Updated July 24, 2023
Kurtosis Formula (Table of Contents)
What is the Kurtosis Formula?
The term “Kurtosis” refers to the statistical measure that describes the shape of either tail of a distribution, i.e. whether the distribution is heavy-tailed (presence of outliers) or light-tailed (paucity of outliers) compared to a normal distribution.
In other words, it indicates whether the tail of distribution extends beyond the ±3 standard deviation of the mean or not.
There are three types of kurtosis that can be exhibited by any distribution:
- Leptokurtic or heavy-tailed distribution (kurtosis more than normal distribution)
- Mesokurtic (kurtosis same as the normal distribution)
- Platykurtic or short-tailed distribution (kurtosis less than normal distribution)
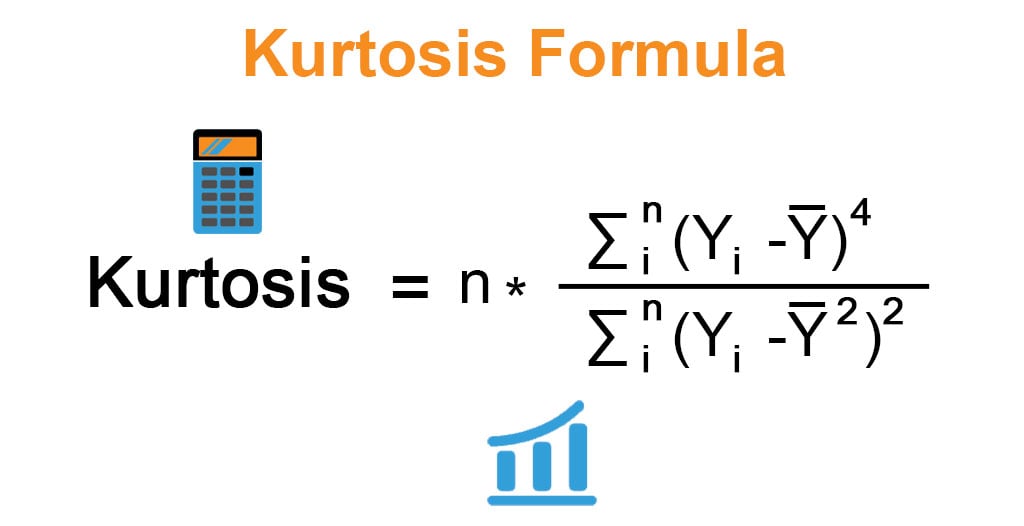
The formula for kurtosis is expressed as the ratio of the fourth moment and variance (s2) squared or squared the second moment of the distribution. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Where
- Yi: ith Variable of the Distribution
- Ȳ: Mean of the Distribution
- n: No. of Variables in the Distribution
Example of Kurtosis Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Kurtosis in a better manner.
Kurtosis Formula – Example #1
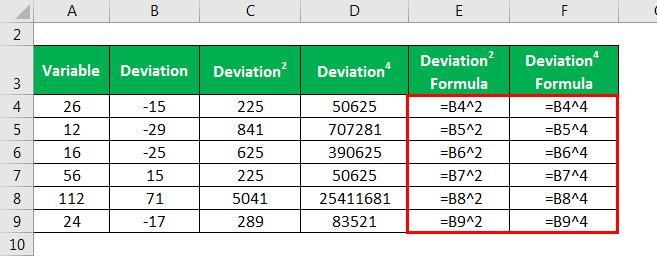
Let us take the example of the following data distribution to illustrate the computation of kurtosis of a leptokurtic distribution: 26, 12, 16, 56, 112, 24.
Solution:
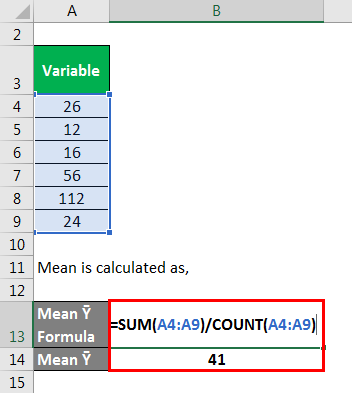
Mean is calculated as,
- Mean Ȳ = (26 + 12 + 16 + 56 + 112 + 24) / 6
- Mean Ȳ = 41
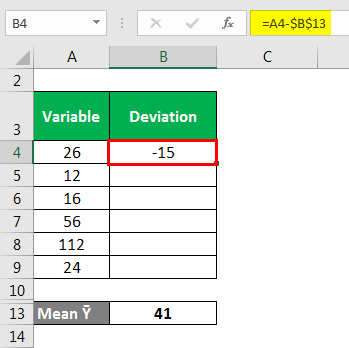
Standard Deviation is calculated as
Deviation2 and Deviation4 is calculated as
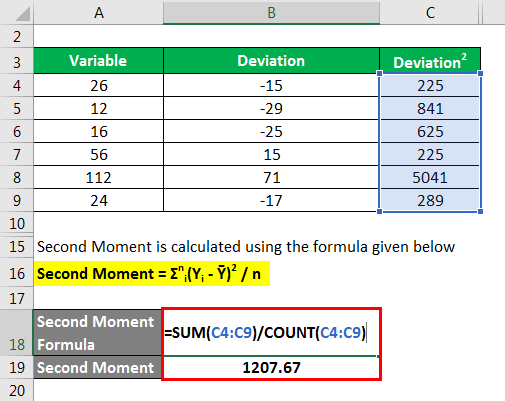
Second Moment is calculated using the formula given below
Second Moment = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)2 / n
- Second Moment = [(26 – 41)2 + (12 – 41)2 + (16 – 41)2 + (56 – 41)2 + (112 – 41)2 + (24 – 41)2] / 6
- Second Moment = 1207.67
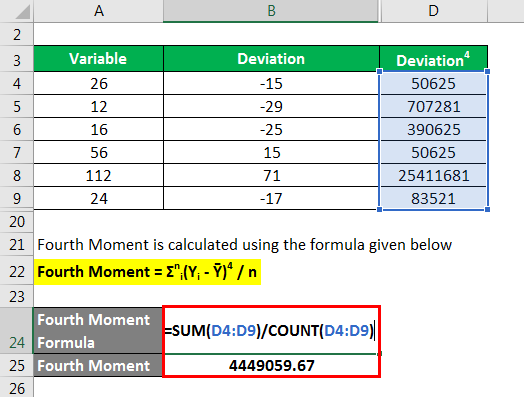
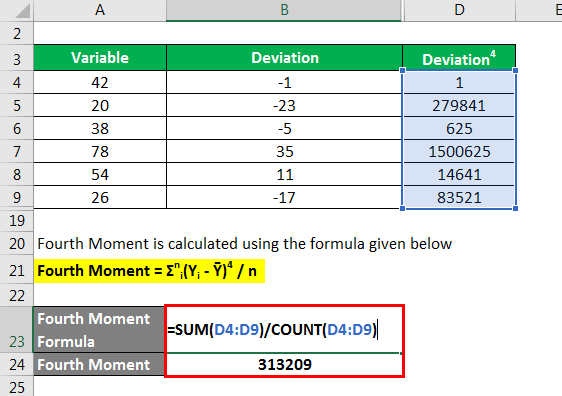
Fourth Moment is calculated using the formula given below
Fourth Moment = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)4 / n
- Fourth Moment = [(26 – 41)4 + (12 – 41)4 + (16 – 41)4 + (56 – 41)4 + (112 – 41)4 + (24 – 41)4] / 6
- Fourth Moment = 4449059.67
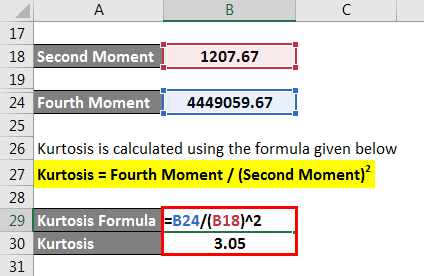
Kurtosis is calculated using the formula given below
Kurtosis = Fourth Moment / (Second Moment)2
- Kurtosis = 4449059.667 / (1207.667)2
- Kurtosis = 3.05
Since the kurtosis of the distribution is more than 3, it means it is a leptokurtic distribution.
Kurtosis Formula – Example #2
Let us take the example of the following data distribution to illustrate the computation of kurtosis of a platykurtic distribution: 42, 20, 38, 78, 54, 26
Solution:
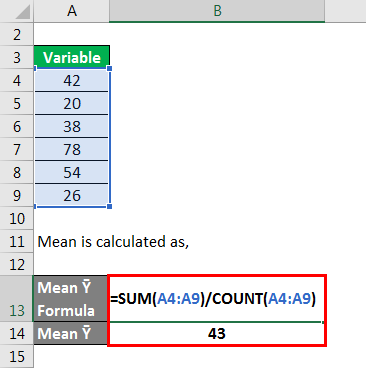
Mean is calculated as
- Mean Ȳ = (42 + 20 + 38 + 78 + 54 + 26) / 6
- Mean Ȳ = 43
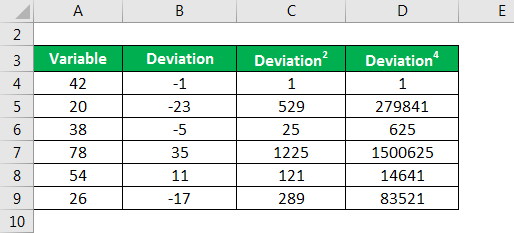
Deviation, Deviation2 and Deviation4 is calculated as same as shown in the example1.
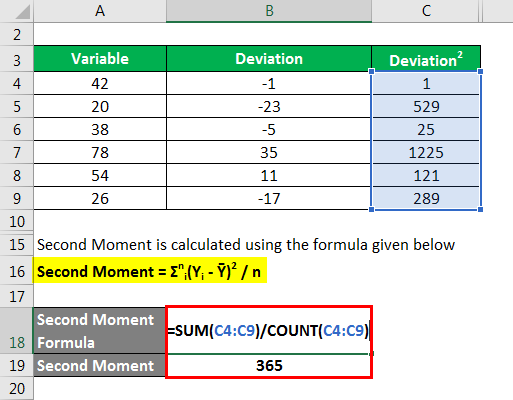
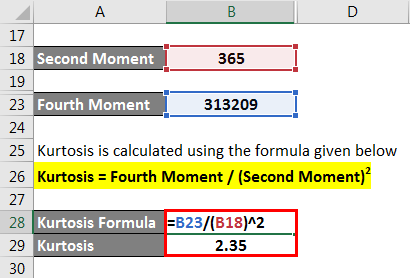
The second Moment is calculated using the formula given below
Second Moment = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)2 / n
- Second Moment = [(42 – 43)2 + (20 – 43)2 + (38 – 43)2 + (78 – 43)2 + (54 – 43)2 + (26 – 43)2] / 6
- Second Moment = 365
Fourth Moment is calculated using the formula given below
Fourth Moment = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)4 / n
- Fourth Moment = [(42 – 43)4 + (20 – 43)4 + (38 – 43)4 + (78 – 43)4 + (54 – 43)4 + (26 – 43)4] / 6
- Fourth Moment = 313209
Kurtosis is calculated using the formula given below
Kurtosis = Fourth Moment / Second Moment2
- Kurtosis = 313209 / (365)2
- Kurtosis = 2.35
Since the kurtosis of the distribution is less than 3, it means it is a platykurtic distribution.
Explanation
The formula for Kurtosis can be calculated by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, after forming the data distribution, determine the number of variables in the distribution which is denoted by ‘n’.
Step 2: Next, compute the mean of the distribution, which is the aggregate of all the variables (Yi) in the distribution divided by the number of variables of the distribution (n). It is denoted by Ȳ.
Ȳ = ΣnYi / n
Step 3: Next, determine the fourth moment of the distribution by summing up the fourth power of deviation between each variable and mean (step 2) which is then divided by the number of variables in the distribution (step 1).
Fourth Moment = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)4 / n
Step 4: Next, determine the variance (s2) or second moment of the distribution by summing up the square of deviation between each variable and mean (step 2) which is then divided by the number of variables in the distribution (step 1).
s2 = Σni(Yi – Ȳ)2 / n
Step 5: Finally, the formula for kurtosis can be derived by dividing the fourth moment (step 3) by the squared second moment of the distribution (step 4) as shown below.
Kurtosis = n * Σni(Yi – Ȳ)4 / (Σni(Yi – Ȳ)2)2
Relevance and Use of Kurtosis Formula
For a data analyst or statistician, the concept of kurtosis is very important as it indicates how are the outliers distributed across the distribution in comparison to a normal distribution. At times, relative kurtosis of distribution is represented in terms of excess kurtosis wherein it is calculated by deducting 3 from the kurtosis, i.e. (kurtosis – 3)
- If Positive, Then It Is a Leptokurtic Distribution
- If Zero, Then It Is a Mesokurtic Distribution
- If Negative, Then It Is a Platykurtic Distribution
The concept of kurtosis finds serious application in the field of risk management and portfolio management where it indicates if there is any chance of extreme values or returns (positive and negative) beyond the ±3 standard deviation of the mean (99.5% confidence interval). Please note that an investor is more comfortable with a platykurtic distribution of return as it indicates stable returns and lower risk of sudden shock of outliers, while leptokurtic distribution means chances of higher return but with higher risk.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Kurtosis Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate the Kurtosis Formula along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –