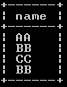Updated June 3, 2023
Definition of MariaDB GROUP_CONCAT Function
MariaDB provides Group_Concat function to the users. The Group_Concat function is used to return non-null concatenated values from the group. When the result is Null, it returns null, meaning there are no non-null values. Commonly the Group_Concat function produces a group of strings into a single string. The maximum returned length of a string in the Group_Concat function is 1M or 1K, and we can determine by using group_concat_max_len server system variables.
If group_concat_max_len is less than 512, then the return type is VARCHAR or VARBINARY otherwise return types is BLOB or TEXT. The choice of return string (binary or non-binary) depends on the input.
Syntax:
select colm 1, colm 2,……colm N group_concat([distinct value] exp 1, exp 2……..[order by clause sort_exp[Asc | Desc],……] [separator] );Explanation:
In the above syntax, we used the group_concat function with different parameters; here distinct keyword is used to remove duplicate string before the concatenating operation. After that, we use order by clause to sort all values in ascending or descending order before the concatenation operation, and for the last parameter, we use a separator. It is used to separate two different resulting strings, the by default separator is comma (,).
How GROUP_CONCAT function works in MariaDB?
Let’s see how the group_concat function works, the group_concat function uses different parameters as follows. Basically, the group_concat function concatenates data from multiple rows into a single field.
Distinct clause is used to remove duplicate values or strings in the group before the concatenation operation. The other parameter we used with the group_concat function is that order by clause, and it is used to make data in some order, such as ascending or descending order this sort of option we can use as per user requirement. The next parameter is the separator; this separator is used to separate two different strings or values using commas.
Another important thing is that the group_concat function ignores the null string, and sometimes it returns a null result if there is no matching row, or we can say all arguments are null.
Examples
Let’s see a different example of the group_concat function for a better understanding as follows. We required different tables for implementation purposes, so first, create tables using the following statement.
create table lang(lang_id int auto_increment,
lang varchar(250) not null,
primary key (lang_id));Explanation
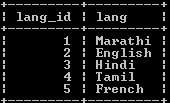
In the above example, we created a table name as lang with two attributes such as lang_id and lang, with different data types as shown in the above statement, and here primary is lang_id, it also has an auto_increment property.
Now create a second table by using the following statement as follows.
create table state_lang(state_id int auto_increment,
lang_id int not null,
state_name varchar(250) not null,
primary key (state_id));Explanation
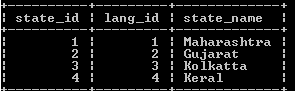
In the above example, we created a table name as state_lang with different attributes such as state_id and state_name with different data types, and here primary key state_id is shown in the above statement.
Now perform the insert operation on created tables by using the following statement.
Insert into lang(lang) values ("Marathi"), ("English"), ("Hindi"), ("Tamil"), ("French");
select * from lang;Explanation
With the help of the above statement, we insert some records into the lang table. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Similarly, we will insert some records into the state_lang table by using insert into the statement as follows.
insert into state_lang(lang_id, state_name) values (1,"Maharashtra"), (2, "Gujarat"), (3, "Kolkatta"), (4, "Keral");
select * from state_lang;Explanation
With the help of the above statement, we insert some records into the state_lang table. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Now see how the group_concat function works as follows.
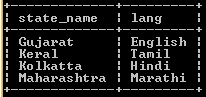
select
state_lang.state_name,
group_concat(lang) lang
from
state_lang
inner join lang
using (lang_id)
group by
state_name;Explanation
In the above example, we used select and group by clause. See here we used inner join to see the result from two different tables, such as lang and state_lang, and we merge the result by using the group_concat function as shown above statement, that means we can make grouping from different tables as per our requirement. In this example, we don’t have matching records. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Let’s see another simple example of the group_concat function using distinct and separator keywords as follows.
create table demoo (name varchar(250) not null);Now insert some records by using the following statement as follows.
insert into demoo(name) values ("AA"), ("BB"), ("CC"), ("BB");
select * from demoo;We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Now use the group_concat function with distinct keywords as follows.
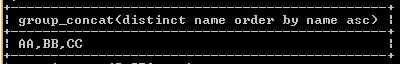
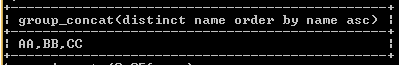
select group_concat(distinct name order by name asc) from demoo;Explanation
In the above example, the select statement utilizes the group_concat function with a distinct keyword and an order by clause to retrieve unique and sorted records from the demo table, as shown in the previous statement. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Example
SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT User ORDER BY User asc)
FROM mysql.user;Explanation
Suppose the user needs to see all distinct users from mysql.user table at that time, we can use the above statement. In the above example, we use a select clause with group_concat function as shown in the statement after that, we use order by clause to sort them. In this example, we don’t need to use a separator because MariaDB takes it by default to separate two different strings. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
In some versions of MariaDB, we can’t use the LIMIT clause with the group_concat function this is the restriction, or we can say this is the limitation of MariaDB version (10.3.3).
Similarly, we can implement a group_concat function with different clauses with different constraints.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the MariaDB group_concat function. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the MariaDB group_concat function and different examples of group_concat functions with different clauses and keywords. This article taught us how and when to use MariaDB group_concat function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB GROUP_CONCAT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.