
Introduction to For Loop in Java
The following article provides an outline for For Loop in Java. Looping is a concept in Java that executes a certain bunch of statements repetitively when a certain condition is true. Java provides three ways of executing the loops.
They are:
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Do while Loop
Steps
Given below are the steps mentioned:
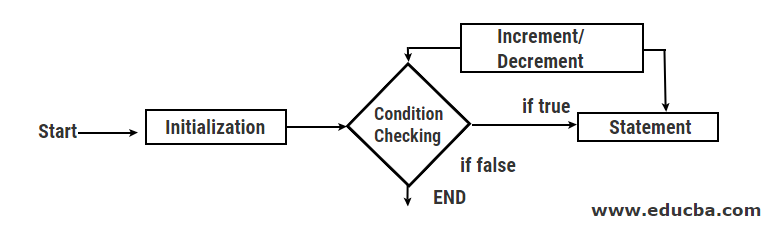
- Initializing Condition – In the Initialization phase, we introduce the variables to be used in the Java program. Generally, the variables are initialized as zero or one.
- Testing Condition – In the test condition, one of the counter variable variables is checked whether it is greater than or less than a certain quantity.
- Statement Execution – In this phase, the print statement or the variable inside the for loop is executed making it easier to generate the output. Sometimes the print statement is also used within this phase.
- Incrementing/Decrementing Condition – In this phase, the loop control variable or the counter variable is incremented by 1 generally to move the code forward. There can also be a decrement of 1 to the loop control variable if the condition of the program demands so.
- Terminating the Loop – When the condition doesn’t satisfy in the testing condition phase, the loop closes and doesn’t work anymore.
Java is an entry-controlled loop as the condition is checked prior to the execution of the statement.
The syntax of a for loop in a Java program can be easily executed using the following.
Syntax:
for (initialization condition; testing condition;
increment/decrement)
{
statement(s) or print statement
}Flowchart:
Examples of For Loop in Java
Given below are the examples mentioned::
Example #1
In the first example, we are going to generate the first 10 numbers in a Java program using for loop. The sample code is given below as well as the output. The name of the class is forLoopDemo. There are three phases in the loop statement. It runs from 1 to 10 generating all the natural numbers in between.
Code:
class forLoopDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// for loop 0begins when x=1
// and runs till x <=10
System.out.println("OUTPUT OF THE FIRST 10 NATURAL NUMBERS");
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++)
System.out.println(+ x)
}
}Output:

Example #2
After the first example, we move on to the second example, where we introduce an array and print certain elements in the array. The syntax for printing the elements in the array is as follows.
Syntax:
for (T element:Collection obj/array)
{
statement(s)
}The sample code, as well as the output, is shown below. In other words, it is also known as enhanced for loop. The simple loop format is also shown in the code below.
Code:
// Java program to illustrate enhanced for loop
public class enhanced for loop
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String array[] = {"Ron", "Harry", "Hermoine"};
//enhanced for loop
for (String x:array)
{
System.out.println(x);
}
/* for loop for same function
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
*/
}
}Output:

Example #3
In example 3, we are going to check an infinite for loop. An infinite for loop is one that runs without stopping. It is one of the disadvantages of using for loop. An infinite loop can be created deliberately. In most cases, an infinite for loop is created by mistake. In the code below, an infinite loop is created because the update statement is not provided.
Code:
//Java program to illustrate various pitfalls.
public class LooppitfallsDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// infinite loop because condition is not apt
// condition should have been i>0.
for (int i = 5; i != 0; i -= 2)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
int x = 5;
// infinite loop because update statement
// is not provided.
while (x == 5)
{
System.out.println("In the loop");
}
}
}Output:
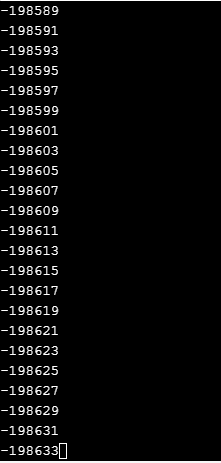
The sample output is shown above as well as the running of the Java virtual machine. The Java virtual machine runs indefinitely, and it doesn’t stop. The JVM can be stopped by right-clicking on the JVM icon as shown and then stopping it. Also, the shortcut is shown, which is Control + Shift + R.
Example #4
In example 4, we are going to see another application for loop, which is a nested for loop. Nested for loop means a for loop within for a loop. That means two for loops are inside each other. They are generally used to print complex patterns in a Java platform. An example of a nested for loop is shown below.
Here the class name is PyramidExample. Then the main() is declared. After that, the two-loop control variables are declared. One is the loop control variable “i”, and the other is the loop control variable “j”. Then the “*” is printed in the loop control. The new line is given so that the given format of the pyramid structure is maintained. In this code, the program is run till 5 times. However, by increasing the value of the “i” th loop control variable, we can make sure that the pyramid is bigger.
Code:
public class PyramidExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();//new line
}
}
}Output:

Example #5
In this example, we are going to see how a for loop goes through each and every element of an array and prints them.
In the below code, the class name is GFG. The package java. io .* is imported here. Also, the throws IO Exception is used at the main(), which throws and removes any exception arriving at the piece of code. The ar.length() returns the length of the array. The variable x stores the element at the “i”th position and prints it. This code is one of the easiest ways of showing how to access array elements using for loop function.
Code:
// Java program to iterate over an array
// using for loop
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
int ar[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
int i, x;
// iterating over an array
for (i = 0; i < ar.length; i++) {
// accessing each element of array
x = ar[i];
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}Output:
![]()
Example #6
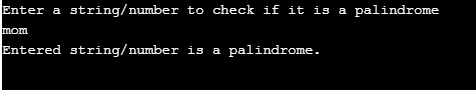
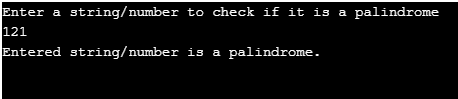
In this example, we are going to see whether a number is a palindrome or not. In this also, a for loop is used. A palindrome number is one which when reversed, represents the same number.
Examples are 121, 1331, 4334, etc.
Code:
import java.util.*;
class PalindromeExample2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String original, reverse = ""; // Objects of String class
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a string/number to check if it is a palindrome");
original = in.nextLine();
int length = original.length();
for ( int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i-- )
reverse = reverse + original.charAt(i);
if (original.equals(reverse))
System.out.println("Entered string/number is a palindrome.");
else
System.out.println("Entered string/number isn't a palindrome.");
}
}Output:
Conclusion – For Loop in Java
In this article, we saw how a for loop is used in many cases. The condition is checked at the beginning of the loop, and then if the condition is satisfied, then it is used in the remaining part of the loop. It is very similar to a while loop which is also an entry-controlled loop. It is in contrast to the do-while loop in which the condition is checked at the exit of the loop.
For loops are used in Java and used in C, C++, Python, and many other programming languages. Mostly they are used to print patterns in menu-driven programs to check the behavior of a number and much more.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to For Loop in Java. Here we discuss the introduction to for loop in Java, for loop steps: initializing condition, testing condition, and statement execution along with some sample code. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


