Introduction to Hibernate Architecture
Before getting into the Hibernate Architecture, let us look at why Hibernate came into the picture and what purpose it solves for us. Hibernate is an ORM (Object Relational Mapping) tool for a java programming language to develop object-based database-independent persistence logic. Hibernate provides a layer of abstraction for retrieving and storing data in a database.
Why Hibernate?
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is database dependent. To be more specific, writing queries to be run from your application using JDBC depends on what database you are working with. If you work with MySQL or Oracle, your queries will be different. So If in the middle of a project you need to change your database that will require a change of code too, and of course we don’t want that. Whereas, hibernate uses a database-independent Hibernate Query Language. In short, hibernate takes care of most of what the developer had to do with JDBC, for eg. Opening a connection to the DB, closing connections, handling various exceptions.
So let’s get into the Hibernate Architecture to better understand how Hibernate has made data persistence so much easier.
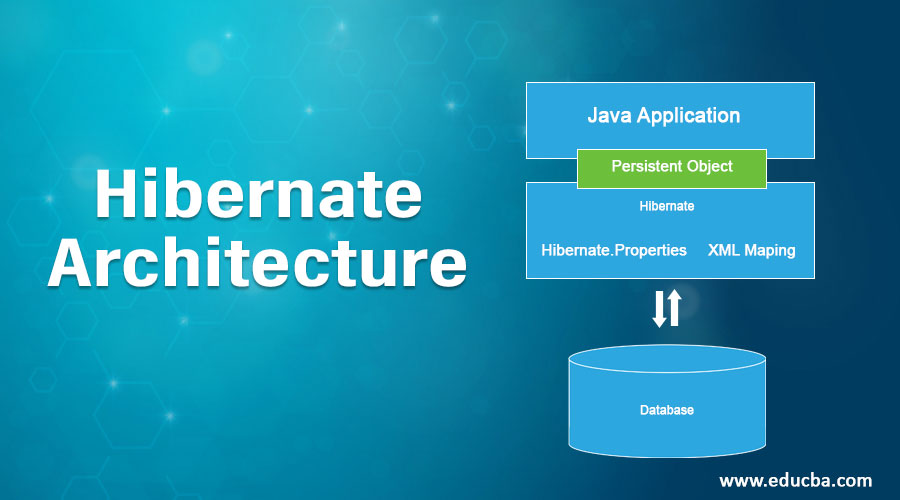
Hibernate Architecture
The main concept being any ORM is to replace writing database-specific SQL queries with manipulating objects.
To put it in simple words,
- you create a POJO (Plain Old Java Object)
- assign values to the fields using setters
- tell hibernate to persists those objects
Hibernate maps Java classes to database tables (which also involves mapping the java data types to SQL data types).
So it takes away the pain of converting the java fields to SQL supported data types. Hibernate does it for you.
It also relieves the developer from the pain of result set handling.
Java Application
While developing the persistence logic we need to take the support of some resources in the java application. Let us look at these resources.
The heart of any Hibernate application lies in its configuration, which is done using,
- Configuration file
- Mapping file
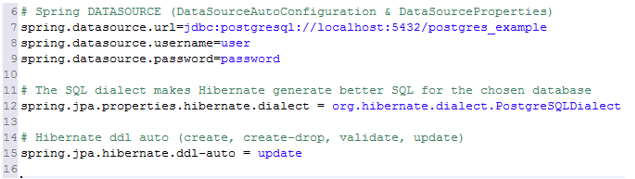
Hibernate Configuration File
We define the properties which tell hibernate what database it has to interact with and which JDBC driver to use. Hibernate uses a configuration file to get all this information.
Although Hibernate is capable of generating database queries, we can specify the dialect to help it generate better SQL for the required database.
For e.g. following are the properties you will typically set in a spring boot application
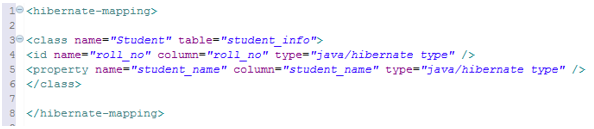
Hibernate Mapping File
It holds all the class-to-table mapping definitions. Every ORM tool needs a mapping file. We use the following ways to tell Hibernate what value of an object has to be stored in which column of the table.
- XML
- Annotations
Syntax of an XML mapping file in spring,
Following is how we annotate the instance variable that should be mapped to a column of a row in the database.
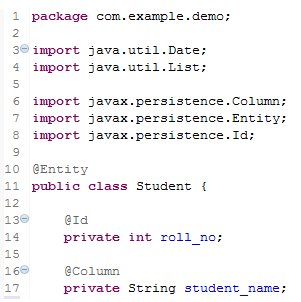
Domain Class
As we know Hibernate is known for developing object-based persistence logic. So a domain class is a POJO that is mapped to a table in the database.
Configuration
To create a connection to the database, Hibernate needs to know the details of the database, classes and other details. A configuration object is created once when an application is initialized. It is mainly responsible for bootstrapping Hibernate to the application. A configuration object uses the configuration file and the hibernate mapping file to perform the following steps:
- Load these files.
- Checks if these files are well-formed and valid.
- Creates in-memory metadata of these two files.
- Return an object which contains this metadata.
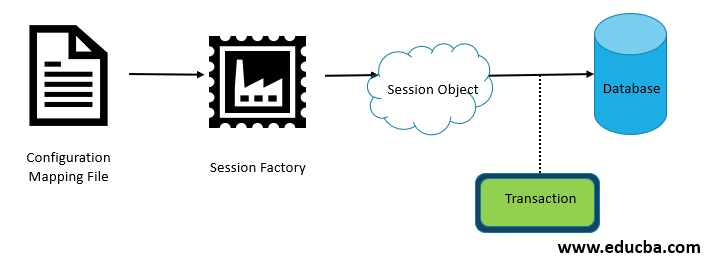
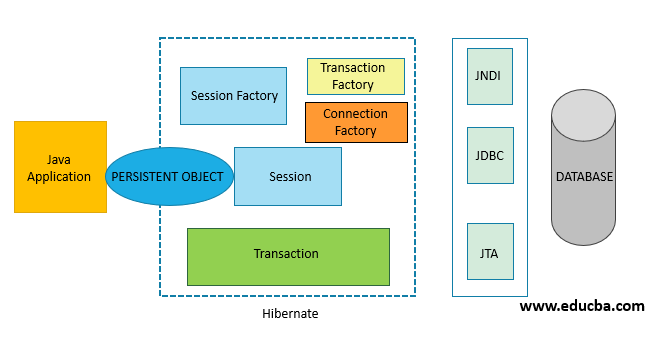
Session Factory
A session factory is used to create session objects. It is created by the configuration object. It provides a layer of abstraction, so we don’t have to worry about how the session object is created. It is a thread-safe global factory class for creating sessions. Using the configuration object, we get access to the in-memory data created from the configuration and mapping file.
From there, it gets the JDBC properties- driver name, data source URL, username, password, etc. Using these properties, it will create connection objects, representing connectivity to the database.
Using these connections, a connection pool is created. All the information from the configuration object and connection pool is used to create and return a session object. Hence, a session factory object is a heavyweight object. Each session factory is configured to work with a specific database using one of the specified Hibernate dialects.
Session
One thing to note is that it is not related to a servlet session or a java mail session. A session is a gateway to our database. It creates a bridge from our application to the database. It is created by the session factory. It takes the connection object and opens a connection/session to the database, and allows the application to perform persistence operations on the database.
In an ORM tool, you perform all operations like INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE using object-oriented semantics, which means you are no longer referring to tables, rows, and columns. It is the sessions work to do all the persistence operations for you.
Transaction
A transaction is a short-lived object which represents a single unit of work like saving or delete an object in a table in the database. It abstracts the application from the underlying transaction done by using JDBC, JTA (Java Transaction API), etc.
Internally, hibernate using JDBC, JTA, JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) to generate SQL queries for the configured database.
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at how the layered architecture of hibernate helps a programmer to work with a database without having to know the details of the underlying API like JDBC, JTA, and JNDI. We learned how Hibernate makes our life easier by handling most of the boilerplate code like opening/closing connection to the database. Hopefully, this gives you a clear understanding of the Hibernate Architecture, which will get you started on using the Hibernate Framework in your applications.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Hibernate Architecture. Here we discussed Hibernate Architecture to better understand how it has made data persistence much easier along with Java Application. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


