Updated April 1, 2023
Difference between Inductive vs Deductive
Inductive reasoning is a type of reasoning which is used for supporting the conclusion and support the conclusion. The conclusion can be probable or any hypothesis. The other name of inductive reasoning is bottom-up reasoning or cause & effect reasoning. Inductive reasoning takes many instances and forms one general conclusion from those instances. Deductive reasoning is another type of reasoning in which instances are true then the developed conclusion will always be true. Another name of deductive reasoning is top to bottom reasoning. In deductive reasoning, the general principles are used for developing one specific conclusion.
Head to Head Comparison between Inductive vs Deductive (Infographics)
Below are the top 9 differences between Inductive vs Deductive:
Key Differences between Inductive vs Deductive
Following are the key differences between Inductive vs Deductive
- The basic difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is the methodology they used. Deductive reasoning is a type of valid reasoning which begins from any general statement or any hypothesis and examines all the possibilities to reach the general conclusion. The hypothesis and theories can be examined using deductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning uses the general principle and then generates the specific conclusion taken from those principles. Inductive reasoning is completely opposite to deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning uses specific observation to generate one broad generalization. In this type, the data is used for making the conclusions and this process is known as inductive logic. The approach always follows from specific to some general form.
- The other major difference between inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning is that deductive reasoning begins from hypothesis and theories and tests them to reach to specific observation while on other hand the inductive reasoning begins with the observations and reach to general theories and facts.
- The other difference between these two reasoning is used and working in real life. Deductive reasoning follows the path from idea to observation while on other hand the inductive reasoning follows the path from observation to information. Deductive reasoning uses the premises which are assumed to be true and correct and the conclusion drawn from those premises are always correct and true while in inductive reasoning if the conclusion is true then it is not necessary that premises are true the premises are measured on their basis of strength and how much they support the conclusion.
- The key difference is the practical use of both reasoning. Deductive reasoning is hard to implement and use, as the collection of true facts and premises is a difficult job while on another hand inductive reasoning is easy to implement as the conclusion or end result is easy to get so that it can be easily implemented in real life.
- Deductive reasoning is more quantitative and precise while on other hand inductive reasoning is more qualitative and general. It can be better understood by the following example,
If X = Y and Y = Z then X = Z.
The above example is of deductive type as we have two facts which are true and using these two observations the conclusion is made that X = Z. In town, all cars present are drive on the left side of the street. Therefore, all the cars present in all towns are driven on the left side of the street. - One of the major key differences is the end result given by deductive and inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning gives the correct result only if the premises are absolutely correct. In inductive reasoning, if the conclusion is true then it does not guarantee that the facts are absolutely true. Inductive reasoning gives a better result and is a better tool compared to deductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning requires the actual facts to be drawn to an actual conclusion which requires more time and extra effort which makes this reasoning weak compare to inductive reasoning.
Comparison Table of Inductive vs Deductive
Let us look at the comparison table of Inductive vs Deductive.
|
Factor |
Inductive Reasoning |
Deductive Reasoning |
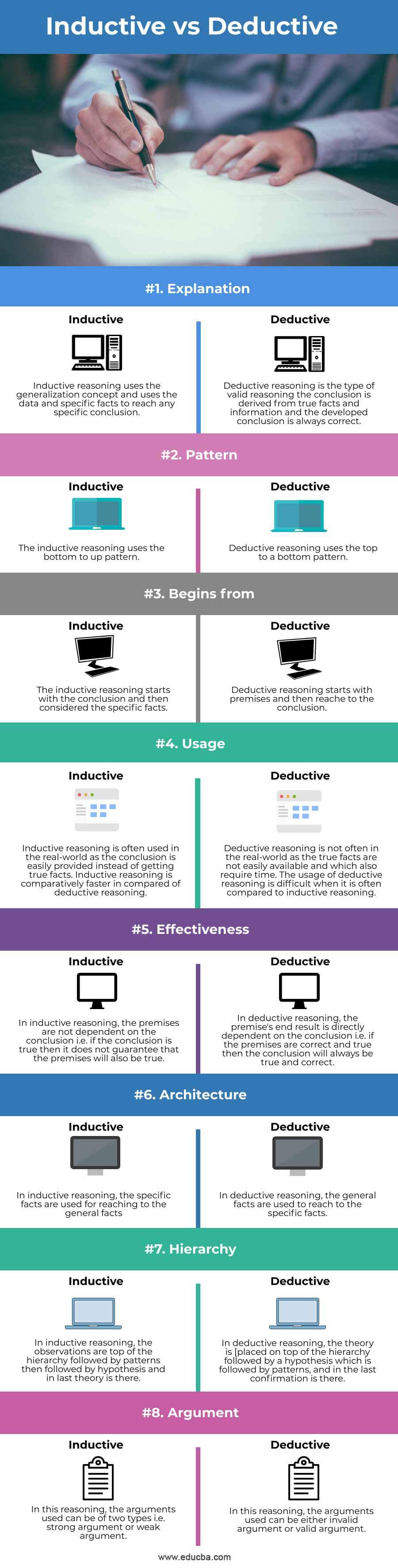
| Explanation | Inductive reasoning uses the generalization concept and uses the data and specific facts to reach any specific conclusion. | Deductive reasoning is the type of valid reasoning the conclusion is derived from true facts and information and the developed conclusion is always correct. |
| Pattern | Inductive reasoning uses the bottom to up pattern. | Deductive reasoning uses the top to a bottom pattern. |
| Begins from | Inductive reasoning starts with the conclusion and then considered the specific facts. | Deductive reasoning starts with premises and then reaches a conclusion. |
| Usage | Inductive reasoning is often used in the real world as the conclusion is easily provided instead of getting true facts. Inductive reasoning is comparatively faster in comparison of deductive reasoning. | Deductive reasoning is not often in the real world as the true facts are not easily available and which also require time. The usage of deductive reasoning is difficult when it is often compared to inductive reasoning. |
| Effectiveness | In inductive reasoning, the premises are not dependent on the conclusion i.e. if the conclusion is true then it does not guarantee that the premises will also be true. | In deductive reasoning, the premise’s end result is directly dependent on the conclusion i.e. if the premises are correct and true then the conclusion will always be true and correct. |
| Architecture | In inductive reasoning, the specific facts are used for reaching the general facts | In deductive reasoning, general facts are used to reach specific facts. |
| Hierarchy | In inductive reasoning, the observations are top of the hierarchy followed by patterns then followed by hypotheses and in the last theory is there. | In deductive reasoning, the theory is [placed on top of the hierarchy followed by a hypothesis which is followed by patterns, and in the last confirmation is there. |
| Argument | In this reasoning, the arguments used can be of two types i.e. strong argument or weak argument. | In this reasoning, the arguments used can be either invalid arguments or valid arguments. |
Conclusion
Deductive reasoning uses facts and theories to reach a conclusion. In inductive reasoning, the conclusion is used to make generalizations of facts and theories. Deductive reasoning works from the top to the bottom approach while on another hand inductive reasoning uses the bottom to the top approach. Deductive reasoning is less sue compared to inductive reasoning in the real world.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Inductive vs Deductive. Here we also discuss the inductive vs deductive key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –