Updated June 14, 2023
Definition of Linux Diff Command
The diff command in Linux facilitates the comparison of data between two files line by line. When the command detects any differences between the files, it presents these differences alongside the corresponding line numbers. Diff command also helps in comparing the data between two directories.
The abbreviation of diff is different. Please note that the diff command in Linux utilizes specific symbols and instructions to ensure the similarity of two files.
Special symbols include:
- a: This represents that context has been added.
- c: This represents that the context has been changed.
- d: This represents that context has been deleted.
Syntax:
Here is the basic syntax of the diff command:
diff [options] file1 file2The result of the diff command in Linux can be in the below format:
- It can be in a normal format
- It can also be a context
- It can also be in a unified format.
How does Diff Command work in Linux?
Below are the options available in the diff command in Linux. Options with their description are also mentioned below for better understanding. –help command will give you all the options available for diff commands in Linux.
| Options | Description |
| –normal | The output displayed is a normal difference (the one that is displayed by default) |
| -q, –brief | It reports only if the files differ |
| -s, –report-identical-files | It reports if two files are the same and have no differences between them |
| -y, –side-by-side | The diff command displays the output in a two-column format. |
| -t, –expand-tabs | It will help in expanding the tabs to spaces in the output format. |
| -r, –recursive | It will recursively help in comparing any subdirectories that are found |
| -i, –ignore-case | This option allows you to ignore case differences in file data. |
| -a, –text | This option will treat all the files as text |
| –help | Prints the options that are available and will exit |
| -v, –version | output version information and exit |
Examples of Linux Diff Command
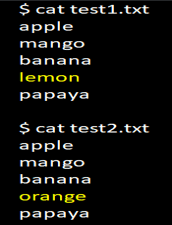
Let us consider there are two files, test1.txt and test2.txt. Now we will compare them by using the diff command.
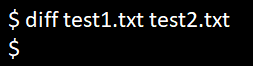
cat test1.txtcat test2.txtNo Option
When the diff command is used for the above two files and no result is shown, it indicates that there are no differences between the files.
Syntax:
diff file1 file2Example:
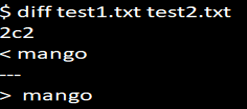
diff test1.txt test2.txtWhen there is a difference in both the files and when we use the diff command, the output will be displayed as shown below:
cat test1.txtcat test2.txt4c4 means that 4th line in test1.txt should be changed to make the two files(test1.txt and test2.txt) the same.
diff test1.txt test2.txtOption -c
The result will be displayed in context format when we use option ‘c’ in the diff command.
Syntax:
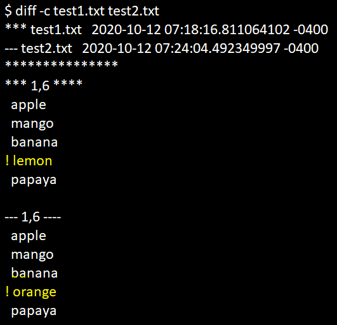
diff -c file1 file2Example:
cat test1.txtcat test2.txtdiff -c test1.txt test2.txtIn the output, the first two lines will give you information on file names and the modification dates of the two files. The first file will be represented with three stars (***), and the second file will be represented with three hyphens(—).
When the output has a single hyphen, “-” means the line will need to be removed, and the symbol “+” means the line needs to be added to the file. Any file that does not need any modification is expected to be prefixed with two spaces.
Option -u
When we use the option ‘-u’ in the diff command, the result will be displayed in a unified format.
Syntax:
diff -u file1 file2Example:
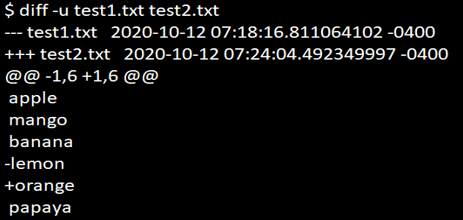
diff -u test1.txt test2.txtHere the output is more same with context format (option -c), but in option -u (unified format), the output will be displayed concisely; in the output, the first 2 lines will represent the file name with its changed time and date.
The first file will indicate three hyphens (“—”), and the second file will indicate three-plus symbols in the output(“+++”). The symbol’-lemon’ will represent that the line would need to be added to the first file, and the symbol ‘+orange’ will represent that the line would need to be removed from the first file to make it similar to the second file.
Option -i
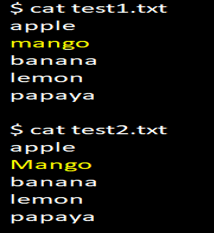
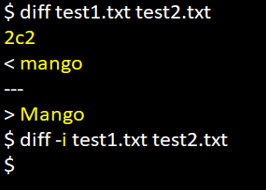
Generally, the diff command in Linux is case-sensitive. If we want to ignore any case sensitive in the diff command, we can use option -i in the argument, as shown below.
Syntax:
diff -i file1 file2Example:
cat test1.txtcat test2.txtdiff test1.txt test2.txtThe screenshot above illustrates that when no option is specified in the first example, the output displays the differences without ignoring case-sensitive data.
So if we need to ignore the case-sensitive text, we will need to use option -i, as shown in the above screenshot.
Option -s
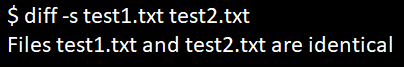
We must display the message in a few situations if both files are similar. So we can use option -s to display the message as shown below.
Syntax:
diff -s file1 file2Example:
diff -s test1.txt test2.txtOption -b
There are situations when two files are identical, but there would be a white space difference between the two files. To ignore the white space difference, we can use option -b, as shown below.
Syntax:
diff -b file1 file2Example:
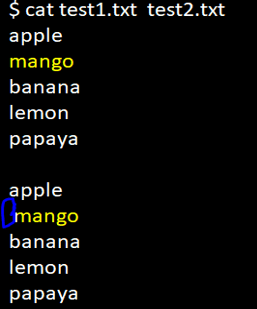
cat test1.txt test2.txtIn the screenshot below, we can see that when no option is mentioned in the diff command,
the white space difference is mentioned in the output.
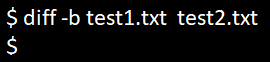
diff test1.txt test2.txtHowever, if we want to ignore the two files’ white spaces, we can use the -b option. We can see in the below screenshot that by using the -b option in the diff command, the output has ignored the whitespaces.
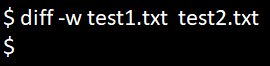
diff -b test1.txt test2.txtThere are some situations where there might be one or more white space differences between the two files. We can use option -w and the diff command in Linux to ignore all the white space differences.
diff -w test1.txt test2.txtConclusion
The diff command in Linux compares the data between two files line by line and displays any differences found, along with the line numbers. Diff command also helps in comparing the data between two directories. Please note that the diff command in Linux utilizes specific symbols and instructions to ensure the similarity between two files.
The diff command is a very useful command in comparing two files line by line. People generally use inline comparisons to identify the differences between files. The above article on the diff command in Linux will give you a clear understanding of how to use the diff command in Linux.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Diff Command” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.