Updated July 5, 2023
Difference Between GNSS vs GPS
GNSS, which stands for Global Navigation Satellite Systems, and GPS, which stands for Global positioning systems, are the most common terms that we know when we discuss ‘satnav’ or satellite navigation. Satellite navigation provides autonomous geo-spatial positioning with the help of the network of satellites that provides global coverage and determines the minor electronic receivers’ locations using the time signals transmitted along the line of sight by the radio and from the satellites. GNSS and GPS are often used interchangeably, but there are major differences. This article highlights these differences.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between GNSS vs GPS (Infographics)
Below are the top comparisons between GNSS and GPS:
Key Differences Between GNSS vs GPS
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between GNSS and GPS:
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems, or GNSS, is a global term encompassing the world’s or global satellite positioning systems. But GPS is one of the major components of GNSS, and to be more specific, it refers to the NAVSTAR Global Positioning System GPOS developed by the USA Department of Defence, which was specific to military use earlier but later made accessible to the civilian population.
- GNSS includes other satellite-based positioning systems, such as GLONASS, developed by Russians and European unions Galilieo and Chins Beidou. At the same time, GPS is one such component under GNSS.
- GNSS, in collaboration with GPS, is used to locate positions precisely anywhere on the Earth. This GNSS and GPS work together to get accurate locations. But the main difference is that the GNSS is compatible with other satellite networks, which can be beyond GPS. All the GNSS receivers are compatible with receiving the signals from the GPS systems, but vice versa; all the receivers of GPS are not compatible with GNSS.
- Both GNSS and GPS will be composed of three basic segments, which are the satellite (Space segment) that sends the signals continuously; controls stations on earth (Ground Segment) which monitor and track each of the satellites and last, the user segment, which will be the GPS or GNSS receivers. This GNSS and GPS are currently used in various fields where continuous position tracking is required, such as transportation, agriculture, marine navigation, machine control, vehicle navigation, cellular and mobile communications, etc.
- The GNSS provides a wider satellite network that always provides better accuracy, availability, and redundancy. Thus even if one of the satellite systems fails, the GNSS receiver can pick up the signal from another receiver. GPS also has a network of 32 medium earth orbit satellites in six different orbital planes. Thus we can say that GPS is a subset of GNSS.
Comparison Table of GNSS vs GPS
Let’s look at the top comparisons between GNSS vs GPS.
Below is the comparison table between GNSS and GPS on certain features. From the above part of the article, you might have seen that GNSS is a generic name for the group of satellites that sends out the signal to the receivers, and GPS is one of the many such different groups of satellites. So this comparison table will be more towards GPS and other satellite-based navigation systems in the column termed as GNSS rather than literal GNSS and GPS comparison.
|
Feature |
GNSS(All Satellite Navigation Systems Except GPS) |
GPS |
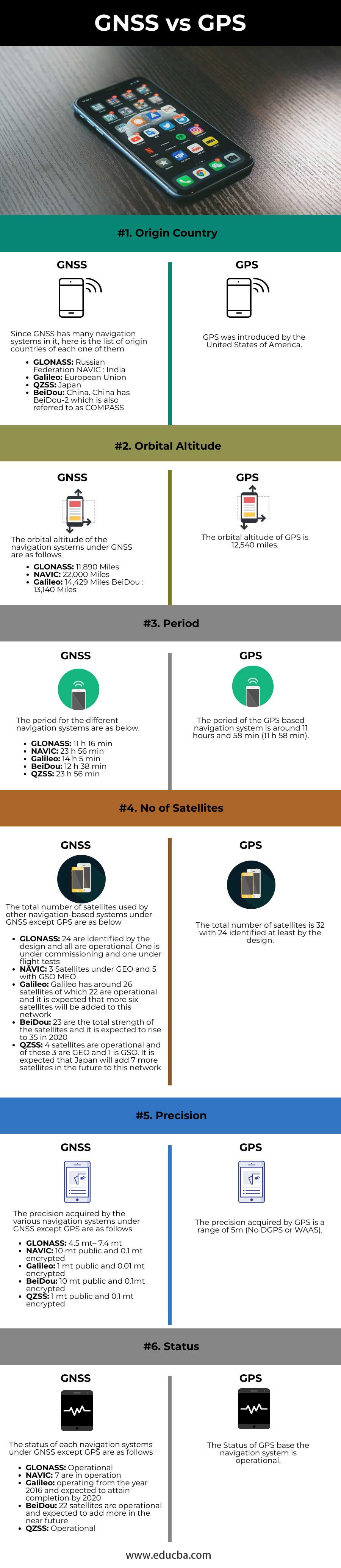
| Origin Country | Since GNSS has many navigation systems, here is the list of origin countries of each one of them.
|
The United States of America introduced GPS. |
| Orbital Altitude | The orbital altitude of the navigation systems under GNSS is as follows:
|
The orbital altitude of GPS is 12,540 miles. |
| Period | The period for the different navigation systems is as below:
|
The period of the GPS-based navigation system is around 11 hours and 58 min (11 h 58 min). |
| No of Satellites | The total number of satellites used by other navigation-based systems under GNSS except GPS are as below:
|
The total number of satellites is 32, with 24 identified at least by design. |
| Precision | The precision acquired by the various navigation systems under GNSS, except GPS, are as follows:
|
The precision acquired by GPS is a range of 5m (No DGPS or WAAS). |
| Status | The status of each navigation system under GNSS except GPS is as follows:
|
The Status of the GPS-based navigation system is operational. |
The data source in the above comparisons table is from the official site “GNSS signal – Navipedia”. gssc.esa.int. Retrieved 2018-11-17.
Conclusion
Thus, GPS is a popular GNSS base positioning system that is quite common in the civilian domain for positioning. And similarly, there are other navigation-based systems under GNSS which we have seen in this article. Using the network of satellites in GNSS for user positioning increases the precision level called Precision Point Positioning PPP that will be obtained.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “GNSS vs GPS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.