Introduction to MySQL
MySQL is one of the popular relational database management systems; before introducing MySql, we will see the basic concepts related to the database.
The database is used to store the data; that is, the database is an application that holds the collection of related data. The other source of storing the data can be flat files, but the problem is storing, managing, and accessing the data is not fast and challenging; therefore, the excellent option is to use a database management system. Different types of Database Management Systems use various APIs to store and manage their data.
Database Management Systems
Differences between Database Management Systems based on the data models they follow are:
- Relational Database Management Systems
- Hierarchical Database Management Systems
- Network Database Management Systems
- Object-oriented Database Management Systems
A. Relational Database Management Systems
The abbreviation for Relational Database Management Systems is RDBMS, which stores data in different tables and establishes relations between the tables using primary keys and other keys known as Foreign Keys. We will learn more about relational database management systems to understand MySql more clearly because MySql is a relational database management system.
Let us revise the terminology related to the RDBMS:
1. Database: A database is used to store a collection of tables with related data.
2. Table: A table is a collection of related data organized as rows and columns. A table in a database looks like a simple spreadsheet. You can use a table to represent or store data related to objects or entities, or even describe relations.
3. Column: The column is also called the field. The column store the data value for the specific field; for example, the column name is to store the employee name, which stores only the employee name.
4. Row: A row is also called a record. The row is the set of field values relevant to a specific entity in the table. For example, the employee table contains fields such as id, name, salary, address, etc.
5. Constraint: Constraints are rules which restrict the type of data that can be stored in a table. The constraint helps maintain the data integrity in a table and the database.
Some of the constraints are as follows.
- Primary Key: A primary key is unique and should not have a duplicate or null value. You can use unique values in the primary key to identify each row or entity.
- Foreign Key: A foreign key refers to the primary key of another table. The primary and foreign Key establishes the connection between the tables.
- Composite Key: People also refer to a composite key as a compound key. The composite Key is a key that has multiple columns as a primary key because identifying each row as one column is not sufficient.
- Not null: Not null constraint restricts a column from entering a NULL value.
- Unique: Unique constraint restricts a column from entering unique values.
- Check: Check constraint restricts a column from entering values from the domain specified.
- Default: If you enter a null value, default constraints will enter the default specified value.
B. Hierarchical Database Management Systems
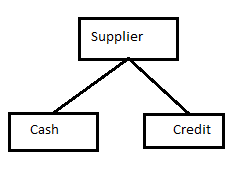
Now, in this topic of Introduction to MySQL, we will discuss Hierarchical Database Management Systems, which organize or represent the data into a tree-like structure stored in the parent node and child node relationships. The collection of fields or records represent the data, with only one value for each area, and they establish links with other records through parent and child relationships. In a hierarchical database model, a parent record can have multiple children, but a child record has only one parent. You must access each tree node until the record is found to navigate a hierarchical database model.
For example, the Supplier can pay either cash or credit, which represents in a hierarchical database model as:
C. Network Database Management Systems
We will discuss network Database Management Systems which represent the data into a network structure and create a relationship between entities using the link between them. It is an interconnected records network. The network database model is similar to a hierarchical database model except that one node can have only one parent, and a network child node can have multiple parents node, which represents many-to-many relationships.
D. Object-oriented Database Management Systems
Object-oriented Database Management Systems, also called OODBMS. It represents the data as objects and supports the classes of objects and their properties like inheritance and all; it works with an object in programming languages and similarly works in database objects. You can represent composite or larger objects and objects linked to each other by an ‘is-part-of’ relationship using a table.
MySQL Database
Small and big business applications can use MySQL Database since it is popular in relational database management systems.
Some of the key features of MySQL are:
- Open-source – MySQL is an open-source license. So we get it free, nothing to pay to use it.
- Implemented language – MySQL Written in C and C++.
- Powerful – MySql handles a large subset of the data with the functionality of the most powerful database packages. So it makes MySQL a compelling program.
- SQL data language – SQL data language is used by MySQL, which is a standard database language commonly used in most databases. So it is compatible with other databases also.
- Operating systems – On many operating systems, MySQL works with many languages like C, C++, PHP, PERL, JAVA, and so on.
- Large data sets – MySQL works well and quickly with large data sets.
- Web development – You can also use MySQL in web applications because it works with PHP and most web development languages.
- Supports large databases – MySQL works with large databases. The default file size limit for a table is 4GB, but you can increase it depending on the operating system. A table can hold up to 50 million rows or more.
- Multi-layered design – MySQL is a multi-layered server design with independent modules. MySQL utilizes multiple CPUs if available as it is fully multithreaded and uses kernel threads.
- Client/server environment – MySQL Server works in embedded or client/server systems.
Uses of MySQL
As we discussed the introduction to MySQL, now we are going to learn about the uses of MySQL as follows:
- Wikipedia, Facebook, Google, Flickr, YouTube, and all famous companies use mysql.
- WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, and all Content Management Systems (CMS) use MySQL.
- Developing a website as well uses MySQL.
How to get MySQL?
You can freely download MySql from the website https://www.mysql.com and install it since it is open-source.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Introduction to MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.