Updated April 19, 2023
What is Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree
In a binary tree, there are many operations we can perform one of the main operations is traversing the tree. The process of getting, modifying, and checking the data of all nodes in a tree is called Tree Traversal. Using Tree traversal, we can get the data of all nodes or update and search any node. As we know, in linear data structures like arrays, linked lists, and stacks, we perform sequentially traversing. But, the binary trees can be traversed in many different ways.
A sequence of processing of all nodes in a binary tree differentiates the traversing binary tree type. The main classification is based on the order of the root node, left subtree or left child node, and right child node.
There are mainly three types of traversing:
a. Inorder Traversal
b. Preorder Traversal
c. Postorder Traversal
Syntax:
1. In Inorder traversal, traversal starts from the leftmost node of the binary tree and ends with a rightmost node of a binary tree. The root node in Inorder traversal always calls between the left subtree and right subtree. There are two ways to perform Inorder traversal:
2. Recursive approach
In the recursive approach, starting from the root node, the first call recursively leaves the child node until we get NULL, then get the current data, and then calls the right subtree until we get NULL.
3. Iterative approach
In the iterative approach, create a stack and push the nodes until we find NULL in the left child, then pop in the stack accordingly.
How Inorder traversal of binary tree works?
- InOrder traversing is one of the traversing techniques to get all nodes of a binary tree, In inorder traversing, the left subtree is processed before the current node, and the right subtree is after the current node.
- To perform Inorder traversing, traverse the left subtree until getting the leftmost node. Then visit the root node, then traverse the right subtree of every node.
- In the recursive approach, the traversal node is stored in the stack memory of the machine, whereas in the iterative approach, the stack data structure is used for storing the traversal node.
Now Let’s understand both approaches with an example.
Examples
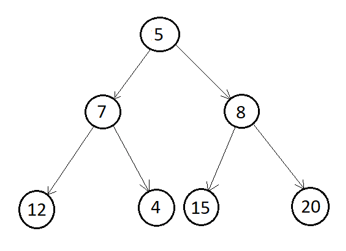
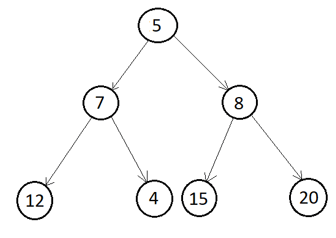
Let us take the below binary tree and traverse all nodes in Inorder traversing using recursive and iterative methods.
1. Recursive approach
In the recursive approach, as we discussed above, the first call recursively left the child node until getting a NULL value, then get the node value, and then calls recursively right the child node until getting NULL. So now print the value of all nodes inorder to traversing.
Step 1. Construct a binary tree as above using the GenerateBTNode function.
Step 2. Call displayTreeInorder and pass the root node.
Step 3. First, call displayTreeInorder and pass the left child of the current node recursively until we get NULL.
Step 4. After that, print the value of the current node.
Step 5. Call the same displayTreeInorder and pass the right child of the current node recursively until we get NULL.
Step 6. When all recursive functions are complete, inorder traversal of the binary tree is complete.
struct BTNode
{
int value; // element value
struct BTNode * left; // To store address of left child
struct BTNode * right; // To store address of right child
};
struct BTNode *GenerateBTNode (int data) {
struct BTNode *node = new BTNode;
node->value = data;
node->right = NULL;
node->left = NULL;
return node;
}
void displayTreeInorder (struct BTNode *root) {
if(root != NULL) {
displayTreeInorder(root->left);
cout << root->value << " ";
displayTreeInorder(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
BTNode *root = NULL;
root = GenerateBTNode(5);
root->left = GenerateBTNode(7);
root->right = GenerateBTNode(8);
root->left->left = GenerateBTNode(12);
root->left->right = GenerateBTNode(4);
root->right->left = GenerateBTNode(15);
root->right->right = GenerateBTNode(20);
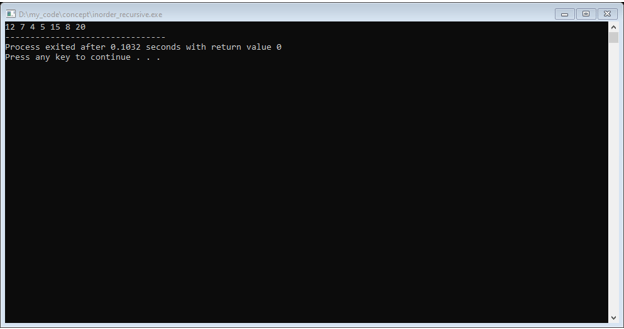
displayTreeInorder(root);
}
Output:
2. Iterative approach
In the iterative approach, the stack data structure is used. We need to store the current or parent node so that after processing the left subtree, we can process the node so we push the node in the stack data structure. After processing the node, we pop that respective node.
Step 1. Construct a binary tree as above using the GenerateBTNode function.
Step 2. Call the displayTreeInorderIterative function and pass the root node.
Step 3. Create a dummy node as a temp and initially set temp as root.
Step 4. Create a stack of BTNode type.
Step 5. Push the temp node and update the temp node to the left child of the node.
Step 6. Do step 5 until we get NULL.
Step 7. If we reached NULL, then it means that we reached the leftmost node of a tree.
Step 8. Then we simply print the value of the node and update the temp to the right child of the node and pop the stack, and do step 5 again.
Step 9. When the stack is empty and the temp node is NULL, then we completely traversed the binary tree.
struct BTNode
{
int value; // element value
struct BTNode * left; //To store address of left child
struct BTNode * right; //To store address of right child
};
struct BTNode *GenerateBTNode(int data) {
struct BTNode *node = new BTNode;
node->value = data;
node->right = NULL;
node->left = NULL;
return node;
}
void displayTreeInorderIterative (struct BTNode *root) {
stack <BTNode* > S;
BTNode *temp = root;
while (temp != NULL || !S.empty() ) {
if( temp != NULL) {
S.push(temp);
temp = temp->left;
}
else {
temp = S.top();
S.pop();
cout << temp->value << " ";
temp = temp->right;
}
}
}
int main() {
BTNode *root = NULL;
root = GenerateBTNode(5);
root->left = GenerateBTNode(7);
root->right = GenerateBTNode(8);
root->left->left = GenerateBTNode(12);
root->left->right = GenerateBTNode(4);
root->right->left = GenerateBTNode(15);
root->right->right = GenerateBTNode(20);
displayTreeInorderIterative(root);
}
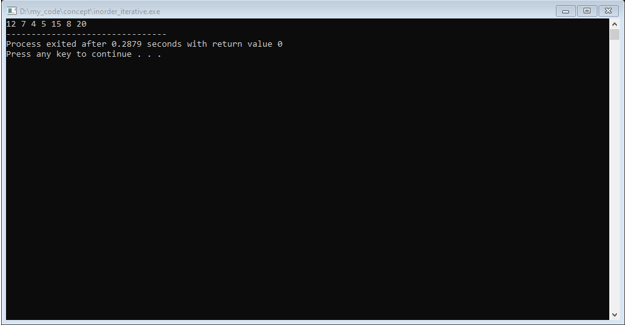
Output:
Conclusion
Inorder traversing is based on Depth First Search(DFS) algorithm. There is another traversing also based on Breadth-First Search(BFS) called Level Order traversing. In Binary Search Tree, inorder traversal gives the sorted list of all nodes. The Time Complexity of Inorder traversal is O(N).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Inorder Traversal of a Binary Tree. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, and How they work in Inorder traversal of binary tree? examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –