Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Arrays in Matlab
An array is a collection of numbers or string of characters stored in the memory. Each element is an array that has an index number and indexing starts from 0th position and can be referred to as the first element in an array. In Matlab, we use an array which can collect numbers and can be accessed using an index. There are various special functions present in Matlab to perform operations in array-like zeroes(), diag(), ones(), etc.
Various Operations of Arrays in Matlab
Multidimensional arrays in MATLAB have two dimensions or more than that. In two dimensions, elements in the array can be represented by using rows and columns while in three dimensions or more uses sheets or pages of elements. There are many operations that can be performed in an array. Please find the below examples for your reference:
Example:
M1= [4,3,2;7,6,5;9,8,7]
This is the first page of the 3-D array. We can also keep on adding pages by using the “cat” function.
M=cat (dimension, M1)
Here,
- M = new array.
- Dimension = dimension to append the arrays.
- M1 = array to be concatenated.
M1 = [4,3,2;7,6,5;9,8,7]
M2 = [9,8,7;6,5,4;3,2,1]
M = cat (1,M1,M2)
Output:
We can also use various functions like rand (), ones (), zeroes () functions to create multi-dimensional arrays.
1. rand ()
This function is used to create an array of randomly distributed numbers ranging from 0 to 1.
rand (4,3): This will create an array of random numbers having 4 rows and 3 columns.
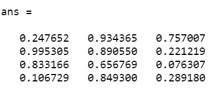
Example:
rand (4,3)
Output:
2. zeros ()
This function is used to create an array of zeroes depending on the number of rows and columns.
zeros (4): This creates an array of zeroes.
Example:
zeros(4)
Output:
3. ones ()
This function creates an array of ones depending on the number specified.
ones (4): This creates an array of ones.
Example:
ones (4)
Output:
Working of Arrays with Examples
We can also create character arrays in MATLAB which includes a combination of characters. Like number arrays, there are also various operations that can be performed using character arrays. We can always convert an array to character data type by using the char function.
Arrays are MATLAB and can be indexed by following different ways of indexing methods:
1. Indexing the Element by Position
This approach is used to find the element of an array by specifying the row number and column number to find a single element. We can also access the multiple elements by specifying the row number and the position of elements in the respective row. We can also access the range of elements by specifying the row and column range. Please find the below examples for better understanding:
Example:
I = [10,11,12,13;14,15,16,17;18,19,20,21;22,23,24,25]
I= 4*4
Output:
- To find the single element of an array:
I (2,3)
Output:
This gives the third element from the second row.
- To find the multiple elements in an array:
I (2, [1,2])
Output:
This gives the first and second elements from the second row.
- To find the range of elements in an array:
I (1:3,2:4)
Output:
2. Indexing With the Help of Single Index
Irrespective of mentioning the rows and columns in the syntax, we can directly mention the single index and find the element. This method is also known as linear indexing. Here the elements will be stored in a single column. Please refer the below example:
Example:
J= [20,23,31; 34,45,56;78,87,67]
JLin=J (:)
Here it stores the above elements in a single column.
Output:
We can access the element by using a single index number like JLin (5) which gives 45.
3. Indexing Using Logical Values
While using conditional statements, we use indexing with the logical values like True or False and we can find the elements which have a true value. Please find the below example
Example:
L1 = [11,23,45;67,78,89]
L2 = [10,24,46;68,77,88]
i=L1<L2
Output:
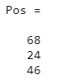
This checks the elements using the conditional statements(L1<L2) and assigns the value 1 if it IS true and 0 if it is false. To find out the elements which have value as 1.
Pos= L1(i)
Output:
Pos= L2(i)
Output:
Conclusion
Using arrays in various programming language has made the manual tasks easy and are used by the programmers. There are many advantages of using array-like accessing the elements in the array is easy which can be executed using simple steps, there are no performance issues in the program, proper usage of memory, faster execution and helpful in implementing the programs using stack, linked list, trees, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Arrays in Matlab. Here we discuss the basic concept, operations of Arrays in Matlab along with various examples and its implementation. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –