Updated July 24, 2023

Definition of Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis includes evaluating data from current and historical financial statements to understand a company’s financial performance throughout the industry. It helps to set a trend line of a company’s performance over a period, which tells whether the company is showing growth.
What is Ratio Analysis?
Financial analysis of the company is done by analyzing many factors; ratio analysis is a very important part of financial analysis to understand its financial statements, position in the market, liquidity, operating efficiency, etc. it is based on a fundamental analysis of the company. It helps the investor understand the company’s performance through its financial statements.
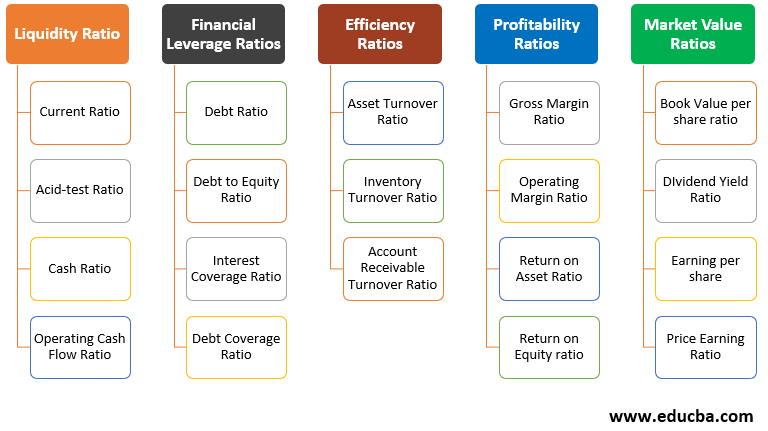
Categories of Ratio Analysis
Here we discuss the categories of ratio analysis:
- Liquidity Ratios: Company’s ability to pay out the short-term debt.
- Leverage Ratios: Evaluate the company debt level in the capital structure.
- Efficiency Ratios: Company’s efficiency in the utilization of its resources.
- Profitability Ratios: The ability of the company to generate income from revenue.
- Market Value Ratios: Evaluation of the company’s share price.
Understanding Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis assists in comprehending a company’s financial health and performance over a period by examining historical financial statements and conducting fundamental and quantitative analyses.
Successful companies mostly have solid ratios indicating good financial health and growth over time and management ability to handle problems in various aspects of the business. It is important to perform ratio analysis from all aspects of the company to make decisions since a single ratio might be deceitful. However, after understanding all ratios, investors get a complete picture of company performance over a period and future expectations from the company.
Importance of Ratio Analysis
The importance of ratio analysis is given below:
1. Financial Statement Analysis
Understanding financial statements are important for the stakeholders of the company. Ratio analysis helps understand the comparison of these numbers; furthermore, it helps estimate numbers from income statements and balance sheets for the future. For e.g. Equity shareholder looks into the P/E ratio, the Dividend payout ratio, etc., while creditors observe Debt to Equity ratio, Gross margin ratio, Debt to asset ratio, etc.
2. Efficiency of Company
Ratio analysis is important in understanding the company’s ability to generate profit. Return on Asset and Returns on Equity tells us how much profit the company can generate over the firm’s assets and equity investments in the firm. In contrast, gross and operating margin ratios show the company’s ability to generate profit from sales and operating efficiency.
3. Planning and Forecasting
From a Management and investor point of view, ratio analysis helps to understand and estimate the company’s future financials and operations. Ratios formed from past financial statement analysis help estimate future financials, budget, and plan for the company’s future operations.
4. Identifying Risk and Taking Corrective Actions
The company operates under various business, market, and operations-related risks. Ratio analysis helps understand these risks and helps management prepare and take necessary actions. Leverage ratios help perform sensitivity analysis of factors affecting the company’s profitability, like sales, cost, and debt. Financial leverage ratios like the Interest Coverage ratio and Debt Coverage ratio tell how much the company depends on external capital sources and the company’s ability to repay debt.
5. Peers Comparison
Investors and management compare with Competitors Company to understand efficiency, profitability, and market share. Ratio analysis is helpful for companies to perform SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis in the market. It also tells whether the company can perform growth over a period from past financials and whether the company’s financial position is improving.
6. A Better Source of Communication
Ratio analysis is important while presenting the company’s financials to its stakeholders. Ratios make it easy to understand than complex and huge numbers. Sometimes numbers can be deceitful, which leads to investors losing confidence. Still, ratio analysis helps the investor understand the company’s situation after comparison and helps them keep investing in the business.
7. Financial Solvency
The company’s ability to pay short-term debt is determined by liquidity. Current Ratio, Acid-test ratio tells us whether a company can pay its short-term obligation within a year. The company continuously runs analyses on past financial statements to understand and prepare for payment of short-term obligations.
8. Decision Making
Ratios provide important information on the operational efficiency of the company and the utilization of resources by the company. It helps management to forecast and plan for the future, new goals, concentrate on the different markets, etc.
9. Trend Line
Ratio analysis gives us the trend line, indicating whether a company can perform over a period. Companies gather data from past reporting periods trend line formed can be used to understand and judge future performance and any possible issue which cannot be found from just a one-year ratio analysis.
10. Important Tool
Ratio analysis is an essential tool for conducting a company’s financial analysis. It enables various actions, including comparing with peer companies, measuring the company’s efficiency in different aspects, and creating a financial model to forecast future performance.
11. All-in-One Package
Ratio analysis includes ratios, which measure various aspects of business like liquidity, efficiency, solvency, leverage, profitability, and market value. It gives reliable information to investors and management from all perspectives to make their own decisions. An investor should not depend on just one ratio to make investment decisions but should thoroughly analyze various ratios and understand their meaning related to the company’s future performance.
Conclusion
Ratio analysis is an important part of understanding business operations and the ability to perform in the market. For an investor, it is important to perform ratio analysis from all angles of business instead of just one or two angles because some ratios might provide positive insights. In contrast, others will show a negative impact on company performance. To understand the full picture 360, degree analysis is very important and can be done only after analyzing all ratios.
There are certain limitations on ratio analysis, like a company doing year-end changes in financial statements to improve ratios. This window dressing can be deceitful for investors, price level changes are ignored in ratio analysis, and there are no specific standards for every ratio.
Although ratio analysis only shows but does not help improve the business’s performance, it is still treated as an important tool that provides 360-degree analysis to understand company finances and make necessary decisions for the future.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Importance of Ratio Analysis. Here we discuss the introduction and categories of ratio analysis and its importance. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
- What is the Cost-Benefit Analysis Formula?
- How Statistical Analysis is Performed?
- Need for Statistical Analysis Regression
- Examples of SWOT Analysis
- Balance Sheet Ratios | Types
- Coverage Ratio | Advantages and Disadvantages
- Complete Guide to Ratio Analysis Types
- Financial Leverage with Excel Template


