Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to Internet Control Message Protocol
ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network layer protocol used to address network communication problems across network devices. It is not a transport protocol that sends the data between the machine. The most common internet control message protocol has been used in the router. Internet Control Message protocol has been used for sending an IP packet larger than the bytes permitted under the IP Protocol for executing dos attacks.
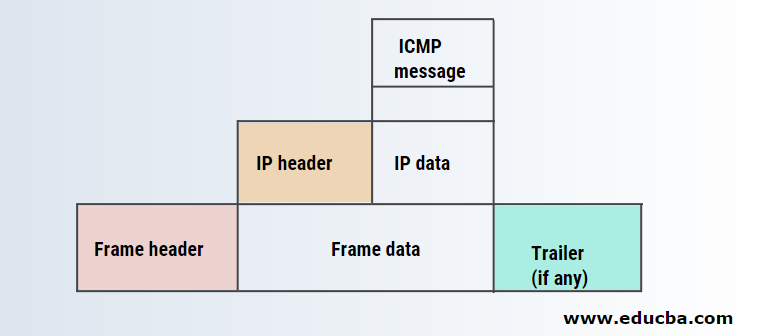
The below-mentioned diagram shows the process of encapsulation in the Internet Control Message Protocol.
Why do we need it?
The Internet protocol provides a connectionless delivery of the datagram. The goal behind this is to make use of network resources efficiently. In other words, it is designed to transfer a datagram from one host to another. But it has two deficiencies, i.e. lack of assistance and lack of error mechanism. To solve these two problems, the Internet Control Message Protocol comes into the picture.
Internet Control Message Protocol messages
There are two types of Internet Control Message Protocol messages – 1) Error reporting messages and 2) Query messages. Error reporting messages are used to detect a router or host’s problems while transforming the IP packet. The query messages help the network manager to get specific information from any router or host.
Internet Control Message Protocol message Format
The below-mentioned diagram shows the format of the Internet Control Message Protocol message.

- Type: This field is of 8 bits which defines the types of messages.
- Code: This field is of 8 bits which defines the reason for the specific messages type.
- Checksum: This field is of 16 bits used to detect the error while transforming the datagrams.
- Rest of header: This field is for each type of message.
- Data section: This filed is an error message. It carries information about the original packet that has an error. In the case of query messages, this field carries extra information based on the query type.
Types of Internet Control Message Protocol Messages
Here are the types of Internet Control Message Protocol messages given below
1. Error Reporting Messages
Error reporting messages are used to report problems that the router or host may face while transforming the datagrams. Remember that error reporting messages don’t correct the router’s error; it simply summarises the error report. Error messages are always sent to the source, i.e. sender site, because datagrams contain only the source and the destination IP address. Internet Control Message Protocol uses an IP address of the source to send an error message.
There are five types of error reporting messages –
- Destination unreachable message
- Source quench message
- Time exceeded message
- Parameter problem message
- Redirection message
- Destination unreachable message: The host or router sends the destination unreachable message to the source, which initiated the datagram when the host or router cannot route the datagram. In other words, when the router cannot send a datagram to the recipient, it sends the destination unreachable message to the source.
- Source quench message: The router sends source quench messages to the datagram source when the host or router discards the datagram due to the lack of flow control and congestion control.
- Time exceeded message: Time exceeded message can be generated in two cases. Let’s discuss those cases.
Case 1: When the host or router decrement the time to live value of the datagram to zero, the Internet Control Message Protocol sends the time exceeded message to the source address and discards the datagram.
Case 2: When the destination address does not receive all datagram fragments in a specified time interval, Internet Control Message Protocol sends a time exceeded message to the source address and discards the datagram.
In time exceeding message, routers use code 0 to show the value of time to live field is 0 and destination host use code 1 to show all data fragments received at the specified time. - Parameter problem message: The destination host or router creates this message. If the router or destination host identifies an ambiguous activity or missing value in any field of the datagram, it sends the parameter problems message to the source address and discards the datagram.
- Redirection message: A router or host sends this message on the same local network.
The routing table produces traffic as it updates tables dynamically. Mostly host uses static routing. When the host comes up, its routing table has a limited number of entries. It only knows the IP address of one router and the default router. Because of this reason host may send a datagram of one network to another, i.e. wrong router. In this case, the wrong router that receives datagrams forward to the correct router. But to update the host routing table, it sends a redirection message to the host.
2. Query Messages
Query messages help network managers to get specific information from any router or host. In other words, it can diagnose some network problems through query messages.
There are four types of query messages –
- Echo request and reply message
- Timestamp request and reply message
- Address mask request and reply message
- Router solicitation and advertisement message
- Echo-request and reply message: This message is designed for diagnostic purposes. These messages are used to identify whether two systems can communicate with each other or not.
The host or router sends the echo request message, while the echo reply message is sent by the host or router that receives an echo request message.
Network managers use these messages to check that IP protocol operations.
Using the ping command, each request and reply message can test the host’s reachability or router. - Timestamp request and reply message: Timestamp request and reply messages are used to determine the round trip time each IP datagram takes while traveling from one host to another host. It can also synchronize the clocks between hosts.
- Address mask request and reply message: These messages are used to identify the mask of the host.
For example, suppose the host known its IP address 192.168.1.25, but it does not know the mask of the corresponding host; in that case, to know the host’s mask, it sends an address mask request message for the router on the LAN network. In case the host knows the router’s IP address, it sends a request directly to that router, and if it does not know, it broadcast the request message. The router that receives the address mask request responds with an address mask reply and provides the mask to the host. - Router solicitation and advertisement message: Suppose a host wants to send data on another host that lies on another network and needs to know the routers’ IP address connected to its own network. It also wants to know whether the router of its own network is functioning or not. In that situation, router solicitation and advertisement messages can help. Host broadcast router solicitation message and router that receives the message broadcast the routing information using a router advertisement message.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Internet Control Message Protocol. Here we discuss the basic concept, types of Internet Control Message Protocol messages, and why do we need them. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


