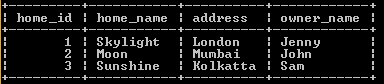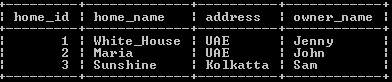Updated June 3, 2023
Definition of MariaDB UPDATE Statement
MariaDB provides the update facility to users like MySQL, Update command is used to modify the content of columns. The update command uses the SET clause to specify the column name for modification and assign a new value for that field. The assigned value can, by default value or some expression dependent on the table’s property. When we use the default, we need to use the default keyword. The update command also uses a where clause to specify conditions for the update, and we can also use order by clause to make them in order, the order by clause is optional. We can specify how many rows will be updated using the LIMIT clause in the update command.
Syntax:
update table name set column 1 field = new assigned value,column 2 field = new assigned value,........... column N field = new assigned value
where [Condition.......] order byExplanation:
In the above syntax, we use the update command followed by the table name, as shown in the above syntax. After that, we need to specify the column field with the assigned new value per our requirement. Finally, we use the where clause to specify the condition for the update command, and order by clause is optional.
How does UPDATE Statement work in MariaDB?
We need exiting data or tables to perform an update command in MariaDB. For update purposes, we need different clauses such as SET, WHERE, and LIMIT clause, which we can use as per our requirement. The LIMIT and order by clause are optional in the update statement. Update command works for single column field updating and multiple column updating.
Example
Let’s see a different example of how update statements work in MariaDB.
First, we need to create table busing following the create a statement as follows.
create table home_table(
home_id int not null auto_increment,
home_name varchar(100) not null,
address varchar(40) not null,
owner_name varchar(50) not null,
primary key ( home_id )
);Explanation:
For example, we created a table name as home_table with different attributes such as home_id, home_name, address, and owner_name with different data types, as shown in the above statement. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
After that, we need to insert some records by using insert into the statement as follows.
insert into home_table
( home_name, address, owner_name)
values
("Skylight", "London", "Jenny"),
("Moon", "Mumbai", "John"),
("Sunshine", "Kolkatta", "Sam");
select * from home_table;Explanation:
With the help of the above statement, we inserted some records into the home_table. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Now we have a table with records to perform update commands as follows.
- Update single column
Suppose we need to change the home name from the above table. At that time, we used the following statement as follows.
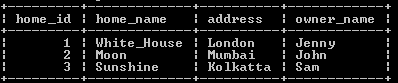
update home_table
set home_name = 'White_House'
where home_id = 1;Explanation:
In the above example, we use an update statement to update the value of the thehome_name column, here, we need to change the home_name of 1, such as White_House, instead of Skylight at that time, we use the above statement. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
- Update Multiple Column
Let’s see how we can update multiple columns at the same time in MariaDB as follows.
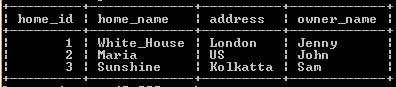
update home_table
set home_name = 'Maria',
address = 'US'
where home_id = 2;Explanation:
In the above example, we updated two columns at the same time see here statement start with the update command with table name home_table followed by modified values of both column names with new assigned values as shown above statement, and finally, we use where clause to specify the condition. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Now let’s see how we can use the LIMIT clause in the update statement as follows.
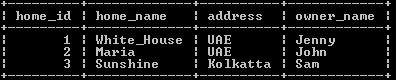
update home_table set address = "UAE" limit 2;Explanation:
In the above example, we use the LIMIT clause to set the exact value of two rows, as shown in the above-mentioned statement. Here we set UAE values to row 1 and 2. The result of the above statement we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Let’s see how we can use order by clause in the update statement as follows.
update table name set column name =new assigned value where
[condition…..] order by;Explanation:
In the above syntax, we can use the update statement we set, where, and order by clause as shown in the statement. With the help of order by clause, we can arrange column in ascending order and descending order.
So in this way, we can use update statements by using different clauses and different rules such as with expression and with default values, etc.
Rules and regulation for using the update
The update command has the following distinct rules.
- Update all rows from the table: in which we can update all rows from the specified table.
- Update Single row: In this rule, we can update a single row from a specified table.
- Update with default: in this rule, we can perform an update command with a default value, but this depends on table properties.
- Update Multiple Columns: In this rule, we can update more than one column at the same time.
- Using LIMIT clause: We can provide LIMIT to how many rows we need to update from a specified table.
- Update Only Specific Rows: With the help of the where clause, we can update only selected rows from specified tables.
- Update with value and expression: In this rule, we can update the value of a specific column with some mathematical expression.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the MariaDB update statement. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of MariaDB update statements, and we also see different examples of MariaDB update statements with different clauses. We also learned the rules of MariaDB update statements. This article taught us how and when to use MariaDB update statements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB UPDATE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.