What Is a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)?
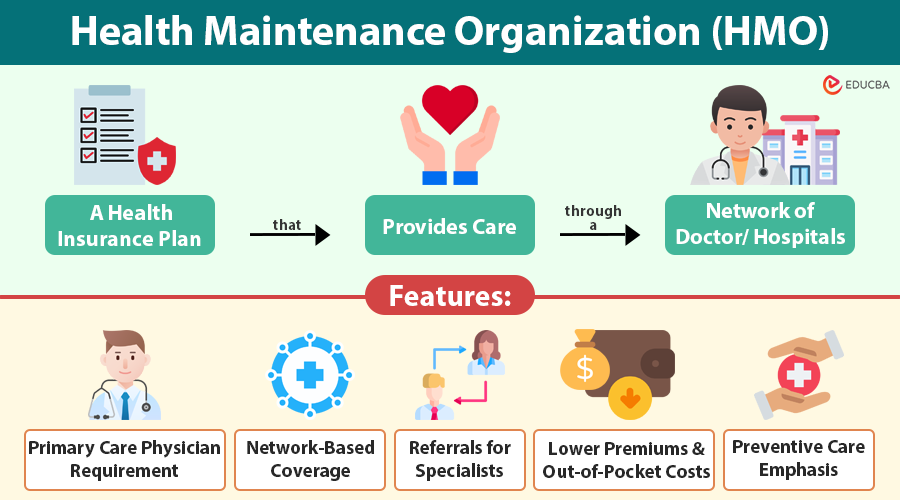
A Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) is a type of health insurance plan that manages and organizes your medical care through a network of doctors and hospitals. It contracts with a network of healthcare providers—doctors, specialists, clinics, and hospitals—to offer comprehensive medical care to its members at lower costs.
The primary concept of HMOs is coordination—your primary care physician (PCP) manages all your healthcare and is typically the first doctor you see for any medical needs. Unlike other plans, HMOs usually do not cover out-of-network care unless it is an emergency. This structure helps control costs while emphasizing the importance of preventive care.
HMOs are particularly prevalent in health insurance plans offered by employers and government programs, such as Medicaid and Medicare Advantage.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)?
- Key Features of a Health Maintenance Organization
- How Does an HMO Work?
- Benefits of Choosing a Health Maintenance Organization
- Drawbacks of a Health Maintenance Organization
- HMO vs. PPO: What is the Difference?
- Who Should Choose an HMO?
Key Features of a Health Maintenance Organization
The key features of a Health Maintenance Organization are:
1. Primary Care Physician (PCP) Requirement
When you enroll in an HMO, you are required to select a primary care physician from the HMO’s approved provider list. This doctor becomes your go-to for everything from routine check-ups to diagnosing new symptoms.
The PCP’s role is not just medical but also administrative—they coordinate any necessary specialist referrals, diagnostic tests, or follow-up treatments. This system ensures that your care is comprehensive, not duplicated, or fragmented.
2. Network-Based Coverage
HMO plans operate within a closed network of providers. This means that you must receive care from doctors and facilities that have contracted with the HMO to be eligible for insurance coverage.
If you seek treatment outside the network (except in emergencies), your care typically will not be covered, and you will be required to pay the full cost out-of-pocket. This rule helps HMOs manage costs but can limit flexibility for patients.
3. Referrals for Specialists
Unlike PPO plans, where you can see a specialist directly, HMOs require a referral from your PCP to consult a specialist. This ensures that you consult specialists only when necessary and follow a care path that aligns with your medical history and needs.
For example, if you need to see a cardiologist for heart-related symptoms, your PCP will evaluate you first and then refer you to a network cardiologist if needed.
4. Lower Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs
One of the main reasons people choose HMOs is affordability. Premiums (monthly payments) are often lower than those of PPO plans, and out-of-pocket expenses, such as deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance, are more predictable and affordable.
Because providers agree to negotiated rates with the HMO, costs are better controlled, which benefits both insurers and policyholders.
5. Preventive Care Emphasis
HMOs prioritize preventive care, including annual physicals, vaccinations, screenings, and wellness checkups. These services are usually free or very low-cost, helping members stay healthy and catch problems early.
By focusing on prevention, HMOs help reduce the risk of serious illnesses and long-term healthcare costs.
How Does an HMO Work?
Managed care forms the foundation of HMOs, where healthcare providers guide and monitor your treatment to ensure quality, efficiency, and affordability. Here is a step-by-step look at how an HMO works:
Step 1: Enrollment
When you sign up for an HMO plan, you pick a primary care doctor from the plan’s approved network.
Step 2: Regular Visits
For any health concerns, you first consult your PCP. They handle most routine care and minor illnesses.
Step 3: Specialist Referral
If your condition requires specialist attention, your PCP will provide a referral to a relevant in-network specialist.
Step 4: Covered Services
Services received from approved providers within the network are covered under your plan, subject to co-pays and deductibles.
Step 5: Emergency Coverage
Emergency care is typically covered even if it is outside the HMO network, as long as it meets emergency criteria.
This model simplifies healthcare usage, reduces unnecessary procedures, and improves communication between providers.
Benefits of Choosing a Health Maintenance Organization
Here are some benefits of choosing a Health Maintenance Organization:
1. Affordable Premiums
HMOs are known for their budget-friendly premiums. Since members must use network providers and go through a PCP, insurers can better manage costs, which translates into lower monthly payments for members.
2. Coordinated Care
By having a single PCP oversee your care, HMOs offer better continuity and coordination. This is especially helpful for people who have long-term health issues or take several medications.
Your PCP has a comprehensive view of your medical history and ensures that treatments from different specialists work together effectively.
3. Preventive Services
HMO plans typically cover preventive care, such as vaccines, health checkups, and screenings, at no additional cost. This helps members catch health problems early before they become serious.
This not only saves costs but also improves health outcomes.
4. Simplified Billing and Claims
The HMO manages all care within a closed network, which streamlines and simplifies the billing process. You usually will not have to file claims yourself—providers handle the paperwork, reducing the administrative burden on patients.
Drawbacks of a Health Maintenance Organization
Here are some drawbacks of Health Maintenance Organization:
1. Limited Choice of Providers
One major downside is the restricted provider network. If your preferred doctor or hospital is not in the HMO’s network, you will either need to change providers or pay the full cost out-of-pocket.
This can be especially challenging if you live in a remote area or require specialized care.
2. Referral Process Can Be Slower
The need for referrals might delay your care. For example, if you develop a skin condition, you must first see your PCP before being referred to a dermatologist—even if you already know what kind of care you need.
3. No Out-of-Network Coverage (Except Emergencies)
Unlike PPOs, HMOs do not cover non-emergency services outside the network, which limits your options if you travel frequently or need a specialist not available within the network.
4. Less Flexibility for Second Opinions
HMOs make obtaining a second opinion more challenging because they tightly manage referrals and control access to specialists. If you are facing a major medical decision, this lack of flexibility may be frustrating.
HMO vs. PPO: What is the Difference?
To better understand HMOs, it is helpful to compare them with PPOs—another popular type of health insurance plan.
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
| Primary Care Physician (PCP) | Required | Not required |
| Specialist Referral | Required | Not required |
| Out-of-Network Coverage | Emergency only | Available (higher cost) |
| Monthly Premium | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Coordination of Care | Centralized through PCP | Member-managed |
| Best For | Budget-conscious, preventive-focused | Those wanting choice and flexibility |
Who Should Choose an HMO?
HMO plans are a good choice for people and families who:
- Prefer predictable healthcare costs and lower monthly premiums.
- Do not mind choosing a designated PCP for all their medical needs.
- Are comfortable with receiving care within a specific network of providers.
- Focus on regular check-ups and early detection to maintain your health.
- Live in areas where HMO networks are broad and accessible.
However, if you travel often or have specific specialists in mind outside the network, a PPO might offer more flexibility.
Final Thoughts
A Health Maintenance Organization provides a cost-effective, preventive care-focused model for healthcare. While it requires members to follow a structured care path through a designated network, it also offers the benefits of lower costs, coordinated care, and an emphasis on wellness.
If you are seeking a health insurance plan that is easy to manage, affordable, and preventive, an HMO may be a smart choice. Understanding how it works helps you make more informed choices for your health and finances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can I switch my primary care doctor in an HMO plan?
Answer: Yes, most HMO plans allow you to change your PCP if you are not satisfied with the care or want a provider closer to home. The process usually involves submitting a request to your insurance provider, and the change may take effect from the next billing cycle or month.
Q2. Do HMOs cover mental health and behavioral health services?
Answer: Yes, HMO plans typically cover mental health services, including counseling, therapy, and psychiatric evaluations. However, you will still need a referral from your PCP to access these services within the network.
Q3. What if I need urgent care while I am traveling?
Answer: If you experience a medical emergency while traveling, most HMO plans will cover the emergency treatment, even if it is provided by an out-of-network provider. However, urgent care (non-life-threatening issues) may not be covered unless it is from a participating provider, so it is best to check your plan’s travel coverage policies.
Q4. What if I need long-term care or rehabilitation services?
Answer: HMO plans may cover some long-term care or rehabilitation services (like physical therapy or home health care). However, they often require pre-approval and must be provided by in-network facilities. The plan may not fully cover long stays in nursing homes or assisted living facilities.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide to Health Maintenance Organizations has helped you understand how they work and whether they are the right fit for your healthcare needs. Explore these recommended articles to gain more insights into health insurance types, provider networks, and choosing the right coverage for your lifestyle.