Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to Hadoop Distributed File System
In the Hadoop stack, we are having a huge amount of data. It will store on the Hadoop ecosystem. The data will not present on a single node. The data is distributed on multiple data computes nodes. The Hadoop distributed file system i.e. the HDFS service is responsible to manage the complete data level activity on the Hadoop. All the Hadoop services will store their data on the Hadoop distributed file system. In this, only HDFS service is not running. It will consist of multiple services or concepts in it like name node, data node, journal nodes, zkfail over the controller, NFS gateway, etc.
Syntax
As such, there is no specific syntax available for the Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS). Generally, we are using the number of services on it. As per the requirement or need, we can use the necessary components of the HDFS file system and use the appropriate syntax of it. Every service or component is having its own working methodology. As per the requirement, we need to use the proper syntax of it.
How Hadoop Distributed File System Works?
As we have discussed, the Hadoop distributed file system is distributed on the number of data nodes. The HDFS file system is designed for high scalability, reliability, fault-tolerant. In the Hadoop distributed file system, we are having the replication concept. By default, we are having the replication factor is 3 i.e. the data or the file will be distributed on different 3 nodes. In some case, if we will face any issues on any data node but still we will get the data because we are having the 3 copies of the data. In the HDFS, the data is store in the block. The size of the block is 128 MB. As per the requirement, if you want to increase the size of the block, we can also increase the block size as well. In the HDFS file system, it will take the data from the different resources and store on the HDFS level. While storing the data, it will split the data into different nodes across the cluster. It is also supporting effective parallel processing as well.
As we have discussed, in the Hadoop distributed file system we are having multiple components or services. The name node is responsible to manage the complete Hadoop distributed file system. It is having the complete block-level information on the HDFS file system. It will get the block-level information from HDFS metadata. We can store a huge amount of data on an HDFS file system like in TB or more. The data will store in terms of the block level i.e. the default block size is 128 MB.
When any user or client wants to read or write any operation on HDFS level. The client first will trigger Hadoop or HDFS command. It will be on HDFS shell or the hue or any third-party application. The first request will go to the namenode. (If the namenode will not live then the HDFS command or HDFS request will not work). Namenode will check the information from its metadata. If the block information is present then it will serve the request. Otherwise, it will through an error message
Below are the list of services which is important to manage the Hadoop distributed file system
- Name Node
- Secondary Name Node
- Journal node
- HDFS Gateway
- Data Node
- Name Node: The namenode is able to track the files, blocks, manage the file system. It will also manage the HDFS file system metadata. The metadata is having detailed information of a file or block-level information on the HDFS level. In specific, the namenode is having detailed information of the count of blocks, locations of the files, or data on the data node. It will also take care of the HDFS file replication part. The HDFS namenode has direct contact with the HDFS client.
- Secondary Name Node: In the Hadoop distributed file system, the secondary namenode is master Daemons or Services or Nodes. The secondary namenode is also known as the checkpoint node. The edit log is a key point to sync up with the live namenode and the secondary namenode. The edit log is responsible to make the secondary namenode will become the active namenode. The edit log will give detailed information to the secondary namenode what was the last update of the namenode from the same information the secondary namenode will start their work and become active (as namenode).
- Journal Node: The journal node is responsible to manage the active status of the namenode. The active namenode status is depending on the calculated quorum and opportunities quorum.
- HDFS Gateway: The HDFS gateway is acting as a client. It is responsible to manage the data communication from the HDFS ecosystem to the external world.
- Data Node: In the HDFS file system, the datanode is master Daemons or Services or Nodes. The datanode is responsible to store the actual file on the HDFS level. It will store the data in terms of blocks. When the client request the data then the actual data will share by the datanode only. (Here, namenode will only share the information of the data or file block information). The datanode is a slave daemon.
Example of the Hadoop Distributed File System
Following are the examples are given below:
Hadoop lsCommand
In the Hadoop environment, the Hadoop distributed file system will manage the huge amount of data in the distributed manager. To manage the data in distributed mode, we need to understand the related HDFS services.
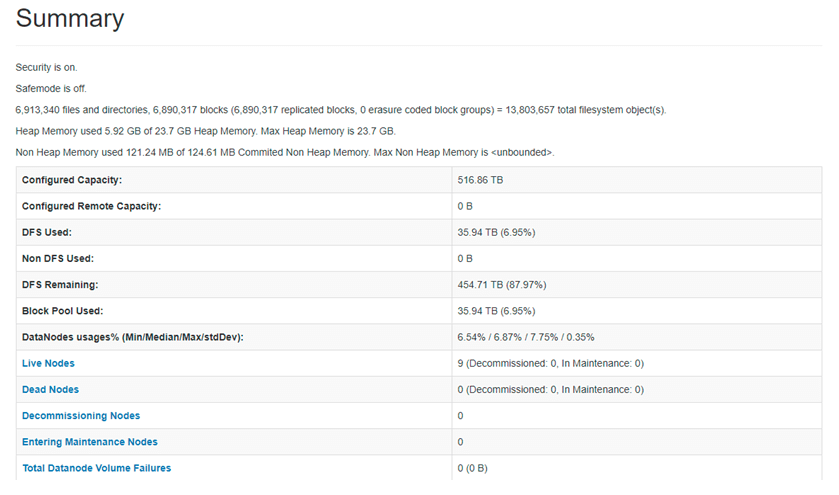
Screenshot:
Explanation: As per the above screenshot, we are getting detailed information on the HDFS distributed file system.
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of the “Hadoop distributed file system” with the proper example, explanation, and screenshot. The Hadoop distributed file system will manage the massive amount of data. The data is distributed on different data nodes. To manage the Hadoop distributed file system, we need to consider the different HDFS services like Name Node, Secondary Name Node, Journal node, HDFS Gateway, Data Node, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Hadoop Distributed File System. Here we also discuss the introduction and how Hadoop distributed file system works? along with the example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –