Updated June 19, 2023
Definition of Java Concurrent HashSet
Java concurrent HashSet was introduced in Java 8. Before Java 8, it was impossible to create a concurrent HashSet because the Concurrent HashSet class was not included in the Java util concurrent package. Since Java 8, the newly added method neKeySet has been used to create the concurrent HashSet that Concurrent HashMap supported. Concurrent HashMap can be used to create the Concurrent HashSet.
Key Takeaways
- We can create the concurrent HashSet in Java. The concurrency API of Java contains the concurrent version of a class of popular collection.
- We create the concurrent HashSet without writing our own class, and we can use the concurrent HashMap class with any value.
Overview
Concurrent HashSet allows us to use the new keyset and KeySet methods to return the set from the correct set. It will provide access to necessary functions such as remove and contain. We can use those methods in the concurrent HashMap class but not in the interface, so we must use the concurrent HashMap variable at the same time.
We can use type conversion to convert a concurrent HashMap object into a ConcurrentMap variable. The problem with the Concurrent HashMap is that it only has a single map, does not contain a set, and does not perform set operations on the concurrent HashMap using virtual values. When some methods require a set method, we can pass that method.
Why Use Java Concurrent HashSet?
HashSet has no built-in types because it is always derived from the concurrent HashMap. Various types of maps can be used to create the class of maps. The concurrent HashSet API will contain the major features of streams and lambda expressions and the changes that make code easy.
The below feature shows why we are using Java concurrent HashSet as follows. It contains multiple features.
- The concurrent HashSet is suited for small applications. We can exceed the number of read-only operations necessary for preventing interface.
- Concurrent HashSet is thread-safe.
- Rasters do not support the variable of operations that was deleted.
- The traversal iterator is fast and does not encounter interference from other threads.
- The raptors do not keep snapshots when the array is unchanged at the time of iterator building.
The below example shows how we are using concurrent HashSet. We are creating the class name as concurrent as follows.
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
class concurrent
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ConcurrentHashMap<String,Integer> stud = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
stud.put ("ABC",24);
stud.put ("PQR",26);
stud.put ("XYZ", 20);
stud.put ("MNP",20);
stud.put ("BCD", 30);
Set cs = stud.keySet ();
System.out.println ("Set: " + cs);
Set <String> ps = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();
ps.add ("fl");
ps.add ("Rey");
ps.add ("Cel");
System.out.println ("before set: " + ps);
ps.add ("Cls");
System.out.println ("after set: " + ps);
if(ps.contains("Rey"))
{
System.out.println ("Y");
}
else
{
System.out.println ("N");
}
System.out.println (ps.contains("Rey"));
ps.remove ("Cel");
System.out.println ("after set: "
+ ps);
}
}Output:
How to Create Java Concurrent HashSet?
We can create a concurrent HashSet using two methods. We use two ways to create a concurrent HashSet, namely using the KeySet and the newKeySet method.
1. Using newKeySet
The newKeySet method returns the supported type of concurrent HashMap, where the value of the method is Boolean. We can use the function of contains and remove at the time of creating concurrent HashSet by using a new keyset. This method will expose a set of all the keys to the originating application. The difference between the two methods is the default method does not support add and add all method.
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
class concurrent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Set<String> st = map.newKeySet ();
st.add ("ABC");
st.add ("PQR");
st.contains ("PQR");
st.remove ("ABC");
}
}2. KeySet (default value)
We can also create by using the KeySet method. The below example shows how we can create the concurrent HashSet by using KeySet as follows. We can use the function of contains and remove at the time of creating concurrent HashSet by using KeySet.
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
class concurrent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Set<String> st = map.keySet (26);
st.add ("ABC");
}
}Java Concurrent HashSet Methods
We use this method when creating a HashSet in Java.
- Add() – This method adds the element to the concurrent HashSet.
- Clear() – This method clears the element from the concurrent HashSet.
- Contains() – This method includes the object of HashSet methods.
- ContainsAll() – This method consists of the object of all HashSet methods.
- Equals() – We use this method to check the comparison of two elements used in concurrent HashSet methods.
- Remove() – This method removes the elements from the HashSet.
- Put() – This method puts the elements into the HashSet.
- IsEmpty() – This method checks that our HashSet contains a part or it is empty.
- Iterator() – This method iterates elements from the HashSet.
- RemoveAll() – This method removes all the elements from the HashSet.
- RetainAll() –We use this method to retain all the elements from the HashSet.
- Size() – We use this method to find the size of all HashSet elements.
- toString() – This method converts the element into a string value.
- toArray() – This method converts the element into an array value.
The below example shows how we can use the HashSet method in concurrent HashSet methods as follows.
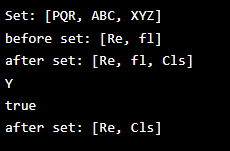
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
class concurrent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
ConcurrentHashMap<String,Integer> stud = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
stud.put ("ABC",24);
stud.put ("PQR",26);
stud.put ("XYZ", 20);
Set cs = stud.keySet ();
System.out.println ("Set: " + cs);
Set <String> ps = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();
ps.add ("fl");
ps.add ("Re");
System.out.println ("before set: " + ps);
ps.add ("Cls");
System.out.println ("after set: " + ps);
if(ps.contains("Re"))
{
System.out.println ("Y");
}
else
{
System.out.println ("N");
}
System.out.println (ps.contains("Re"));
ps.remove ("fl");
System.out.println ("after set: "
+ ps);
}
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Concurrent HashSet allows us to use the newKeySet and KeySet methods to return the set from the correct set. Java 8 introduced the capability to create a concurrent HashSet. Prior to Java 8, creating a concurrent HashSet was impossible as the Java util concurrent package did not include the Concurrent HashSet class.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Concurrent HashSet” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.