Introduction to Python List Functions
There are different types of data types in python like Tuple, Set, Dictionary, etc. The one that is both changeable and ordered is called List in Python. It also allows duplicate values as a member, wherein each member can be accessed separately in an iterative fashion. In this topic, we are going to learn about Python List Functions.
Below is the basic syntax to define a list:
List = ["grapes" , "mangoes" , "bananas" ,"kiwi"]
print(List)Output:
Examples of Python List Functions
Let’s discuss the various functions that can be applied.
1. In Operator
It is utilized to verify whether any specific element is a member of the list or not.
Code:
# Python code to showcase the usage of in operator
lst = [1 , 6 , 7 , 4 , 3]
# checking using in operator
if 1 in lst:
print ("1 is present in the list")
else : print ("1 is not present in the list")Output:
2. Not In Operator
It is utilized to verify whether any specific element is not a member of the list.
Code:
# Python code to showcase the usage of not in operator
lst = [1 , 6 , 7 , 4 , 3]
# checking using not in operator
if 1 not in lst:
print ("1 is not present in the list")
else : print ("1 is present in the list")Output:
- len(): This function returns the length of the list passed as an argument.
- min(): This function returns the minimum element of the list passed as an argument.
- max(): This function returns the maximum element of the list passed as an argument.
Let’s take an example to understand the same:
Code:
# Python code to showcase the usage of len(), max() & min() function
lst = [1 , 6 , 7 , 4 , 3]
print(len(lst))
print(min(lst))
print(max(lst))Output:
3. + Operator
This operator is utilized to append the members of two lists together in a single one.
Code:
# Python code to understand how + operator works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39]
# creating list 2
lst2 = [43 , 45 , 47]
# using + operator in python to concatenate lists
lst3= lst + lst2
print(lst3)Output:
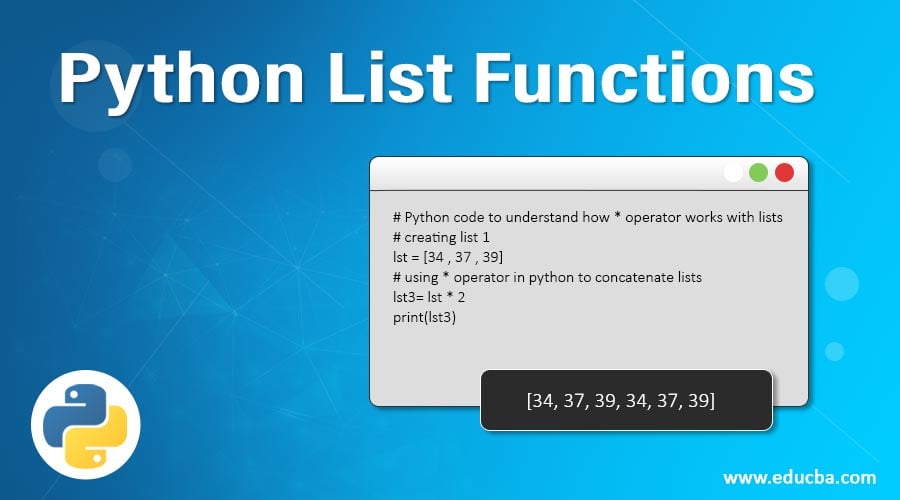
4. * Operator
This operator is utilized to repeat the members of the list the times the operator is used with * operator.
Code:
# Python code to understand how * operator works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39]
# using * operator in python to concatenate lists
lst3= lst * 2
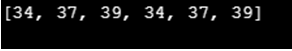
print(lst3)Output:
- count(): This function returns the number of times an element is present in the list
Code:
# Python code to understand how count() function works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39 , 24 , 37, 37, 37, 37, 37, 37 , 37 ,37]
# using count() function with lists to understand its usage
print(lst.count(37))Output:
- remove(): This function is utilized to remove the first occurrence of the specified member from the list
Code:
# Python code to understand how remove() function works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39 , 24 , 37, 37, 37, 37 , 37 , 37 , 37 , 37, 37 , 37]
# using remove() function with lists to understand its usage
lst.remove(37)
print(lst)Output:
Here if we notice carefully, the very first occurrence of 37 is removed from the list
- sort(): This python function is utilized to sort the list passed as an argument in ascending order.
Code:
# Python code to understand how sort() function works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39 , 24 , 37, 34, 35, 38 , 36 , 33 , 17 , 25, 86 , 47]
# using sort() function with lists to understand its usage
lst.sort()
print(lst)Output:
- reverse(): This python function is utilized to reverse the list passed as an argument.
Code:
# Python code to understand how sort() function works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39 , 24 , 37, 34, 35, 38 , 36 , 33 , 17 , 25, 86 , 47]
# using sort() function with lists to understand its usage
lst.reverse()
print(lst)Output:
- clear(): This function is utilized to empty the list passed as an argument to this function.
Code:
# Python code to understand how sort() function works with lists
# creating list 1
lst = [34 , 37 , 39 , 24 , 37, 34, 35, 38 , 36 , 33 , 17 , 25, 86 , 47]
# using sort() function with lists to understand its usage
lst.clear()
print(lst)The Output of this python program is:
Conclusion
There are various functions applicable to Python Lists that usually help us modify, append, sort, clear, and implement multiple other operations on the lists in python to achieve the business-specific operations within python.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python List Functions. Here we discuss the Examples of Python List Functions along with the syntax and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –