Introduction to Hive Inner Join
We will get the appropriate records or data from the two or more different hive tables and get the resulted new hive table in hive inner join. But the selected columns in the join condition having the common value or same data type. In an inner join, we can consider two common columns (having the same datatype or same value) from the two different tables and use the join condition. We can join or combine the records of two tables and get the new join hive table. If we are writing the simply “join” in the join query its nothing but the “inner join” only.
Syntax:
Hive_join_table:
table_reference [INNER] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference {LEFT|RIGHT|FULL} [OUTER] JOIN table_referencejoin_condition
| table_reference LEFT SEMI JOIN table_referencejoin_condition
| table_reference CROSS JOIN table_reference [join_condition]
How does Inner Join work in Hive?
In the hive, we are getting the combined result of two hive tables with subject to common or same column values of both the tables in the join condition.
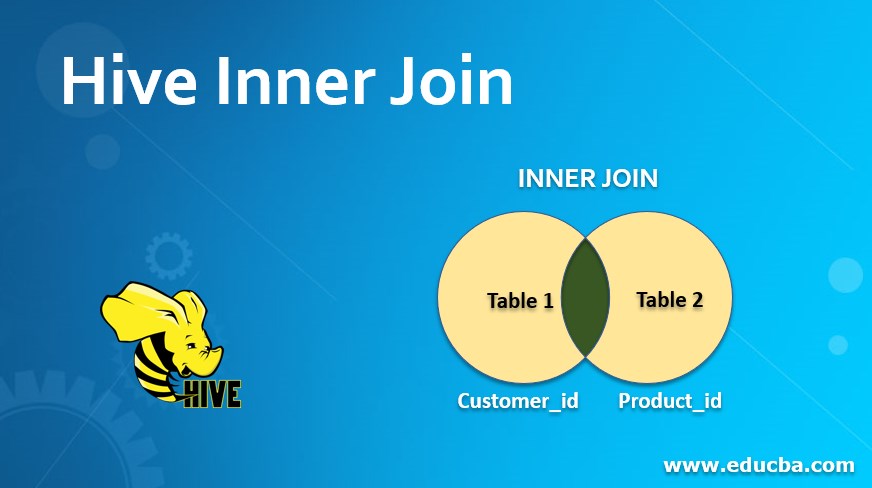
As per the above image, we have two hive tables “table1” and “table2”. Table1 having different columns with “customer_id”. Table2 having different columns with “product_id”. Here, “customer_id” and “product_id” having the same value (like 1,2,3.. etc.) or the same data type. In an inner join, the result will come with a combination of both the matching id of customer_id and product_id. If the values match both the table columns of “customer_id” and “product_id” then only the result/records will come or display. Otherwise, if the value is present in “customer_id” but the same id is not present in “product_id” then the resultant output will not come or vice a versa.
Hive Version 0.13.0
The hive version 0.13.0, it allows the “FROM” clause to join the multiple tables with comma-separated. Moreover, we can omit the “join” keyword in the query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM table1 t1, table2 t2 WHERE t1.customer_id = t2.product_id;
In the latest versions of the hive, we can use the “JOIN” keyword.
- Note #1: In Hive, the query will convert the joins over multiple tables, and we want to run a single map/reduce job. Then it is mandatory that the same column should be used in the join clause.
- Note #2: If we use the different and multiple columns in the same join clause, the query will execute with the multiple map / reduce jobs.
- Note #3: In the hive, every map / reduce stage of the join query. The last table in the sequence and it’s streamed through the reducers whereas the others are buffered.
Explanation
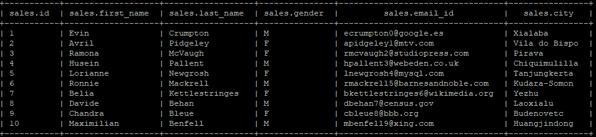
We have two tables (table name: -sales and products) in the “company” database of the hive.
Below are the lists of fields/columns in the “sales” table:
- ID (data type “int”)
- First Name (data type “string”)
- Last Name (data type “string”)
- Gender (data type “string”)
- Email_ID (data type “string”)
- City (data type “string”)
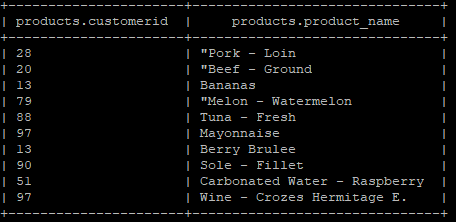
Below are the lists of fields/columns in the “Products” table:
- customer_id (data type “int”)
- product_name (data type “string”)
1. DDL Code for “sales” table
Code:
create external table company.sales
(
id int,
first_name string,
last_name string,
gender string,
email_id string,
city string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
lines terminated by '\n'
tblproperties ("skip.header.line.count"="1");
Output: We have 1000 records in the “sales” table (manually loaded the data).
2. DDL Code for “Products” table
Code:
create external table company.products
(
customerid int,
product_name string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
lines terminated by '\n'
tblproperties ("skip.header.line.count"="1");
We have 1000 records in the “products” table (manually loaded the data).
Sample “sales” table view
Sample “products” table view
Example to Implement Hive Inner Join
In the hive, we have “company” DB. It contains two different tables,’ i.e. sales table and product table in the above two tables sales and products. We have seen two columns having common data types as well as common value. In sales tables – “id” is present and product tables – “customerid” is present. Both the column are referencing to each other. With the help of sales and product tables, we will get the information from those users who buy with products. Now we need complete records or data of those users who buy which products.
SQL Query with Using “JOIN Clause”
Below is the SQL Query
Code #1
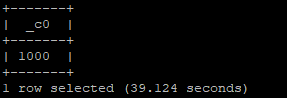
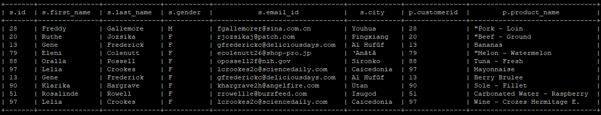
SELECT * FROM sales s JOIN products p ON (s.id = p.customerid) limit 10;
Output:
Code #2
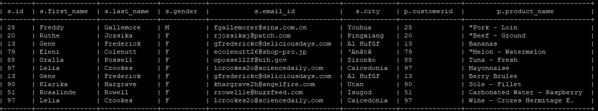
SELECT s.id, s.first_name, s.last_name, p.customerid, p.product_name FROM sales s JOIN products p ON (s.id = p.customerid) limit 10;
Output:
SQL Query without Using “JOIN Clause”
Code:
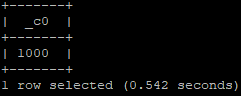
select * from sales s1, products p1 where s1.id = p1.customerid limit 10;
Output:
Advantages of using Hive Inner Join
- The major advantage of hive join is to get the different tables data in a single query.
- No need to add the same or common columns fields in the table.
- Get the result faster.
- Less data store in the indivisible table
- In the hive, mapper and reduces are using to execute the join query. It will minimize the cost of processing and storing the data.
- The map side joins help improve the job or query or application’s performance, and it will take less time to execute.
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Hive Inner Join” with the proper example, explanation, syntax, and code. With the help of the “JOIN” condition, we can get the data or records from two or more different columns. No need to keep or add the same files in multiple tables. We need to keep the separate table and join with the necessary tables with common join vales or data types.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Hive Inner Join. Here we discuss how does inner join works, hive version 0.13.0 with explanation and examples to implement. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –