Output:
Example #3
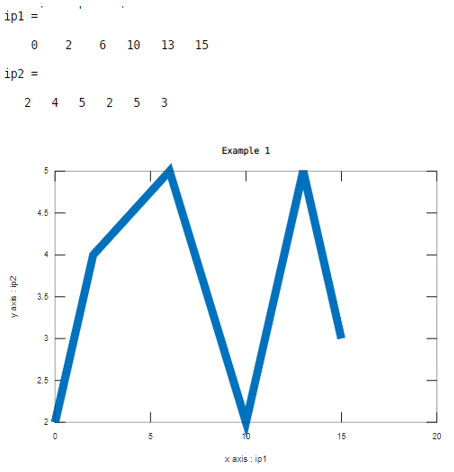
Let us consider two inputs as xaxis and yaxis. Here values of first input are 0, 2 , 6 , 1 0 , 1 3 , 1 5 and values of second input are 2 , 4 , 5 , 2 , 5 , 3 . And the line width value is 10. This example illustrated in table 3
Code:
ip1=[ 0 2 6 10 13 15]
ip2=[2 4 5 2 5 3]
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'LineWidth',10)
title('Example 1')
Output:
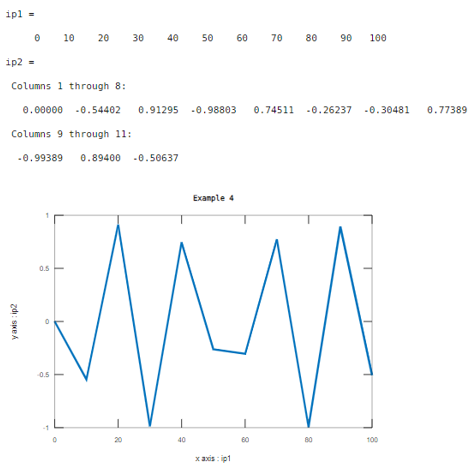
Example #4
Let us consider two inputs as xaxis and yaxis. Here the values of first input are range between 0 to 100 with a step of 10 and the values of second input are sine function. And the line width value is 3. This example illustrated in table 4
Code:
ip1=0:10:100
ip2=sin(ip1)
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'LineWidth',3)
title('Example 4')
Output:
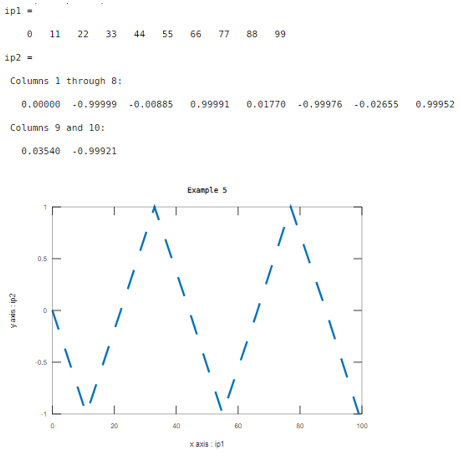
Example #5
Let us consider two inputs as xaxis and yaxis. Here the values of first input are range between 0 to 100 with a step of 10 and the values of second input are sine function. And the line width value is 3. The difference between the previous examples and this example is the pattern of width. This example illustrated in table 5.
Code:
ip1=0:11:100
ip2=sin(ip1)
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'--','LineWidth',3)
title('Example 5')
Output:
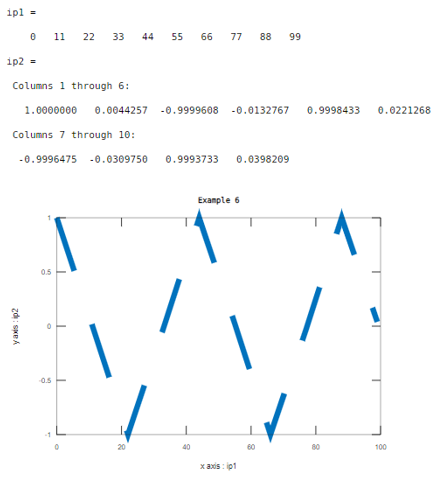
Example #6
In this example, the first input is a range of values from 0 to 100 with the step of 11. And the second input is the cosine signal with respect to the first input. Here line width is 8 and the pattern is dash lines.
Code:
ip1=0:11:100
ip2=cos(ip1)
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'--','LineWidth',8)
title('Example 6')
Output:
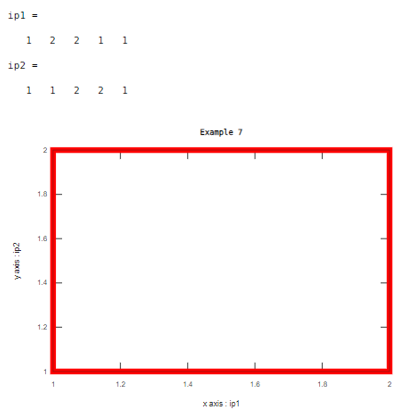
Example #7
In this example, the output is one object which is a rectangle. Line width is 8 and the color of width is red which we need to declare in program .otherwise default color is blue like previous examples.
Code:
ip1=[1 2 2 1 1]
ip2=[1 1 2 2 1]
xlabel('x axis : ip1');
ylabel('y axis : ip2');
plot(ip1,ip2,'LineWidth',8,'color','red')
title('Example 7')
Output:
Conclusion
If the output of the program is a specific object then line width plays an important role, it gives proper view to object .line width is basically used to increase the thickness of width line .along with thickness we can change the color of width and pattern of width.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab LineWidth. Here we discuss the algorithm to implement LineWidth command in Matlab along with the examples and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –