Updated June 3, 2023
Definition of MariaDB Foreign Key
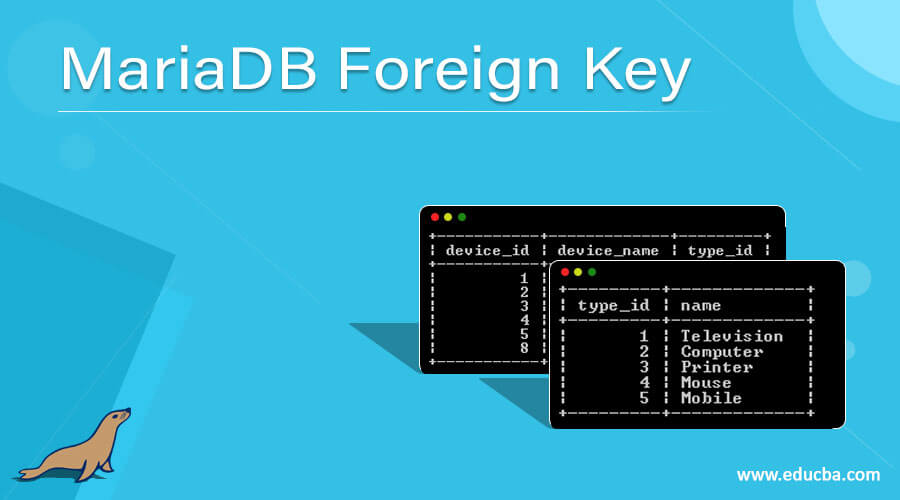
MariaDB provides referential integrity constraints we call as foreign key. A foreign key is a set of columns or columns in a parent table that refers to another set of columns or columns we call a child table. Another way we can say that referential integrity constraint between two tables. Those tables contain foreign keys we call the child table, and the table in which the foreign key is referenced is known as the parent table. The foreign key column in the child table references the primary key from the parent table. Using a foreign key in MariaDB enforces some integrity rules every time.
Syntax:
create table table_name (colm name 1, colm name 2, ………colm name N ) [constraint name] foreign key [foreign key name] (colm name or list) reference parent_table_name (column list or set) [on delete reference_option] [on update reference_option];Explanation:
In the above syntax, first, we use create table statement. After that, we constraint the name to specify the foreign key name, if we skip this constraint, MariaDB will use the default generated name. In the next part, a foreign key is followed by a foreign name with a list of column names separated by a comma within parentheses. After that, we specify the parent name with the column list after the reference keyword, as shown above, syntax. Finally, we determine how foreign key maintains referential integrity between two tables, the child and parent table, by using delete and update clauses.
How does foreign critical work in MariaDB?
Foreign key work when the value of both tables matches that enforced the referential integrity. Let’s see how foreign key works in MariaDB with different parameter, when we use a foreign key in a table at that time, we can control the operation by using different parameters as follows.
On delete no action: This is the default parameter in foreign keys. If any existing referencing key is deleted, then the transaction fails at the end of the query. The key will be updated by using an update clause.
On update, no action: This is a default parameter in the foreign key. If any existing key is updated from the parent table, then the transaction fails at the end of the query. The foreign key we can delete by using the delete clause.
Examples
Let’s see how foreign keys work in MariaDB with the help of different examples as follows.
There are two ways to create foreign keys, or we can say to add foreign in the table as follows.
1. Create foreign keys at the time of table creation.
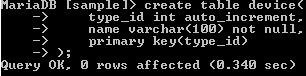
create table device(
type_id int auto_increment,
name varchar(100) not null,
primary key(type_id)
);Explanation:
In the above example, we use create table statement, here, we created the table name as a device with different attribute, such as type_id and name with different data types, as shown above statement. We assign type_id as a primary key. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Let’s create another to implement foreign key constraints.
create table device_type(
device_id int auto_increment,
device_name varchar(100) not null,
type_id int,
primary key(device_id),
constraint fk_de_type
foreign key(type_id)
references device (type_id)
);Explanation:
In the above example, we use a create table statement. Here we created a table name as device_type with different attributes such as device_id, device_name, and type_id with different data types as well here, we define the foreign key name as fk_de_type as shown in the above statement, type_id is a reference of device table that means (type_id). The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Now we insert some records into the device table using the following statement as follows.
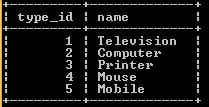
insert into device(name)
values
('Television '),
('Computer'),
('Printer'),
('Mouse'),
('Mobile');
select * from device;Explanation:
With the help of a statement, we inserted the above records into the device. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Now insert some record into the device_type table using the following statement.
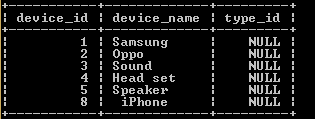
insert into device_type (device_id, device_name)
values
(1, 'Samsung'),
(2,'Oppo'),
(3,'Sound'),
(4, 'Head set'),
(5, 'Speaker'),
(8,' iPhone');
select * from device_type;Explanation:
With the help of a statement, we inserted the above records into the device_type table. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
We can perform different operations with the help of restrict reference, null reference, and cascade reference option.
2. Second way to create foreign keys is by using the alter table command.
In this method, we can use the alter table command to add foreign keys to the table.
After successfully creating a foreign key, we can perform different operations on the table, and the effect shows on both tables; we can perform the update, delete, and alter operations.
Rules and regulations for using the foreign key
Foreign keys are referential integrity constraints in MariaDB and work between parent and child tables. We can create foreign keys at the time of table creation, or we can use an alter command to create a foreign key. When we use reference_option in the foreign key, the reference_option accepts the following five different values.
Cascade: When we make some changes, it means to update or delete in the parent table, then corresponding rows from the child table automatically update or delete.
Set Null: When we deleted rows from the parent table, then corresponding rows from the child table are null.
Restrict: if reference rows are updated from the parent table, then referencing rows from the child table is restricted.
No action: It works the same as restrict function as mentioned above.
Set Default: The default value worked with the obsolete PBXT storage engine in MariaDB. in which that foreign key set the default value in MariaDB, if the default value of the foreign key is not available, then MariaDB shows an error message.
Conclusion
We hope you understand the MariaDB Foreign Key from this article. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of MariaDB Foreign Key, and we also see different examples of MariaDB Foreign Key. We also learned the rules of MariaDB Foreign Key. This article taught us how and when to use MariaDB Foreign Key.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Foreign Key” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.