Updated July 31, 2023
What is the Marginal Revenue Formula?
The marginal revenue formula can help companies calculate how much extra money they can make by selling more units of their existing products. They can use this to decide if they should produce more items of a product and how much they can earn from each additional sale.
Imagine you start a business where you earn money by creating and selling items. If you create one item and sell that one item, you will earn a particular amount. Now, if you start selling more pieces of that product, you will be able to earn a little extra money. This extra revenue is called marginal revenue. So, if you want to calculate how much extra money you can make by selling more pieces of the items, you can use the marginal revenue formula.
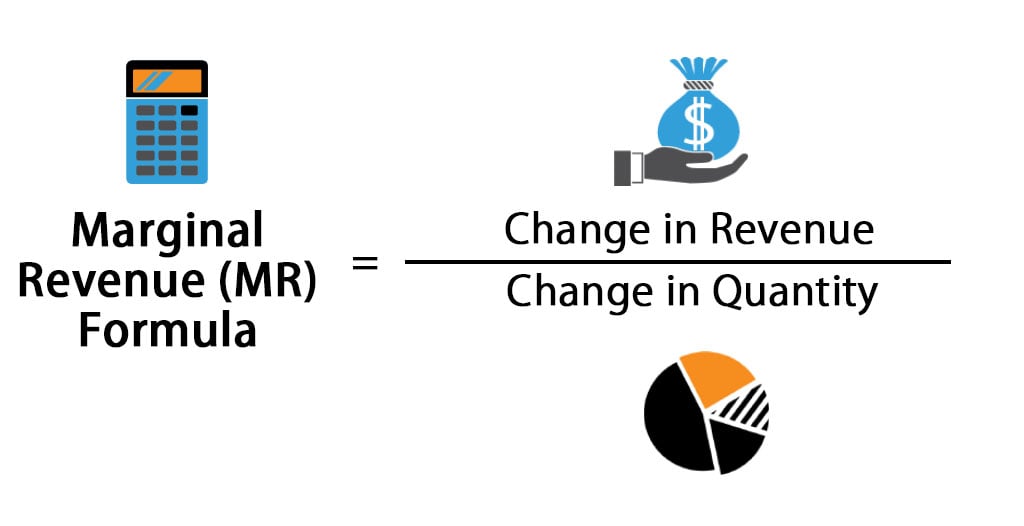
Marginal Revenue Formula
The formula to calculate Marginal Revenue is,
OR
Where,
- Change in Revenue is the difference between the current income and the initial income the company generated from product sales.
- Change in Quantity is the increase or decrease in the number of units that the company sells of the product.
How Does the Formula Help?
Let’s understand how the marginal revenue formula can help businesses maximize their profits. For this, we will use a simple example of a farmer named Emma who grows grapefruits.
Emma sells one grapefruit for $3. So, when she sells two, she earns $6. Then, she decides to sell three grapefruits for $10. In this case, let us use the marginal revenue formula to see how much extra money she made by selling one more grapefruit.
Marginal revenue = change in revenue / change in quantity = (10-6)/(3-2) = 4
So, when we compare the revenue Emma earned from selling 3 grapefruits ($10) and the revenue she earned from selling 2 grapefruits ($6), we can see that she earned an extra $4. This extra money is called “marginal revenue” because it represents the change in revenue from selling one more grapefruit.
Thus, by calculating the marginal revenue, Emma can evaluate whether producing and selling more grapefruits is financially beneficial.
If the marginal revenue is higher than the cost of producing an additional grapefruit, Emma can make more profit by increasing her production. She can decide if she should allocate more resources, such as time and land, to grow additional grapefruits.
On the other hand, if the marginal revenue is lower than the cost, Emma may reconsider expanding her production. Focusing on her current production levels or exploring alternative crops might be more profitable.
Emma can make informed decisions about her grapefruit farming by analyzing the marginal revenue. She can ensure that she earns maximum profit while effectively managing resources.
How to Calculate Marginal Revenue Formula?
Here are the steps you can use to calculate the marginal revenue:
Step 1: Calculate the initial total revenue (multiply the price per unit by the number of units sold).
For example, if you sold 10 product units for $5 each, the total revenue would be 10 * $5 = $50.
Step 2: Determine the new total revenue (multiply the new quantity of units sold by the price per unit).
For instance, if you increase the quantity from 10 to 13 units, you must determine the total revenue earned from selling 13 units. Let’s say the total income from selling 13 units is $65.
Step 3: Find the change in total revenue (subtract the initial total revenue from the new total revenue).
Thus, the change in total revenue would be $65 – $50 = $15.
Step 4: Calculate the change in quantity (subtract the initial quantity from the current quantity).
For example, the change in quantity will be 13 – 11 = 3.
Step 5: Use the marginal revenue formula (divide the change in total revenue by the change in quantity).
Thus, according to the example, the marginal revenue will result from dividing $15 by 3, which equals $5.
Examples of Marginal Revenue Formula
Example #1
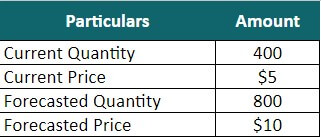
Steve Machine Works Pvt Ltd. manufactures office printing & Stationery items. The company is currently planning to introduce the production of a new category of pens. Currently, they are producing 400 pens and selling them at $5 each. They forecast to produce 800 pens and sell them at $10. We need to find the Marginal revenue of Steve Machine Works Pvt Ltd.
Given,
Solution:
Step 1: Let us calculate the current and forecasted revenue.
Current revenue = 400 * 5 = $2,000
Forecasted Revenue from Production = 800 * 10 = $8,000
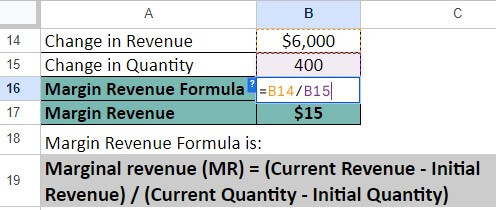
Step 2: Let us find the change in revenue and quantity.
=$8,000 – $2,000 = $6,000
=800 – 400 = 400
Step 3: Now, we calculate Marginal Revenue using the below formula:
= $6,000 / 400 = $15
Thus, the marginal revenue of Steve Machine Works Pvt Ltd is $15.
Example #2
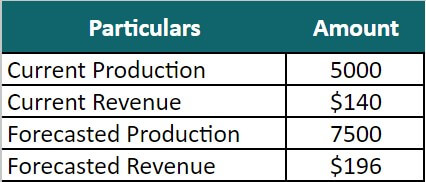
Francis & Sons are producing and selling commodities. Currently, they are producing 5,000 units and selling them at $140 each. However, they plan to introduce a new production line and expect to increase the current production by 50%, making it 7500. They will increase the selling price per unit by 40%, making it $196. We need to calculate the marginal revenue for Francis & Sons if they introduce the new production line.
Given,
Solution:
Step 1: Let us calculate the current and forecasted revenue.
Current revenue = 5000 * 140 = $7,00,000
Forecasted Revenue from Production = 7500 * 196 = $14,70,000
Step 2: Let us find the change in revenue and quantity.
Change in revenue = Forecasted Revenue – Current Revenue
=$14,70,000 – $7,00,000 = $770,000
Change in Quantity = Forecasted Quantity – Current Quantity
=7,500 – 5,000 = 2,500
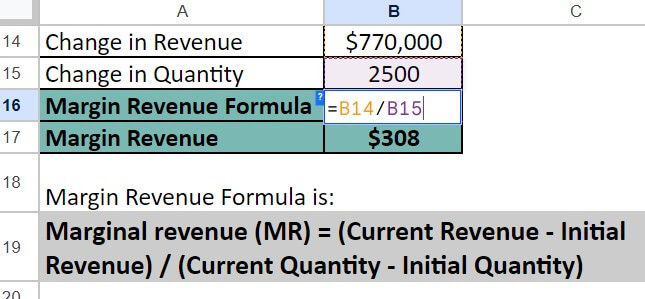
Step 3: Now, we calculate Marginal Revenue using the below formula:
Marginal Revenue (MR)= Change in Revenue / Change in Quantity
= $770,000 / 2,500 = $308
Therefore, the marginal revenue of Francis & Sons is $308.
Example #3
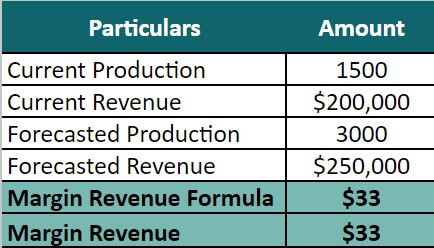
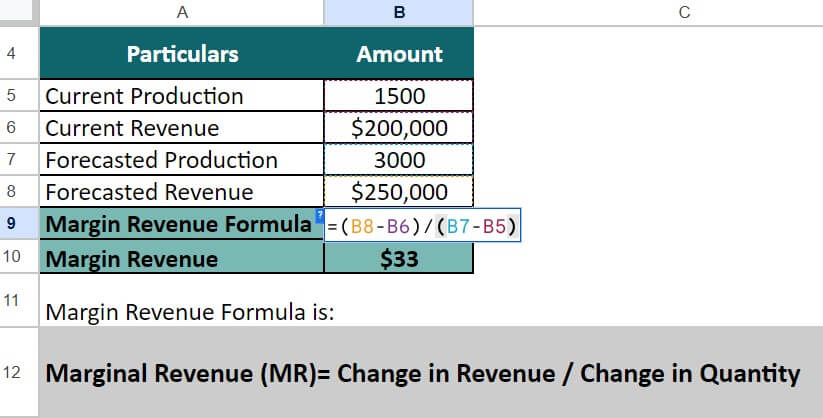
Elens Group of Companies has shown the following details:
- Current Production = 1500
- Current Revenue = $200,000
- Forecasted Production = 3000
- Forecasted Revenue = 250,000
Now we need to calculate the marginal revenue for the Elens Group of companies based on the provided data.
Given,
Solution:
We can calculate Marginal Revenue by using the below formula
Marginal Revenue (MR)= Change in Revenue / Change in Quantity
Marginal Revenue = (2,50,000 – 2,00,000) / (3,000 – 1,500)
= 50,000 / 1,500 = $33
So, the Elens Group of Companies has a marginal revenue of $33.
Marginal Revenue Calculator
Use the following calculator for Marginal revenue formula calculations.
| Change in Revenue | |
| Change in Quantity | |
| Marginal Revenue Formula | |
| Marginal Revenue Formula | = |
|
|
Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue or the change in revenue resulting from selling an extra unit. On the other hand, marginal cost is the additional cost or the change in cost due to producing an extra unit. Marginal revenue helps understand how producing and selling more units will affect a business’s revenue. In contrast, marginal cost helps us know how producing and selling more units will affect the business’s production cost.
Businesses can find the optimal production volume and pricing that maximizes their profitability by comparing marginal revenue and cost. If revenue exceeds cost, producing and selling more units is profitable; otherwise, if revenue is lower than cost, producing additional units may lead to lower profitability or losses.
Marginal Vs. Average Revenue
| Marginal Revenue | Average Revenue | |
| Definition | It is the additional revenue companies earn from selling one more unit. | It is the revenue the company earns on average for each unit they sell. |
| Formula | Change in total revenue / Change in quantity | Total revenue / Quantity sold |
| Interpretation | It helps find the perfect level of production or pricing decisions. | It helps find the average earning per unit and evaluate the profitability of the overall sales. |
Importance
- It helps in production planning by assessing whether increasing production volume is financially beneficial or not.
- It gives an insight into the current demand for a product or service. If the revenue is positive, it indicates a growing market, while negative indicates a declining market.
- It helps identify the output level that achieves the highest possible profit by comparing it to marginal cost.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can marginal revenue be zero or negative?
Answer: Yes, marginal revenue can be zero or negative. It depends on specific situations and market conditions. In a competitive market, marginal revenue tends to be positive initially and then declines due to the downward-sloping demand curve. However, in some situations, zero or negative marginal revenue can occur.
Q2. What do MC and MR mean in economics?
Answer: MC or marginal cost refers to the additional cost that occurs by producing one more unit of a product or providing one more unit of service. On the other hand, MR or marginal revenue is the extra revenue you can earn by selling one more unit of a product or service.
Q3. Differentiate between marginal and total revenue.
Answer: Total revenue is the net income generated by selling goods and services, whereas marginal revenue is the increase in the revenue from selling one extra unit of product or service.
Recommended Articles
This EDUCBA article gives a detailed explanation of the marginal revenue formula. We explain the formula’s uses and relevance using the stepwise guide and comprehensive examples. You can also read the below articles to learn more