Updated July 13, 2023
What is Fannie Mae?
Fannie Mae is an agency that makes mortgages available to the small and medium-income category of people. It is short for Federal National Mortgage Association and is backed and sponsored by the government.
However, the agency itself does not give any loans. It usually buys mortgages from lenders in exchange for money to eventually invest in other assets and markets.
Key Highlights
- Fannie Mae buys conventional loans from lending entities to provide housing mortgages to US citizens.
- Making mortgage investments gives the banks additional liquidity, enabling them to underwrite more loans.
- With affordable interest rates and comparatively lower down payment options, it helps provide loans to small to medium-income populations.
- They can make arrangements to restructure the loans, like reducing monthly payments or halting the settlement in case of borrowers’ liquidity concerns.
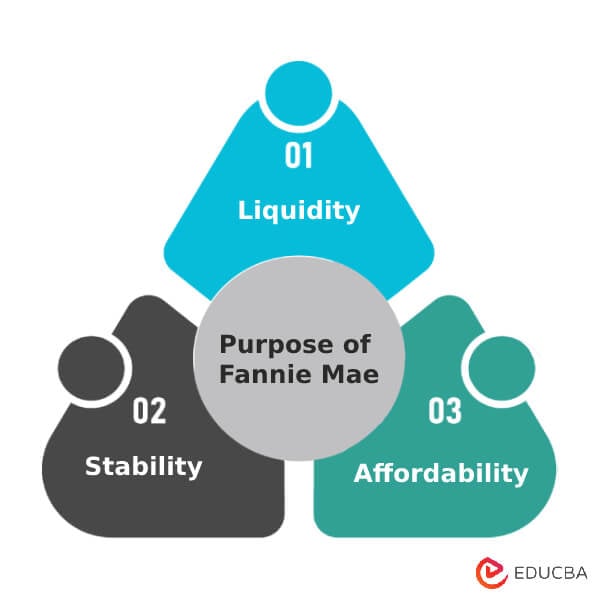
Purpose of Fannie Mae
- The primary purpose is to bring stability and liquidity to the mortgage lending world.
- It allows people to have access to affordable financing and refinancing options.
- Being a government-sponsored organization, it maintains market liquidity by regularly buying loans from lending institutions. The purchases are ethical and follow the recommended protocols.
- They support promoting the 30-year fixed interest rate, a cornerstone of the US housing finance industry.
- They want individuals to buy, mortgage, or lease a property without much hassle.
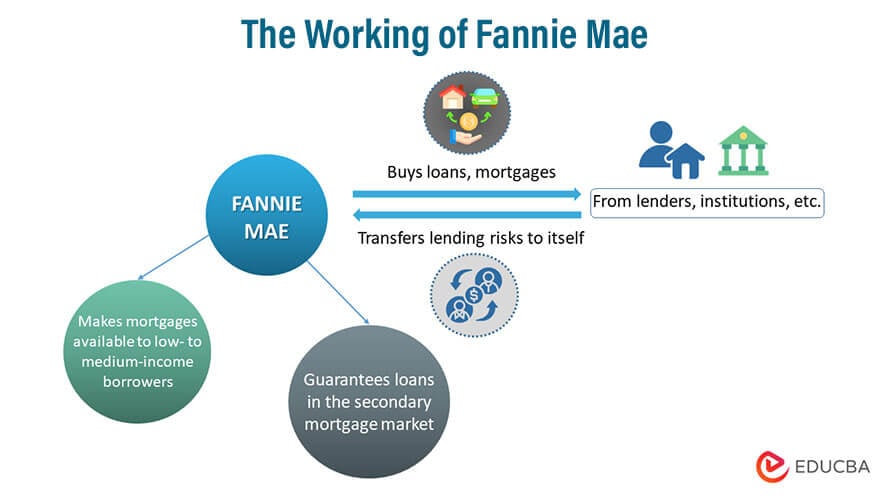
How Does Fannie Mae Work?
The Congress government originally formed it in the late 1930s as a refinancing mortgage company. The purpose was to boost the lending market and work its way through the secondary market. It generally works on a straightforward model. It buys loans and mortgages from lenders, institutions, etc., transferring lending risks to itself. Thus, the transaction helps bring in more liquidity to such organizations. In addition, it helps provide loans to the public, eventually bringing liquidity to the market.
One cannot obtain a mortgage straight from Fannie Mae because it does not create mortgages. The crucial tasks still fall on banks and non-bank lenders. Tasks include gathering customers’ paperwork, approving the mortgage by confirming their earnings, possessions, and property worth, and closing the transaction.
Following the loan’s completion, it purchases loans that satisfy its criteria from the lenders. However, lending organizations cannot get into unethical practices and keep giving loans to the public and institutions. They need to follow ethical lending practices and adhere to strict guidelines.
Fannie Mae Stock
- Its shares have been traded openly since 1968. It was on the New York Stock Exchange up till 2010
- The real estate market was gravely affected after the Great Recession from December 2007 to June 2009. Therefore, the company had to withdraw its shares because it didn’t fulfill the NYSE’s base trading price criteria.
- The company’s governmental conservatorship has existed since the Great Recession.
- Many companies’ stockholders eagerly anticipate their liberation from governmental control so they can trade their shares on free markets.
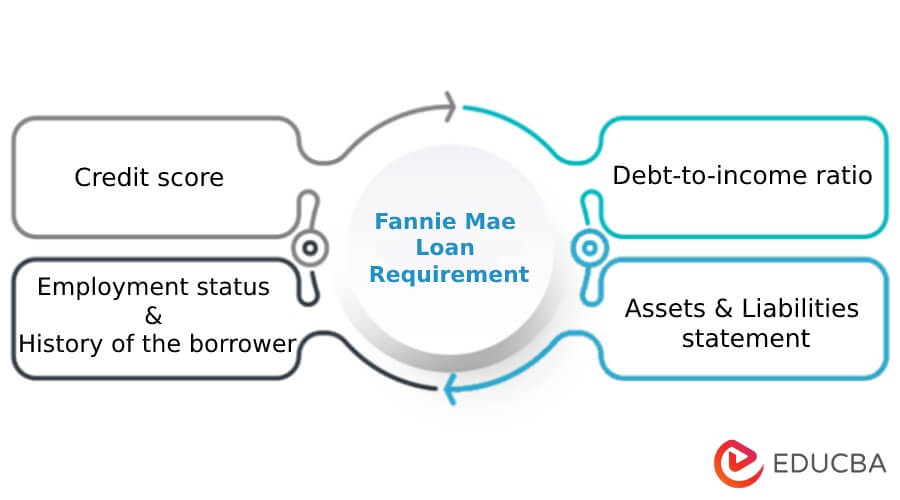
Fannie Mae Guidelines – Eligibility
- Before applying for a loan, borrowers should check their credit score and ensure it equals or exceeds 620
- A maximum value of 45% on the debt-to-income ratio is acceptable. However, as an exception, it should not exceed 50%
- At least a two-year stability in the borrower’s employment/business status is necessary.
- Additionally, the debtor should have an available six-month cash reserve to repay the loan in case they lose their job.
- The borrower must have mortgage insurance if they agree on less than a 20% down payment.
- Other eligibility requirements include property and occupancy type, loan limits, etc.
Fannie Mae Guidelines – Loan Limits
- The provided loans must adhere to the yearly conforming loan restrictions published by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA)
- There are specific maximum loan limits for different states based on various criteria.
- Conforming loan limits range from $647,200 to $1,867,275. The range is wide as it differs for the state you apply for the refinance
- The FHFA increased the loan limit in 2022 to $647,200, which in 2021 was $548,250
- These limits are subject to change yearly. Therefore, one can check a detailed list of loan amounts on its website.
- No minimum initial loan amount is necessary for a full loan with Fannie Mae.
Fannie Mae Guidelines – Mortgage Rates
- Since the start of 2022, rates have increased by more than two points, mainly due to the Federal Reserve raising loan prices. Thus, the company forecasts that the average interest rate on a 30-year mortgage will drop to 4.5 in 2023
- According to the prediction, home sales will experience a dramatic decline in the following year. As a result, it will fall from a national average annual rise of 19.4% in the second quarter to 4.4% by the fourth quarter of 2023.
Freddie Mac vs. Fannie Mae
Freddie Mac
- It purchases mortgages from small banks
- The expansion of the secondary mortgage market was the reason for its creation.
- The down payment limit for loans is a minimum of 3%
- It offers Home Possible loans with certain limitations and requirements.
Fannie Mae
- It buys mortgages from major financial institutions
- The purpose of its formation was to provide housing with affordable funds
- It has a down payment limit of 5% and more
- It offers HomeReady mortgages with specific guidelines and eligibility.
Benefits of Fannie Mae
- Small and medium-income range people can easily avail of loans
- Incredibly competitive rate of interest compared to other mortgage lenders
- Low down payment options
- The market is for lenders to sell their loans and get capital and liquidity in their hands.
- Better interest rates on loans when going for refinancing options, eventually reducing your monthly repayment amounts.
- The borrower can modify loan terms to avail of applicable interest rates. They can also extend/reduce the tenure of the loan or add previously due balances to the principal and repay in the future.
Fannie Mae Mortgage Programs
HomeReady
- It is accessible to both new and returning home purchasers
- One can purchase a home or renegotiate the interest terms using a down payment or preexisting credit
- The borrower’s combined income cannot exceed 80% of the local median household income because the loan is to assist low-income clients
- If there is a first-time homeowner among the applicants, the down payment can be 3% without regard to income.
HomePath
- It lists real estate properties that Fannie Mae took ownership of to resell
- These properties may need some remodeling but are a fair bargain
- It provides the mortgage for as low as a 3% down payment while yielding 3% closing costs.
Tenant-In-Place Rental Program
- It allows tenants of properties undergoing foreclosure to keep paying ground rent.
- One can retain the rental contract in some circumstances or have the option to enter into a new rental agreement.
- The offered leases come with month-to-month options and ones valid for a set period.
HomeStyle Renovation
- People can opt for this program when they want funds to renovate their homes.
- The renovation project can include any minor repairs to large-scale updates.
- The debtors can claim the funds even before starting project work
- The interest rates are competitively low and affordable.
Conclusion
Fannie Mae is a primary provider of mortgage finance in the US. It buys mortgages from lending institutions and contributes to the ease with which money enters the real estate market. It does so by creating and guaranteeing mortgage-related securities. In addition, it also provides loan options for existing homeowners looking to upgrade. It saves valuable money so regional and national banks can keep making mortgage loans. It further facilitates the process for millions of Americans to obtain foreclosures.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Is Fannie Mae a government agency?
Answer: No, Fannie Mae is not a government agency. However, after the great recession, it was off the stock market, and since then, it has been a government-sponsored organization. It is under the Federal Housing Finance Agency’s supervision.
Q2. What is the primary purpose of Fannie Mae? Why is it important?
Answer: The primary purpose of Fannie Mae was to establish an affordable mortgage organization for the citizens. It issues debt instruments and mortgage-backed securities to provide market liquidity. As it buys mortgages from financial institutions, community banks, and other lenders, thus, they can continue to offer credit.
Q3. How many Fannie Mae loans can a person have?
Answer: A person can obtain up to ten loans from Fannie Mae to finance their property. According to the Federal National Mortgage Association, there was an increase in the maximum number of loans allowed from four to ten. However, even though one can secure the maximum loans permitted, it can lead to challenges.
Q4. What happened to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac?
Answer: Shareholders nominally own Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, but since the Great Recession, they have been under governmental conservatorship. Many firms’ stockholders eagerly await their release from governmental supervision to trade their shares on open markets.
Q5. What is a delayed financing exception?
Answer: In delayed financing exceptions, homeowners can apply for cash-out refinancing if they make advance payments. They may also have an impact on one’s cash-out refinance. Borrowers who bought the property within the last six months can qualify for a cash-out to refinance, given that all conditions are satisfied.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Fannie Mae. Here we discuss its definition, purpose, working, eligibility, limits, and more. Have a look at the following articles to learn more –