Updated October 30, 2023
Difference Between Market Cap vs Enterprise Value
The following article provides an online on market cap vs enterprise value. Market cap and enterprise value measures a company’s market value but are expressed in different parameters. It is important to understand that the calculation of both these measures is not identical, and these terms can’t be used interchangeably. Nevertheless, both measures allow you to peek at the company’s overall value, which can eventually be compared with similar companies.
What is Market Cap?
The term “market cap” is one of the simplest ways of understanding a company’s market value or size. This metric assesses the market value of a company only based on its stock. Calculating a company’s market cap is a task as it multiplies its current stock price per share and the total number of outstanding shares. For instance, a company with 1 million outstanding shares and a current stock price per share of $30 will eventually have a market cap of $30 million (= $30 * 1,000,000).
Another major market cap use is splitting companies into different categories, such as small-cap, mid-cap, and large-cap stocks. Such categorization is usually helpful in finding companies for peer comparison within the same industry, as each category has unique characteristics. For instance, company stocks in the large-cap section are usually considered less risky with lower growth potential, and the trend gradually alters in the cases of mid-cap and small-cap stocks.
What is Enterprise Value?
The term “enterprise value” refers to the alternative method of assessing market value, which is a more comprehensive approach. As such, most investors are inclined to use a company’s enterprise value for purchasing its shares. Calculating enterprise value is slightly more complex than market cap, as it involves summating the market cap, and total debt obligations and subtracting the total cash on hand. Some of the companies prefer including factors such as preferred shares and minority interest in the calculation of enterprise value.
The enterprise value of a company signifies a hypothetical purchase price. This method is predominantly used in the asset valuation for the buyer; eventually, the buyer would take up all the responsibilities for all of its existing debt obligations.
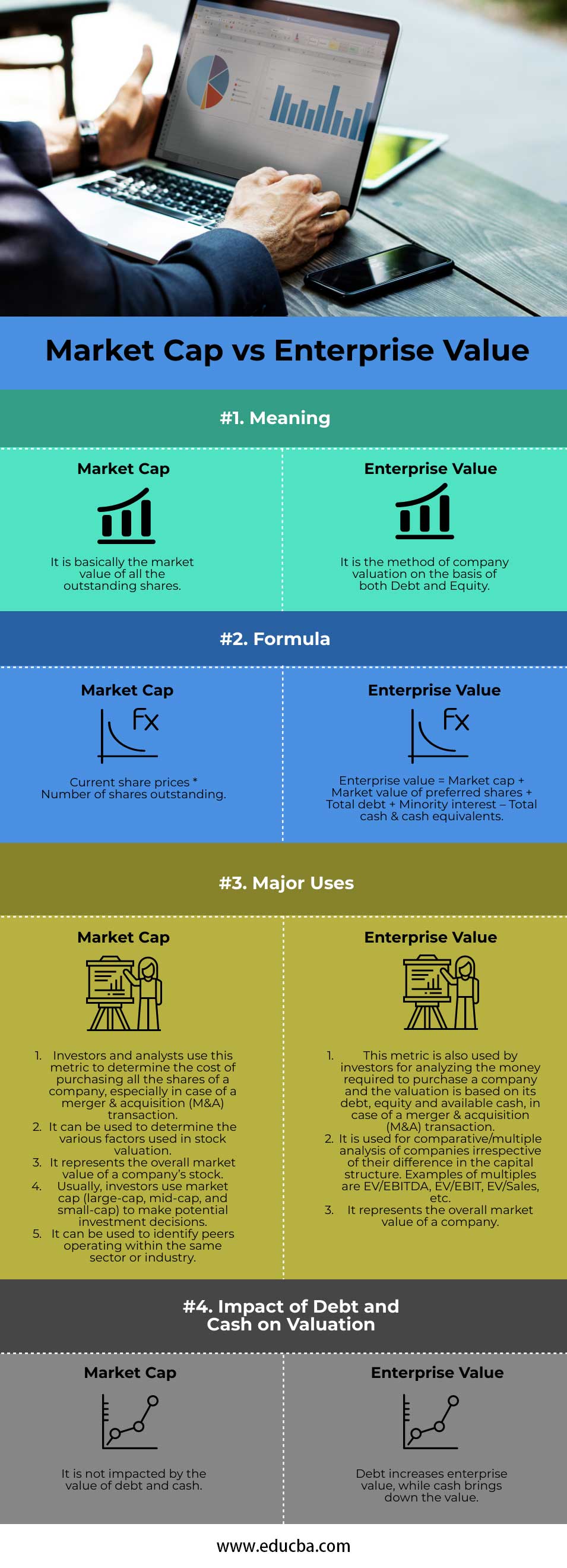
Head To Head Comparison Between Market Cap vs Enterprise Value (Infographics)
Below are the top 4 differences between Market Cap vs Enterprise Value:
Key Differences Between Market Cap vs Enterprise Value
Some of the key differences between market cap and enterprise value are:
- The market cap valuation is entirely based on equity stock, while the valuation of enterprise value considers debt and cash alongside equity.
- While enterprise value is predominantly used in multiples analysis (EV/EBITDA, EV/Sales, etc.), the market is rarely used.
- While market cap categorizes companies into large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap brackets, enterprise value has no such use.
- A company’s enterprise value is expected to be higher if it has a positive debt situation (debt higher than cash & cash equivalent). However, in the case of a net cash position (debt lower than cash & cash equivalent), the market cap is higher than the enterprise value.
Market Cap vs Enterprise Value Comparison Table
Let us discuss the top comparison between Market Cap vs Enterprise Value:
|
Area of Comparison |
Market Cap |
Enterprise Value |
| Meaning | It is the market value of all the outstanding shares. | It is the method of company valuation based on both Debt and Equity. |
| Formula | Current share prices * Number of shares outstanding | Enterprise value = Market cap + Market value of preferred shares + Total debt + Minority interest – Total cash & cash equivalents |
| Major Uses |
|
|
| Impact of Debt and Cash on Valuation | The value of debt and cash does not impact it. | Debt increases enterprise value, while cash brings down the value. |
Conclusion
So, it can be seen from the factors discussed above that both financial metrics have different approaches for identifying the market value of any company. Market cap is one that investors use to find information about the company’s size, value, and growth outlook solely based on its equity value. On the other hand, enterprise value is used by investors for measuring the company’s overall market value that incorporates the value of its equity, debt, and cash & cash equivalents. Although both metrics are very useful in different ways, investors prefer the enterprise value over the market cap because it helps more accurately determine the company’s value. So the analysts can project the company’s future growth in a better way.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Market Cap vs Enterprise Value” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.