Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Financial Reporting Examples
Financial reporting is the summary of the performance of a concern over a given period. The end reporting could be a look into the day-to-day working, position of assets and liabilities at a particular time, the cash flow and positions throughout a period, or any other such analysis, as the case may be, which is required by the interested parties to the concern.
Given the vast coverage of the scope of this reporting, below are some examples describing the various forms in which the reporting exists.
Examples of Financial Reporting (With Excel Template)
Let’s take examples of financial reporting to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1 – Balance Sheet
A balance sheet reports the financial position of an entity on a particular date. These are generally prepared at the end of the financial year i.e. 31st March or 31st December, depending on the custom followed in a particular country. The balance sheet typically reports the following three classes
- Assets – These are a measure of the resources owned by the concern. This will help create future value and enable revenue and inflows of funds in the coming time. The assets exist both in tangible and intangible form, and some of the items depicted in it might refer to the receivables from external parties.
- Liabilities – These depict the resources owned by the concern in financial terms. The concern needs to settle this sometime in the future to continue running the business in a healthy way. Non-fulfillment of such liabilities beyond a period would lead to a loss of reputation, penalties, and, ultimately, a business shutdown. There are primarily two forms of liabilities: short-term liabilities, which are settled within 12 months, and long-term liabilities, which are paid after 12 months.
- Shareholders Equity – is a measure of the amount the concern owes to its owners or shareholders. It will equal the difference between the assets and the liabilities the concern owes to external parties. It includes equity capital, preferred share capital, and retained earnings that the business has kept for utilization.
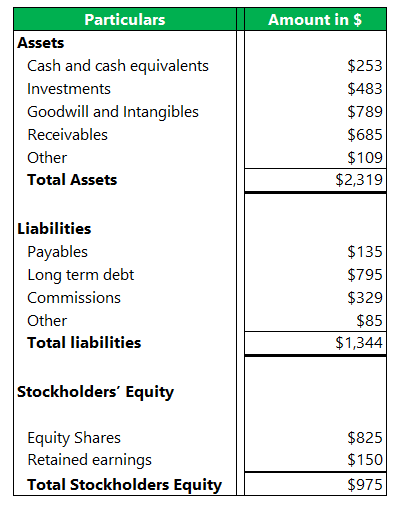
Below is an example of a balance sheet of entity A, which has just started its operations
Example #2 – Notes to Financial Statements
The financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, and cash flows) summarize the year’s financial activities. However, it is important to understand the accounting principles, policies, and assumptions under which they are prepared. Notes to accounts fulfill this purpose. The accounting board governing standards requires the compulsory inclusion of certain notes in the financial reports. On the other hand, other notes are prepared to enhance understanding and explain the items mentioned in the statements.
Usually, the following notes to accounts are present
- Accounting policies – Financial reporting includes a list of important accounting principles, such as revenue recognition, depreciation, inventory method, evaluation of intangible assets, and foreign currency fluctuation. Understanding these principles is crucial for interpreting the information presented in the financial statements. Different results would be obtained if alternative principles were applied. Any changes in accounting methods from previous periods are disclosed to stakeholders, along with an explanation of the resulting impact. This ensures transparency and enables stakeholders to assess the consistency of financial information over time.
- Fair value measurements – All items susceptible to fair value treatment (e.g. investments) will be mentioned here, along with the values followed among the choice between historical and fair value.
- Mergers & acquisitions – any transactions relating to the merger between the reporting entity and any external party is expounded here, along with the details of the deal
- Contingencies – The financial reporting mentions any potential liabilities that may arise in the future, along with their corresponding impact. Additionally, it summarizes any litigations the company faces that could potentially result in penalties or fines.
- Exceptions – Any event beyond the scope of normal business activity that requires communication to stakeholders is highlighted in the financial reporting. These events can potentially impact the entity’s operations in the upcoming years.
Example #3 – Management Discussion & Analysis (MD&A)
This is a section in the annual report following the financial statements and notes to accounts that explains the events that have conspired during the reporting period from the management to the stakeholders. It lists down causes for the entity’s performance, the major factors that affected the growth in the current period, how the performance measures against that of its competitors, and the outlook towards the future. This is an unaudited section of the annual report.
The following are the functions of this section
- Commentary on the performance of the entity, the compliance with the law and regulations, and the major changes that impact its growth in the reporting period
- Actively lists the current risks that affect the entity and the industry, outlines the controls implemented to mitigate these risks, and presents new projects and plans for the future.
- Mentions the major capital expenditures, the liquidity position, and the management plan for future debt intake or equity issuance.
- Explains the critical accounting policies and estimates and how changes in them have affected the concern
Conclusion
Financial reporting is crucial in comprehending a business’s operations and financial position. While financial statements serve as the primary means to capture the company’s operations, it is equally important for the reporting to facilitate understanding and readability of the presented figures. Consequently, there has been a growing emphasis on functional components such as notes to accounts to enhance the clarity and comprehensibility of financial information. These notes provide additional context, explanations, and disclosures that aid in interpreting the financial statements accurately and making informed decisions.
It is important that the reporting captures the major attributes of the functioning without being vague or overly complex. Financial reporting carries significant responsibility towards stakeholders due to its crucial importance, requiring diligent efforts from those involved.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Financial Reporting Examples. Here we discuss the introduction and practical Example of a Balance Sheet, Notes to Financial Statements, Management Discussion & Analysis, a detailed explanation, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –