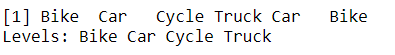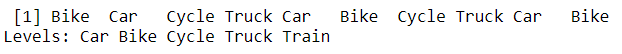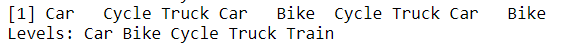Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Factors in R
Factors in R programming language is a type of variable that is of limited types in the data set. Factor variables are also resembled as categorical variables. The factor variables in R have a significant impact on data processing and data analysis. Machine learning algorithms process the factors differently as compared to continuous data. As a programmatic approach of the factor variables are converted to a corresponding integer variable while developing and generating the machine learning models and again mapped to its character values to represent the predictive analysis. An example of factors in R can be the group type of a particular product which is denoted as category1,category2,category3 in the data set.
Advantages of a Factor
- It can store both integers and strings
1. In the case of integers
data = c(5,6,6,6,7,5,7,6,7,5,6,7)
factor_data = factor(data)
factor_data
Output
2. In the case of strings
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"))
y
Output
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"),levels = c("Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Train"))
y
Output
- Very useful when the columns have a limited number of unique values
| Name | Mode of Travel |
| John | Truck |
| Shaw | Car |
| Lee | Cycle |
| Musan | Bike |
| Lozy | Truck |
| Riya | Car |
| Mij | Cycle |
Here we have a limited number of unique values in column 2.
- It helps to rectify the strings with typos (Typing Errors).
How to Create a Factor in R?
We can create factors by using code factors ().
Explore more about factor().
factor(x = character(), levels, labels = levels, ordered = is.ordered(x))
Where,
X is a set of categorical data. As we already discussed it should be a string or integers.
Levels are set of value which can be taken by X. Levels contains all the unique value available in the column (x).
Labels as the name suggest labeling of the data available at X.
Ordered determines if the levels should be ordered in any particular order.
Example #1
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"))
y
Output:
Example #2
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"),levels = c("Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Train"))
y
Output:
In example 2 we can see that we can define “Levels” also.
Now let’s see more about factors by using Str(y).
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"),levels = c("Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Train"))
y
Output:
str(y)
Output:
It is clearly seen that factors are stored as integer vectors and levels are stored as a character vector, and the individual elements are actually stored as indices.
- Now we will see how to access components of a factor
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"),levels = c("Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Train"))
y
Output:
y[2] # helps to access 2nd element
Output:
x[c(3, 4)] # helps to access 3rd and 4th element
Output
x[-1] # access all except 1st element
Output:
- Now we will see how to modify a factor.
y = factor(c("Bike","Car","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Car","Bike"),levels = c("Car","Bike","Cycle","Truck","Train"))
y
Output:
y[3] = "Truck" #modifty third element
y
Output
Adding to a factor:
y[10] = "Car"
y
Output:
Please note that we can’t assign anything in a factor that is not a part of the levels.
y[4] = "Plane"Warning message:In `[<-.factor`(`*tmp*`, 4, value = "Plane") : invalid factor level, NA generated
Output:
In this example we can see that “Plane” is not a part of our level, hence we got a warning message which says “Plane” is an invalid factor level.
Convert Data into a Factor
Data Is Available in Plenty, and It Is Tough Every Time to Write Down a Complete Word in The Code, so For This, We Will Convert the Data Into a Factor First Then Convert the Factor Into a Character or Number as Per Our Convenience.
Let’s now work on some real data. Where we have 50 observations and applicants provide their work direction. Like John travel towards north for his job duties or Sam travel towards South direction for his work duties.
direction <- c("West", "East", "North","West", "South","East","South","East", "South","East", "South","West", "South","East","South","East", "South","South","West","East", "South","West", "South","East","South","East", "South","West","East", "South","West", "South","East","South","East", "South", "South","West", "South","West","East", "South","West", "South","East","South","East", "South", "South","West")
direction.factor = factor(direction)
direction.factor
Output:
Levels: East North South West
Now if we want to convert the factor into a character vector:
We will use as.character() code.
as.character(direction.factor)
Output:
Or we want to convert the factor into a numeric vector:
We will use as.numeric() Code.
as.numeric(direction.factor)
Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Factors in R. Here we discuss the introduction, Advantages of a factor, How to create a factor in R along with the Outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–