Introduction to List Method in Python
A Python list is a versatile data structure enclosed in square brackets, allowing for easy manipulation using various built-in methods. These methods facilitate operations such as adding, removing, slicing, and sorting elements within the list and performing numerical computations like finding the minimum, maximum, or sum of its values. Python lists store individual or multiple elements, which can be integers, characters, or floats. These lists can be manipulated using methods like sort(), copy(), append(), clear(), reverse(), remove(), pop(), insert(), count(), extend(), and index(), etc. These methods enable adding, modifying, deleting, and reordering elements within the list.
Table of Contents
How do Lists work in Python?
Every value that is stored in the list has its address known as index position. By index position, we can get any particular value from the list. All Index value starts from 0. Python reads the list from left to right by default. Square brackets surround every list. We can read the list element, but we cannot specify an index that does not exist in a list that will result in an error.
We can also access the element of the list from backward using the (-)negative index value. Negative starts from -1. If we specify -1, it will return the last element of the list, and so on.
Lists are very helpful as it is used to store data of the same kind together. For example, all the student’s names or scholar numbers of students in a single list. Python list also supports nesting, so we can create a list inside another list.
names = ["Andrew", "Daniel", "Leo", "Aiden"]If we want to get any name, we have to specify the index position with the variable name.
names[0] = Andrew
names[2] = LeoIf we want to reassign any value of the list, then we can simply assign a new value to the list variable with index position.
names[2] = "Dylan"
names = ["Andrew", "Daniel", "Dylan", "Aiden"]Methods Available in Python List Function
Here are some important methods available in list python, which are as follows:
1. append()
You can utilize the “append” function to include a value to an existing list. By simply using the “append” keyword followed by the value you want to add, the new value will be appended to the end of the list. If you pass another list as an argument to the “append” function, it will add the entire list as a single value to the original list.
Syntax:
list.append(value)Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
nums = [1,2,3]
names.append("John")
print(names)Output:
2. sort()
This function is used to arrange the data alphabetically in ascending or descending order. By default, it does the sort in ascending order. If we need to do the sorting in descending order, we need to reverse the keyword.
Syntax:
List.sort()Example:
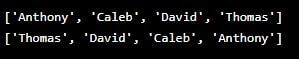
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.sort()
print(names)
names.sort(reverse=True)
print(names)Output:
3. copy()
In Python, the copy() method creates a shallow copy of a list. A shallow copy of a list contains references to the original objects, not copies of the objects themselves. This means that changes made to the elements of the copied list will also affect the original list and vice versa, but the lists themselves are separate objects.
Syntax:
List.copy()Example:
original_list = [12, 25, 32, 45]
copied_list = original_list.copy()
# Modify the copied_list
copied_list.append(5)
# Both original_list and copied_list are unaffected
print(original_list)
print(copied_list)Output:
4. clear()
This function is used to remove all the values from the list and return an empty list with a square bracket.
Syntax:
list.clear()Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.clear()
print(names)Output:
5. reverse()
This function is used to reverse the items of the list. It will read the element from right to left and modify the current list. A reverse flag is given to rearrange the values in the list in descending order.
List.reverse()Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.reverse()
print(names)Output:
6. remove()
If we want to remove any value from the list and don’t know the value’s index position, then we can use the remove() function. We have to pass the value that we want to remove from the list, and it will search that element from left to right, from index position 0, and whichever matching element comes first will be removed.
Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.remove("David")
print(names)Output:
7. pop()
This function is also similar to the remove() function, but in this function, we can remove the value from the list based on an index, not a value. We must know the index position of the value in the list to remove it.
Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.pop(2)
print(names)Output:
8. insert()
This function is also used to insert the value into the list, but we can insert value at a specific index position using this function. The element that exists, in particular, will shift to the next index, which means all the elements after that index will increment by 1.
Syntax:
List.insert(position,value)Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb"]
names.insert(1, "Nolan")
print(names)Output:
9. count()
This function is used to find which element exist and how many times in the list. It will count the total number based on which value is passed inside the function.
Syntax:
List.count(value)Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb", "David"]
count_names = names.count("David")
print(count_names)Output:
10. extend()
This function is similar to the append() function only difference is that if we add a list in another list append() function will make it as a nested list, but in this function, if we add another list, it will add items on that list instead of making it nested. The Python list extends method allows us to join one or more lists into a new list with an extended version of the given two lists.
Syntax:
List.extend(List) Example:
names = ["Anthony", "David", "Thomas", "Caleb", "David"]
age =[42, 54, 45]
names.extend(age)
print(names)Output:
11. index()
This function is used to find the index of any element from the list. We need to pass the name of the value. Values are case-sensitive.
The Python list index method helps in identifying the index position of an element in the list. It can be given with the start and end parameters when we wanted to narrow down the element or value we are searching for inside the list.
Syntax:
List.index(value,([start,end])Example:
lis=["Horse","Shoe","Turtle",179, 200, 544,"Shoe"]
print(lis.index("Turtle"))
print(lis.index(179,2,5))Output:
12. Min&Max
Min and Max methods allow us to identify the least valued element and maximum valued element in the list.
min(List)max(List)Example:
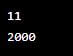
lis=[179, 200, 544, 11, 18, 2000]
print(min(lis))
print(max(lis))Output:
13. Length
The length method in the python list gives us the total length or the total number of characters in the list. It includes all the strings, numbers, special characters, and spaces between the list elements.
Example:
lis1=[179, 200, 544, 11, 18, 2000]
lis2="Dostoevsky is a legendary writer"
print(len(lis1))
print(len(lis2))Output:
In this example, we have declared two lists, one with numerical values and the other one is a statement that contains all string values. In the 1st list, the length function calculates the total elements in the list, which is 6, and in the 2nd list, we have all string values, so all the alphabets and spaces are considered as characters, and we get the total length as 32.
Best Practices
Here are some best practices for using Python list methods efficiently and effectively, along with brief explanations for each:
- Use List Comprehensions for Simple Transformations: List comprehensions apply a function or expression to each element in a list, making transformations efficient and concise.
- Avoid Modifying Lists During Iteration: Modifying a list while iterating can lead to unexpected behavior. If necessary, create a new list or use list comprehension instead.
- Prefer extend() Over Multiple append() Calls: Use extend() to add multiple elements to a list efficiently, rather than repeatedly using append().
- Use in Operator for Membership Tests: To check if an element is present in a list, use the “in” operator. It is faster and more concise than manual iteration.
- Sort Lists with sorted() for Immutability: When you need to sort a list while preserving the original, use sorted() to create a new sorted list, keeping the original list intact.
- Opt for List Slicing for Cloning: To create a copy of a list, use slicing (list_copy = original_list[:]) for clarity and to avoid accidental references.
- Use enumerate() for Index-Value Pairs: When you need both the index and value of list elements, use enumerate() for a more Pythonic and readable approach.
- Profile and Optimize for Large Lists: For performance-critical applications, profile your code and consider using alternative data structures like NumPy arrays for large datasets.
- Minimize Nested Lists for Simplicity: Avoid excessive nesting of lists, as it can make your code harder to read and maintain. Use appropriate data structures for complex data.
- Document Your List Manipulations: Add comments and documentation to explain the purpose and logic behind your list manipulations, making your code more understandable for others and your future self.
Conclusion
The List is the most basic collection or sequence of data. The list is the data structure of the Python enclosed between square brackets. The list is mutable, so their values can be changed. Python provides many inbuilt functions for a list. Using those functions, we can perform various operations on the list.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the List Method in Python. Here we discuss the basic concept, working, and top 13 list method in python and its examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-