Updated June 15, 2023
Introduction to Java LocalDate
In Java, the LocalDate class denotes the Date with a format of yyyy – mm – dd default. It does not indicate the time or time zone, but the date description is represented.
It has certain features:
- Java LocalDate is an immutable class.
- People mainly use LocalDate to represent dates such as birthdays or holidays, where time zone or time information is unnecessary.
- Java LocalDate class can’t be extended as it is the final class.
- As it is a value-based class, you can compare two LocalDate instances using the equals() method.
Java LocalDate Class Declaration:
public final class Local Date extends Object implements Temporal, TemporalAdjuster, ChronoLocalDate, Serializable
Top 18 Methods for Java LocalDate
The following are the commonly used methods in Java LocalDate:
1. getMonth()
The month-of-year field will be returned with the help of the Month enum.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the month
System.out.println(ld.getMonth());
}
}Output:
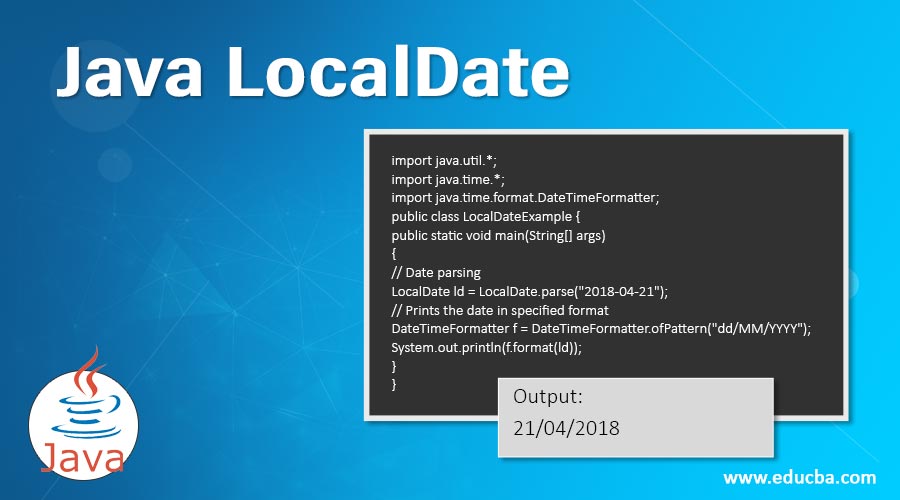
2. format( DateTimeFormatter formatter )
The Date will be formatted using the mentioned formatter.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the date in specified format
DateTimeFormatter f = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd/MM/YYYY");
System.out.println(f.format(ld));
}
}Output:
3. adjustInto( Temporal temp )
The mentioned temporal object temp will be adjusted with the Date of the Object.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ZonedDateTime d = ZonedDateTime.now();
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// adjusts the date
d = (ZonedDateTime)ld.adjustInto(d);
System.out.println(d);
}
}Output:
4. getChronology
The chronology of the calendar will be returned, where the calendar system is ISO.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the chronology in ISO system
System.out.println(ld.getChronology());
}
}Output:
5. getDayOfMonth()
Field day-of-month will be retrieved.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the day of month
System.out.println(ld.getDayOfMonth());
}
}Output:
6. getDayOfWeek()
Field day-of-week will be retrieved.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the day of week
System.out.println(ld.getDayOfWeek());
}
}Output:
7. getDayOfYear()
Field day-of-year will be retrieved.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the day of year
System.out.println(ld.getDayOfYear());
}
}Output:
8. compareTo( ChronoLocalDated1 )
The method will compare this Date to another date.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld1 = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-14");
// Prints the day of year
System.out.println(ld.compareTo(ld1));
}
}Output:
9. lengthOfMonth()
The function will return the length of the month based on the Date.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
// Prints the LENGTH OF THE MONTH
System.out.println(ld.lengthOfMonth());
}
}Output:
10. lengthOfYear()
The function will return the length of the year based on the Date.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2019-02-21");
// Prints the LENGTH OF THE MONTH
System.out.println(ld.lengthOfYear());
}
}Output:
11. withMonth( int month )
The function will return a copy of the Date, with the month changed as specified.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
//month that want to be changed to
LocalDate r = ld.withMonth(10);
// Prints the new date
System.out.println(r);
}
}Output:
12. withYear( int year )
he function will return a copy of the Date, with the year changed as specified.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
//year that want to be changed to
LocalDate r = ld.withYear(1992);
// Prints the new date
System.out.println(r);
}
}Output:
13. withDayOfYear( int doy )
The function will return the Date, with the day of the year changed as specified.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
LocalDate r = ld.withDayOfYear(44);
// Prints the new date
System.out.println(r);
}
}Output:
14. withDayOfMonth( int dom )
The function will return the Date, with the day of the month changed as specified.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-02-21");
LocalDate r = ld.withDayOfMonth(23);
// Prints the new date
System.out.println(r);
}
}Output:
15. isLeapYear()
True or False will be returned based on whether the year has given is a leap year or not, respectively.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2019-02-21");
// Prints the LENGTH OF THE MONTH
System.out.println(ld.isLeapYear());
}
}Output:
16. isAfter( ChronoLocalDatedate )
Checks whether this Date is after the mentioned Date.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2019-02-21");
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld1 = LocalDate.parse("2019-04-21");
// Prints the LENGTH OF THE MONTH
System.out.println(ld.isAfter(ld1));
}
}Output:
17. isBefore( ChronoLocalDatedate )
Checks whether this Date is before the mentioned Date.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2019-04-21");
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld1 = LocalDate.parse("2019-02-21");
// Prints the LENGTH OF THE MONTH
System.out.println(ld.isBefore(ld1));
}
}Output:
18. getYear()
The year field will be returned.
Code:
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Date parsing
LocalDate ld = LocalDate.parse("2018-04-21");
// Prints the month
System.out.println(ld.getYear());
}
}Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java LocalDate. Here we discuss the basic concept and top 18 methods of Java LocalDate, along with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –