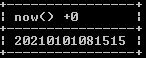Updated June 3, 2023
Definition of MariaDB Timezone Function
MariaDB provides a time zone variable to maintain the track of several time zone settings. Basically, Time_zone is a system variable and it is a primary way to set the time zone. We can use different formats to select the timezone of the MariaDB server, normally, by default, the value of the time zone is SYSTEM, and it is used to indicate the system time zone by using the system_time_zone system variable. We can also use the Coordinated Universal Time zone. If we loaded the time zone table in the mysql database, we can have permission to access different time zones such as Africa, America or Europe, etc.
Syntax:
set time_zone = 'value''Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the set keyword with the time_zone system variable to set the time zone of a specified country or area, which depends on user requirements.
How does Timezone function work in MariaDB?
Time zone uses a different parameter when setting the time_zone system variable, so let’s see how it works. Normally there are two different time zone settings we need to set within the MariaDB server: the global server time zone and the time zone for the current session.
Global Server Time Zone
We can change the global server time zone by using two different ways: by using settings in which we can set the default time zone option and the alternate option by using the command line. We can also change the global server time zone by using dynamic settings, but the user account has permission for the super privilege.
Session Time Zone
When a session connects to the server, it also has its own local time zone we call the session time zone. Basically, the session time zone is generated from the global value of the time_zone system variable. The session time zone we can change by using the dynamic setting of the time_zone system variable.
System Time Zone
The system time zone value can determine when we start the server, and it sets the value of the system_time_zone system variable. Normally the system time zone fetches the current time from the operating system. We can change the system time zone by using different ways as follows.
The first way is that when we start the server with mysqlld_safe at that time, we can set the system time zone with time zone value, and another way is by using the command line option. Using the UNIX operating system, you can select the system time zone by setting the environment variable.
Time Zone Effects on Functions
When we set a time zone variable, some functions are affected as follows.
NOW()
Now function is used to current date and time as a value in YYYY-MM-DD format. The return value is shown in the current time zone. You can use the precision as an optional part of the now function to actively determine the time in microseconds.
Example:
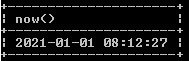
Select now();Explanation:
With the help of the now function, we can fetch the current date and time of the system. The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot
Select now() +0;Explanation
We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Let’s see some examples of now function with precision as follows.
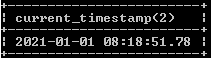
select current_timestamp(2);Explanation
In the above example, we use a precision value which is the current timestamp value, as shown in the above statement. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
SYSDATE()
SYSDATE is also used to return data and time in YYYY-MM-DD format with time format. The precision part of the SYSDATE function is optional. The basic difference between NOW() and SYSDATE() is that SYSDATE() is used to return the time at which time is executed, and the NOW() function is used to return the constant time at which time the statement began to execute.
Example:
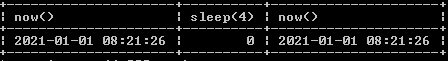
select now(), sleep(4), now();Explanation:
In the above example, we use the now and sleep function to see the difference between the now and sysdate function. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
SELECT SYSDATE(), SLEEP(4), SYSDATE();Explanation
In the above example, we use the sysdate function with a sleep parameter, as shown. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
It also returns the current date in the format YYYY-MM-DD and depends on whether the function uses a string or a number.
This function returns the current time in HHMMSS or HH:MM: SS format and depends on whether the function uses a string or number.
If we call this function without an argument, it returns a UNIX timestamp as an unsigned integer. If we use uinix_timestamp(), it returns a data argument with a UTC value. Maximum value of the Timestamp is 2147483647, equivalent to 2038-01-19 05:14:07.
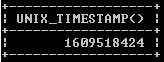
SELECT UNIX_TIMESTAMP();Explanation
In the above statement, we use the UNIX_TIMESTAMP function to see the time stamp value without argument. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Some functions are not affected, listed as follows.
Examples
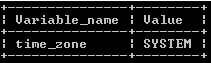
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'time_zone';Explanation:
Suppose we need to see the global of the current server at that time, we can use the above statement. This statement uses the show global variable command with the LIKE clause, and time_zone is the system variable. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
SET GLOBAL time_zone ="Africa/Johannesburg";Explanation
In the above example, we use a set global keyword with a system variable time_zone, as shown in the above statement. Suppose the user needs to set a global time_zone as per requirement; then the user can use the above statement. In this example, ‘Africa/Johannesburg’, we consider the value we can change that value. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood the MariaDB time_zone. From this article, we have learned the basic syntax of time_zone, and as well as we also see different examples of time_zone. From this article, we learned how and when we use MariaDB time_zone.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Timezone” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.