Updated April 12, 2023
Introduction to MariaDB create a database.
MariaDB Create Database is an SQL command which is applied to create a database in the server. This creating or deleting of databases in MariaDB needs privileges normally only provided to the root admins or users. Under these concepts, a user holds two options for database creation: a PHP script and the mysqladmin binary.
In mysqladmin binary, we need to provide a login user name and a database name to be created and enter the password. Whereas while creating MariaDB database, PHP script services the function mysql_query which implements a couple of parameters where one works as an optional returning as a result either the value TRUE being successful and the value FALSE when it becomes unsuccessful in connecting to the server or creating the database.
Syntax
The syntax for the MariaDB Create Database can be defined as follows:
CREATE (OR REPLACE) {SCHEMA | DATABASE} (IF NOT EXISTS) DB_name
(CreateSpecifications)…
CreateSpecifications:
CHARACTER SET (DEFAULT) (=) Name_of_Charset
| COLLATE (DEFAULT) (=) CollationName | COMMENT (=) ‘comment’;Let us explain the keywords used in the above statement:
- The term CREATE DATABASE is applied to create a database provided with the specified name. But if a user wants to implement this statement, the CREATE privilege for the database is required. Here, also CREATE SCHEMA works as a synonym for the keyword CREATE DATABASE. We can also apply the valid identifiers to be used as the database names, so you need to look at the Identifier Names.
- OR REPLACE: This term or say the clause OR REPLACE came into use or added with MariaDB beginning with 10.1.3 version. This is an optional clause term to be implemented which functions as a shortcut for:
DROP DATABASE (IF EXISTS) DatabaseName;
CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName,…..;- IF NOT EXISTS: When the clause IF NOT EXISTS is applied then, MariaDB returns a warning instead of an error message if the particular database exists already.
- COMMENT: With the start of MariaDB 10.5.0, it provides with the functionality to supplement a comment having a maximum of 1024 bytes. But if the comment length surpasses this specified length, then an error code or warning code of 4144 is displayed. This term comment is also implemented to the db.opt file and also to the information_schema.schema.schemata table.
How to create a database in MariaDB?
In MariaDB, when we need to create a new database, we have to be sure that the current users should have the privilege of CREATE statement for the database. Also, one can view and test the privileges by executing one of the succeeding statements:
SHOW GRANTS;
SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_USER();
SHOW GRANT FOR CURRENT_USER;After we have checked this and find everything is fine, then we will move forward to create the database having a name for it:
CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName;If you are not confirmed whether the given database having that particular name already is present or not, we will apply the REPLACE OR CREATE.
REPLACE OR CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName;If there is a prevailing database provided with that specified name, it will drop or remove that database and simultaneously create a fresh one. Therefore, we will use these statements of REPLACE OR CREATE by the following queries:
CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName;
DROP DATABASE DatabaseName;For instance, if the user doesn’t want to substitute any remaining database but avoid instead, then we will use the keyword IF NOT EXISTS:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Database_Name;If there prevails the database, then it yields an error saying that Can’t create database ‘DatabaseName’;
Here, you may also additionally supplement a few distinct setting for the collation and character sets.
CHARACTER SET = Name_of_Charset
COLLATE = Name_of_collateExamples
Let us explain the MariaDB Create Database command through a demonstration which is as follows:
We will create a new database with the help of a command-line query program having the few steps to conclude described below:
Initially, we need to access the MariaDB server by logging in with a user or, say, an admin user account where the CREATE privilege is available for the particular database. For this, we will write the command line program when we have MariaDB installed on our system:
mysql –u root –p
Enter the password: ********Output:
This can be the programming scripts for the initial phase to login into the MariaDB database. Normally, the user is specified as root, and when the command asks for a password then, you need to insert the password of the user account and then press the Enter key on the keyboard.
Next, we will view the current databases present in the server using the SQL statement SHOW DATABASES executed as follows:
show databases;Output:

After this, we will proceed towards creating a fresh database with a name as specified suppose Trainers:
create database Trainers;Output:

Now, again we will view all MariaDB databases present in the server with the query as previous:
show databases;Output:
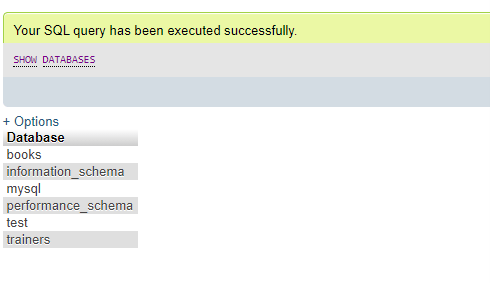
As you can see, the newly created database Trainers is showing on the list, which confirms that the database is created.
With this creation of database, the user can choose this new MariaDB database as the current one to work within the query commands by selecting it using the command as follows:
USE DatabaseName;The USE keyword is used for to select the database present.
In the above syntax, you need to replace the name of the MariaDB database available in the server writing as follows:
USE Trainers;Output:
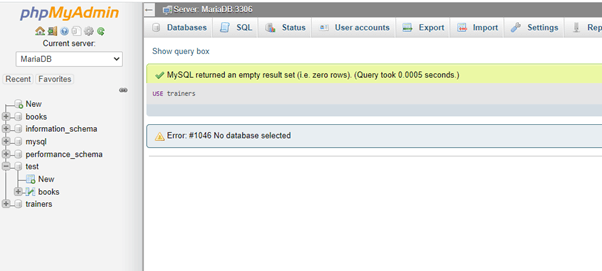
Here, it executes the command, and you can start working with the Trainers database just created. With this, you can go ahead and create different tables within the database name available in the server using the MariaDB create table statements.
Conclusion
- MariaDB is an enhanced branch of the MySQL database management system that provides data processing capabilities for enterprise and small tasks.
- With the help of the MariaDB Create Database command, a user makes a new server database using the query command and specifies the database’s name. For this, we can login through phpmyadmin or by login in through the command prompt.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB create database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

