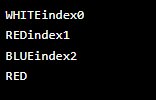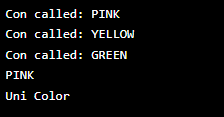Updated December 12, 2023
Introduction to Java Enum
Java enum is a special class in the Java programming language that represents group constants. It contains unchangeable variables such as variable final. We use the enum keyword rather than class or interface when creating an enum class. When we use an enum in Java, we use a comma to separate the constants. Within our class, we also use enum.
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Definition of enumeration()
- Overview of Java Enum
- Java Enum Class
- Java Enum Switch Statement
- Methods
- Example Of value(), ordinal() and ValueOf().
- Constructors
- Java Enum Types
- Importance
Key Takeaways
- We use an enum to create our classes and an enum keyword to create our enum type.
- To define the enum in Java, we use the enum keyword. It is a special class representing the constant group, like the final variable.
Definition of enumeration() in Java
Java Enumeration signifies a set of constants contained within a class that denotes and specifies the functionality of the declarations made before the program’s execution begins. In Java, enumerations act as a final variable; once declared, they help explain the concept being introduced within the program’s set of statements and control flow. The Enumeration in Java came into existence in full fledge after releasing versions of JDK 5. Java Enumeration in Java appears almost like enumerations in other languages besides the fact that the concept of classes and object orientation comes into the picture in Java.
Syntax:
enum (name of user defined datatype)
{
Values of user defined datatype
}Example:
To illustrate the syntax more precisely
enum days
{
sun, mon, tues, wed, thurs, fri
}
}Explanation:
It works so that any enumeration of Java within a class is provided using a keyword with an enum followed by the type of datatype for a user and then giving values of user-defined datatypes. The above example illustrates clearly where the enum is the keyword followed by the name of user-defined datatypes and the value of user-defined datatypes.
Overview of Java Enum
In Java, an enum is a special data type that enables variables to set predefined constants. The variable we have defined is equal to the values we have defined. Because it will be constants, we can say that the enum example compass directions. The enum-type fields are always in capital letters.
The enumeration in Java represents a group by incorporating named constants into the programming language. In Java, we use an enum when we know that all possible values will be available at the time of compilation. It is not necessary to keep the enum type constants fixed all of the time.
Java Enum Class
In Java, we define enums inside and outside of a class. In Java, an enum is defined as a class type, so we do not need to instantiate the enum using new; it will contain the same capabilities as other classes. This feature makes enumeration useful. Like we give the constructor and also add the instance variables.
In the below example, we are defining the enum datatype inside the class as follows:
We are creating the class name as enum_class as follows:
Code:
public class enum_class {
enum Level {
LOWER,
MEDIUM,
HIGHER
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Level mv = Level.MEDIUM;
System.out.println (mv);
}
}Output:
In the below example, we are defining the enum datatype outside of the class as follows. We are creating the class name as enum_class as follows.
Code:
enum Color {
GREEN,
BLACK,
BLUE;
}
public class enum_class {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Color col = Color.BLUE;
System.out.println (col);
}
}Output:
Java Enum Switch Statement
We can also pass the enum data type by using a switch statement. The switch statement utilizes the enum data type to examine values. In the following example, an enum is employed with a switch statement to designate the level.
Code:
enum lev {
LOWER,
MEDIUM,
HIGHER
}
public class enum_class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
lev mv = lev.MEDIUM;
switch (mv) {
case LOWER:
System.out.println ("level 1");
break;
case MEDIUM:
System.out.println ("level 2");
break;
case HIGHER:
System.out.println ("level 3");
break;
}
}
}Output:
The below example shows a switch statement with an enum data type as follows. In the below example, we are giving day as an enum data type as follows.
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
enum Day {S, M, TU, W, T, F, SA;}
public class enum_class {
Day d;
public enum_class(Day day) { this.d = day; }
public void dayIsLike()
{
switch (d) {
case M:
System.out.println ("Mon is second day.");
break;
case F:
System.out.println ("Fri is sixth day");
break;
case SA:
case S:
System.out.println ("Sun is weekend");
break;
default:
System.out.println ("Tue is third day.");
break;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
String str = "M";
enum_class ec = new enum_class(Day.valueOf (str));
ec.dayIsLike ();
}
}
}Output:
Methods
The enum will contain abstract and concrete methods. If the enum class contains abstract methods, then every instance of the enum class implements the same. The below example shows enum methods as follows.
The values method returns all the values present inside the enum. Order is important in enum methods; while using the ordinal method, each enum index is found in the array of indexes. The value of the method returns the enum constant, which was specified by using the existing string value.
The below example shows enum methods as follows:
Code:
enum col
{
WHITE,
RED,
BLUE;
}
public class enum_class
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
col arr[] = col.values();
for (col col : arr)
{
System.out.println (col + "index"
+ col.ordinal());
}
System.out.println (col.valueOf ("RED"));
}
}Output:
Example of value(), ordinal() and ValueOf()
Program to illustrate the working of value(), ordinal(), and ValueOf().
Code:
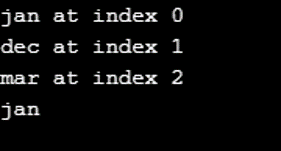
enum Calender
{
jan, dec, mar;
}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Calender arr[] = Calender.values();
for (Calender cal : arr)
{
System.out.println(cal + " at index "
+ cal.ordinal());
}
System.out.println(Calender.valueOf("jan"));
}
}Output:
Constructors
Enum contained the constructor and was executed separately for every enum constant on which we are loading the enum class. We cannot explicitly create the objects of the enum, so we cannot invoke the constructor of the enum directly.
The below example shows the enum constructor as follows:
Code:
enum col {
PINK,
YELLOW,
GREEN;
private col()
{
System.out.println ("Con called: "
+ this.toString());
}
public void colorInfo()
{
System.out.println ("Uni Color");
}
}
public class enum_class {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
col cl = col.PINK;
System.out.println (cl);
cl.colorInfo ();
}
}Output:
Java Enum Types
The Java enum type is a special data type that allows a variable to be set with predefined constants. The variable is equal to the value which we have predefined. In Java, we define the enum type by using the keyword as an enum. In the below example, we are defining the enum type of color as follows.
Example:
Code:
enum Col {
BLUE,
PINK,
BLACK
}We use the enum type at any time to represent the fixed set of constants, including the natural enum types. The below example shows how we can define the types as follows.
In the below example, we are defining the constant set of numbers as follows:
Code:
public class enum_class {
enum number {
ONE,
TWO ,
THREE
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
number num = number.TWO;
System.out.println (num);
}
}Output:
The below example shows Java enum types. In the below example, we are defining the enum type of days as follows.
Code:
public class enum_class {
enum day {
MON,
TUE,
WED
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
day d = day.TUE;
System.out.println (d);
}
}Output:
Importance
Enum inherits from the enum class so that it won’t inherit any other classes. Below is the importance..
- It improves the type of safety.
- We are using it easily in a switch.
- Enum in Java is traversed.
- Contains the constructors, methods, and fields.
- It implements the interfaces but will not extend any class; it will internally extend the enum class.
We are using an enum to create our data types. We use the enum data type to define enum in Java.
Below are the important characteristics as follows:
- The constant of the enum is not overridden.
- Enum does not support the object’s creation.
- It does not extend the other classes.
- Enum implements class-like interfaces.
- We are using an enum in a method.
- We are using an enum in a constructor.
Conclusion
In Java, an enum is a special data type that enables variables to set predefined constants. The variable we have defined is equal to the values we have defined. It is a special class used in the Java programming language to represent group constants. It contains unchangeable variables, such as variables as final.
FAQ’s
Q1. Are Enum constants unique in Java?
Answer: Yes, Enum constants are unique within the scope of the Enum type. Each constant is distinct, and the Java compiler guarantees its uniqueness.
Q2. Can I have duplicate values in a Java Enum?
Answer: No, each Enum constant must have a unique name within the Enum type. Defining two constants with the same name will result in a compilation error.
Q3. How can I check if two Enum constants are equal in Java?
Answer: Enums are compared using reference equality (==). If two Enum constants are the same instance, they are considered equal. Enums, by design, restrict the creation of multiple instances of the same constant.
Q4. What happens if I compare Enums with equals() instead of == ?
Answer: Enums implicitly override the equals() method, making it equivalent to using ==. Therefore, using equals() for Enum comparison is redundant and unnecessary.
Q5. Can I create an Enum with a custom equality criterion?
Answer: Enums in Java use reference equality (==), and you cannot override the equals() method. If you need custom equality, consider using a class with a predefined set of instances instead.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Enum. Here, we discuss the introduction, java enum class, switch statement, methods, constructors, and types. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –