Updated March 18, 2023
What is Hive Function?
As we know, today Hadoop is one of the versatile technologies in big data. Hadoop has the ability to cope up with large dataset, but as the data growth is proportional, writing map-reduce programs become difficult. To perform SQL queries, present in HDFS one such technology was introduced by Hadoop called apache Hive started by Facebook. Hive is highly used by the data analyst. They are deployed for three functionalities namely: Data Summarization, data analysis on distributed file and data query. Hive provides SQL like queries called HQL – high query language supports DML, user-defined functions. Hive compiler converts this query internally into map-reduce jobs which simplifies the work of Hadoop in writing complex programs. We could find a hive in application like Data warehousing, data visualization, and ad-hoc analysis, google analytics. The key advantage is they make use of SQL knowledge which is a basic skill implemented across data scientists and software professionals.
Different Hive Functions in Detail
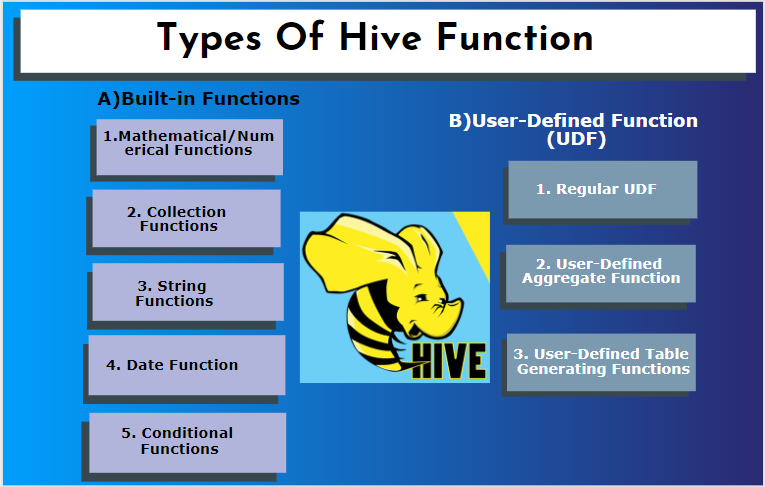
Hive supports different data types that are not found in other database systems. it includes a map, array, and struct. Hive has some built-in functions to perform several mathematical and arithmetic functions for a special purpose. Functions in a hive can be categorized into the following types. They are built-in functions and user-defined functions.
A) Built-in Functions
These functions extract data from the hive tables and process the calculations. Some of the built-in functions are:
1. Mathematical/Numerical Functions
These functions are mainly used for mathematical calculations. These functions are used in SQL queries.
| Function Name | Example | Description |
| ABS (double x) | Hive > select ABS (-200) from tmp; | It will return the absolute value of a number. |
| CEIL (double x) | Hive > select CEIL (8.5) from tmp; | It will fetch the smallest integer greater than or equal to value x. |
| Rand (), rand (int seed) | Hive > select Rand () from tmp;
Rand (0-9) |
It returns a random number, depends on seed value the random numbers generated would be deterministic. |
| Pow (double x, double y) | Hive > select Pow (5,2) from tmp; | It returns x value raised to the y power. |
| FLOOR (double y) | Hive > select FLOOR (11.8) from tmp; | It returns a maximum integer less than or equal to give value y. |
| EXP (double a) | Hive > select Exp (30) from tmp; | It will return the exponent value of 30. the natural algorithm values. |
| PMOD (int a, int b) | Hive > select PMOD (2, 4) from tmp; | It gives the positive modulus of the number. |
2. Collection Functions
Dumping all the elements together and returning single elements depends on the data type included.
| Function name | Example | Description |
| Map_values (Map <K.V>) | Hive> select Map values (‘hi’ ,45) | It fetches unordered array elements. |
| Size (Map <K.V>) | Hive> select size (map) | Returns the number of elements in the datatype map. |
| Array_contains (Array b) | Hive>select array_contains (a [10]) | Returns TRUE if the array contains the value. |
| Sort_array (Array a) | Hive>select sort_array ({10,3,6,1,7}) | Sorts the input array in ascending order according to the natural ordering of the array elements and returns the value. |
3. String Functions
Using string functions data analysis is performed excellently.
| Split (string s, string pat) | Hive > select split (‘educba ~ hive~ Hadoop,’~’) output: [“educba”,” hive”,” Hadoop”] | It splits string around pat expressions and returns an array. |
| load(string s, int Len, string pad) | Hive > select load (‘EDUCBA’, 6,’H’) | It returns strings with right padding with the length of the string. (pad character). |
| Length (string str) | Hive > select length (‘educba’) | This function returns the length of the string. |
| Rtrim (string a) | Hive > select rtrim(‘TOPIC’);
Output: ‘Topic ‘ |
It returns the result by trimming spaces from the right ends. |
| Concat (string m, string n) | Hive > select concat (‘data’,’ ware’) Result: Dataware | It results in the string by doing concatenation of two strings; this can take any number of inputs. |
| Reverse (string s) | Hive > select reverse (‘Mobile’) | Returns the result of a reversed string. |
4. Date Function
It is necessary to have data format in a hive to prevent Null error in the output. It is necessary to have date compatibility to go with hive introduced date functions.
| Unix_timestamp (String date, string pattern) | Hive > select Unix_ timestamp (‘2019-06-08’ , ‘ yyyy-mm-dd’); Result: 124576 400 time taken: 0.146 seconds |
This function returns date to the specific format and returns seconds between date and Unix times. |
| Unix_timestamp (String date) | Hive > select Unix_ timestamp (‘2019-06-08 09:20:10’, ‘yyyy-mm-dd’); | It returns the date in ‘yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm: ss’ format into Unix timestamp. |
| Hour (String date) | Hive > select hour (‘2019-06-08 09:20:10’);Result: 09 hours | It returns the timestamp hour. |
5. Conditional Functions
| If (Boolean test, T value true, t false) | Hive>select IF(1=1,’TRUE’,’FALSE’) as IF_CONDITION_TEST; |
It checks with the condition if the value is true returns 1 and false returns 0. |
| Is not null(b) | Hive >Select is not null (null); | This fetches not null statements. if null returns false. |
| Coalesce (value1, value2) | Example: hive > select coalesce (Null, null,4, null, 6). it returns 4. | It fetches first not null values from the list of values. |
B) User-Defined Function (UDF)
Hive uses user-specific functions according to the client requirements it is written in java programming. It is implemented by two interfaces, namely simple API and complex API. They are invoked from the hive query. Three types of UDFs:
1. Regular UDF: It works on a table with a single row. It is created by creating a java class, then packaging them into a .jar file; the next step is to verify with a hive classpath. then finally executing them in a hive query.
2. User-Defined Aggregate Function: They use aggregate functions like avg/ mean by implementing five methods init (), iterate (), partial (), merge (), terminate ().
3. User-Defined Table Generating Functions: It works with a single row in a table and results in multiple rows.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned how to work in the hive platform with built-in functions and user-defined functions in detail through this article. Most organizations have programmer and SQL developer to work on the server-side process, but an apache hive is a powerful tool which helps them to use Hadoop framework with no prior knowledge on programs and map-reduce. Hive helps new users to start and explore data analyzing without any barriers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Hive Function. Here we discuss the basic concept, two different types of functions and sub-functions in the Hive. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –