Updated August 22, 2023
Exponential Moving Average Formula (Table of Contents)
What is the Exponential Moving Average Formula?
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a moving average that gives more weight to the recent data than the simple moving average. It is also known as the exponentially weighted moving average. Giving more weight to the most recent data makes the EMA sensitive to recent price changes. Calculating the EMA requires a multiplier, and the calculation needs to start with a simple moving average.
Traders use the EMA as a technical indicator to obtain buy and sell indicators based on historical averages. Traders usually use 20 days, 30 days, 90 days, and 200-day moving averages.
Formula –
Example of Exponential Moving Average Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the exponential Moving Average Formula calculation in a better manner.
Below we will look at different ways exponential moving averages can use. We can calculate the moving average for one day; in another example, we look at how different weights impact the data. And in the third example, we look at the volatility of data using moving average for three and seven years and exponential moving average assigning different weights.
Exponential Moving Average Formula – Example #1
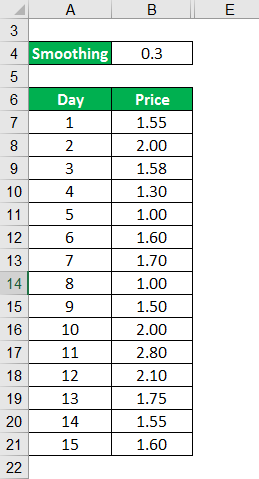
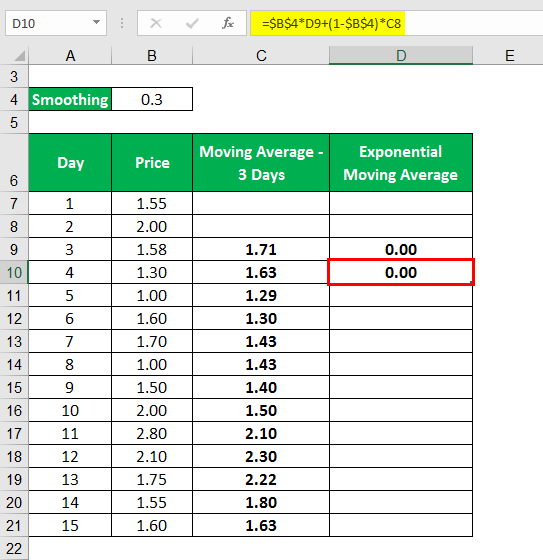
Let us understand this concept by looking at a simple example. Consider the price of a commodity for the next ten days. Let us calculate a 15 day EMA considering Day 1 as the oldest and D15 as the latest value.
Solution:
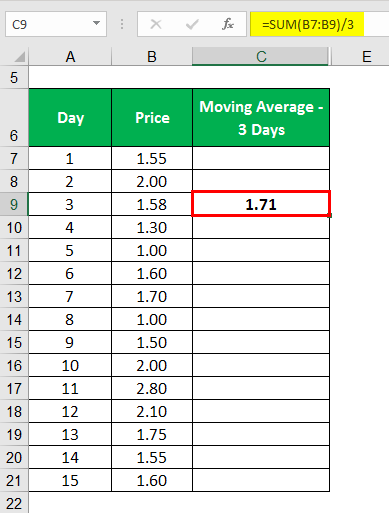
First, we calculated the Moving average of three days. Then using the moving average, we calculated the exponential moving average.
The moving average is calculated as
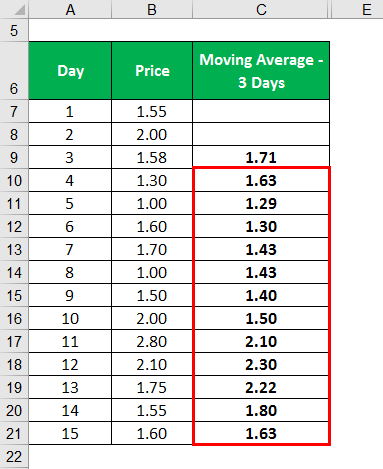
Similarly, we will Calculate the below.
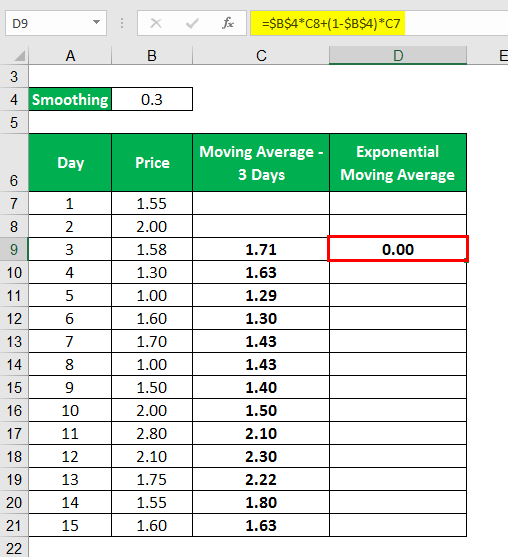
The exponential Moving Average is calculated as
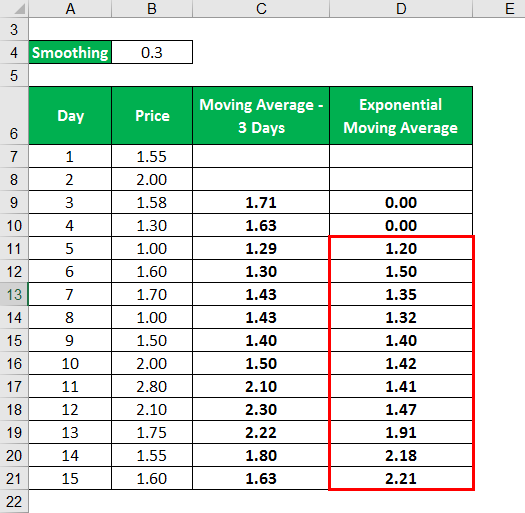
Calculating as the same,
Similarly, Calculated as below.
Similarly, the calculation of the remaining days can be done.
Exponential Moving Average Formula – Example #2
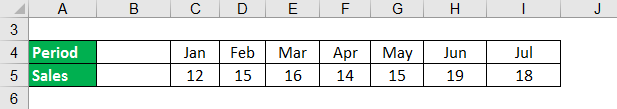
Let us use the sales data below to forecast revenue for April through July using trend projections and simple exponential smoothing. Let us calculate what length of moving average and smoothing constant works best.
Solution:
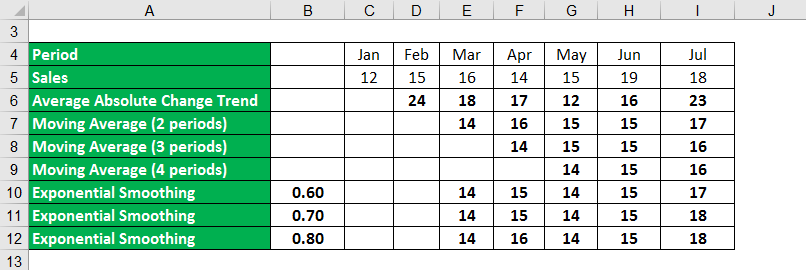
In the above example, we have calculated the absolute change trend and moving average of two, three, and four periods by taking the average using those periods. To calculate the exponential average using the smoothing method, we have considered the alpha to be 0.6, 0.7, and 0.8. Using these as weights, we have calculated the average.
- Step 1: Calculate the moving average for two periods in March – SUM({12,15})/2
- Step 2: Calculate the exponential moving average for March- 0.6*15+(1-0.6)*12
Exponential Moving Average Formula – Example #3
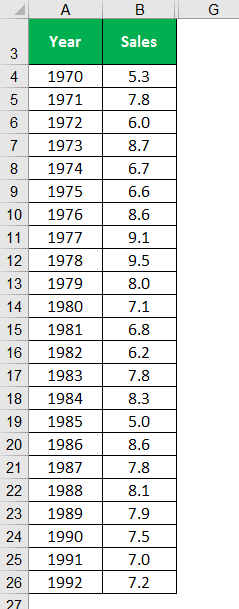
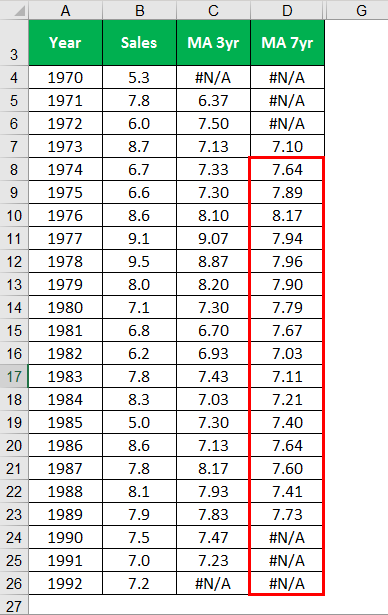
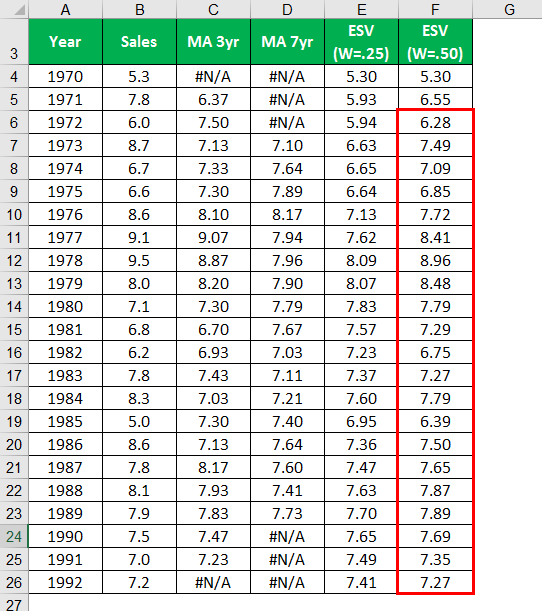
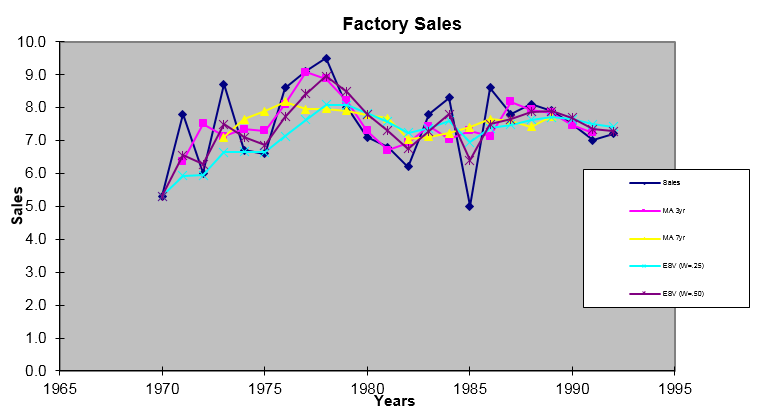
Below are the years and the factory sales of firm A. Let us calculate the ESV using 0.25 and 0.50 weights and plot a graph to understand these trends.
Solution:
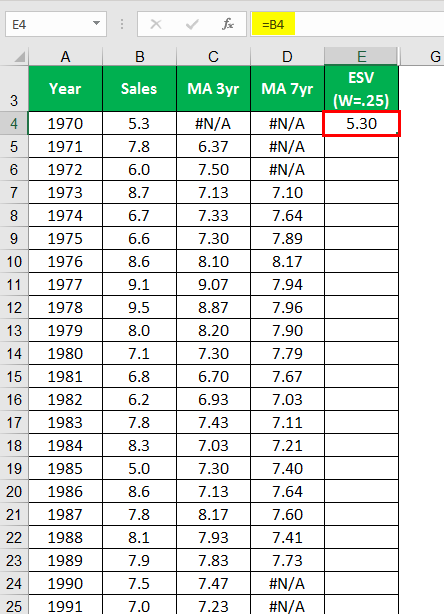
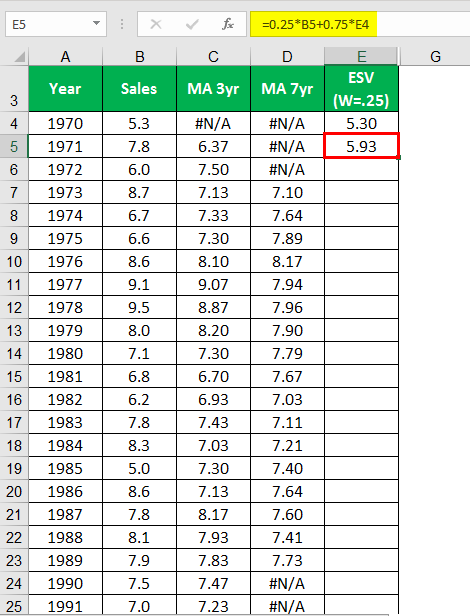
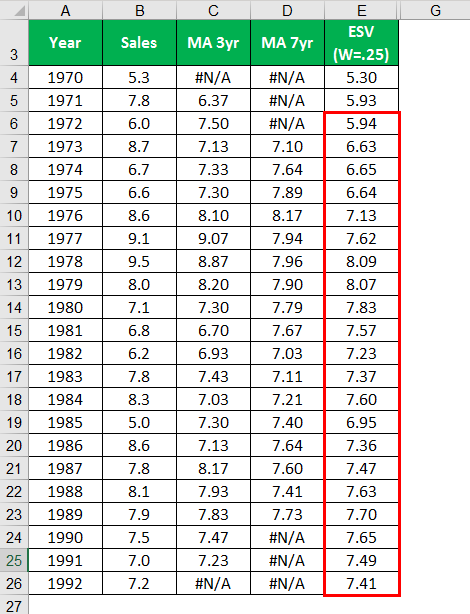
MA for three years is calculated by using the average function in Excel; similarly, MA for seven-year is calculated. The exponential moving average for (W = .25) is calculated by giving 0.25 weight to the sales and 0.75 to the value obtained by the exponential average. While ESV at 0.5 gives equal weight to both the sales and the value obtained by the exponential average.
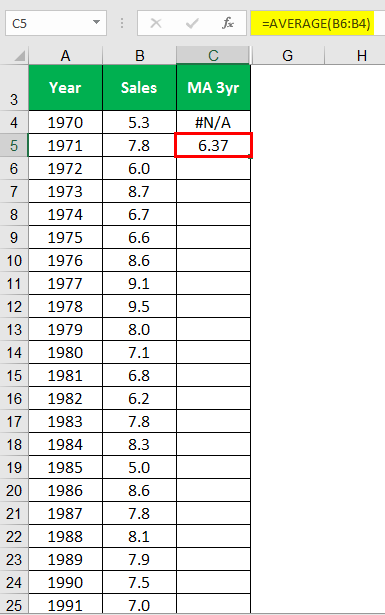
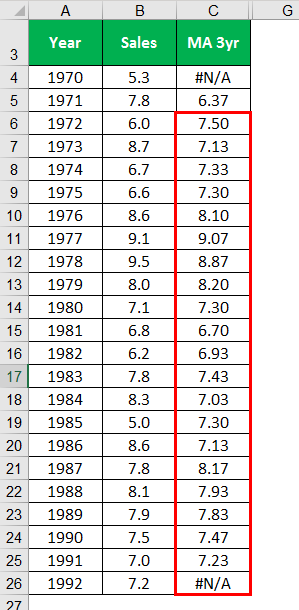
Calculating Moving Average 3 years for the year 1971.
Similarly, calculate for all the years.
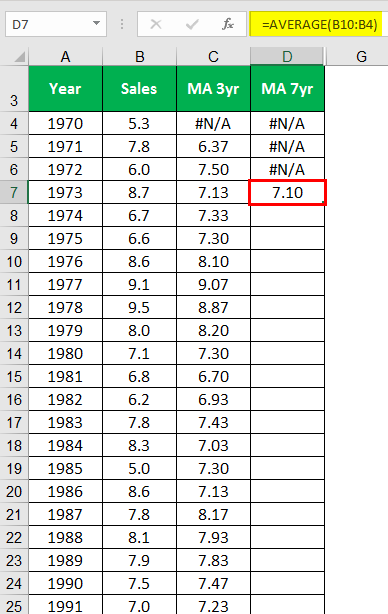
Calculating the Moving Average 7 years for the year 1973.
Similarly, calculate for all the years.
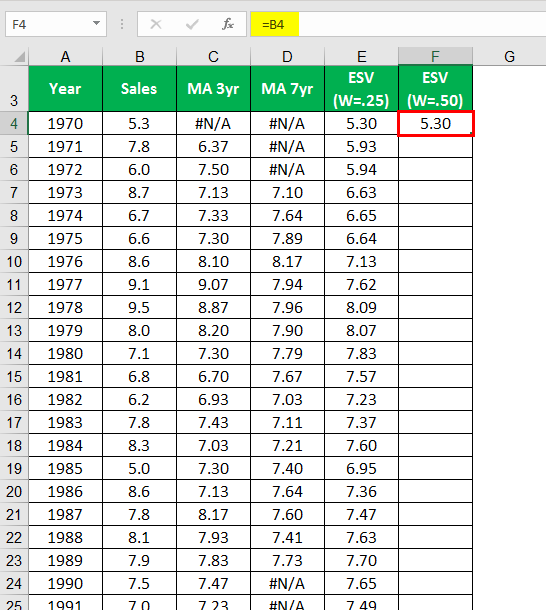
Calculating ESV (W=25) for the year 1970.
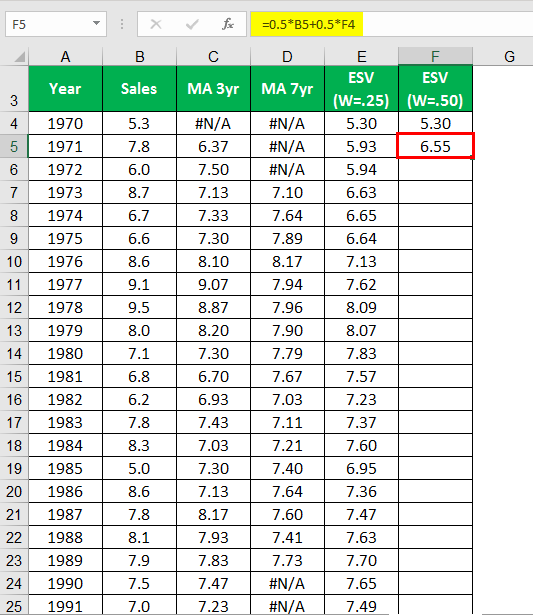
Calculating ESV (W=25) for the year 1971.
Calculating, Similar to all the remaining years.
Calculating ESV (W=50) for the year 1970.
Calculating ESV (W=50) for the year 1971.
Calculating, Similar to all the remaining years.
Take a close look at the above graph; we observe that the sales are very volatile when taken without any average; while using the weights, we can see that the lines have averaged out and are more smooth even when compared to the moving average.
Explanation
The formula for Exponential Moving Average can calculate by using the following steps:
Step 1: Calculate the Simple moving average for a particular period. The calculation of the simple moving average is quite straight forward. First, we simply find the closing prices of the stocks for a particular period. Then we divide the total sum of all these prices with the same number of period.
Step 2: Next, calculate the multiplier for finding weights. This is calculated as ( 2 / ( time period + 1)). So if we want to calculate the moving average for 90 day period, we will calculate the multiplier as ( 2/(90 + 1)) = 0.021.
Step 3: Now, finally, to calculate the EMA, we will use the formula above – (Closing Price – EMA of the previous day) * multiplier + EMA of the previous day.
Relevance and Use of Exponential Moving Average Formula
The exponential Moving Average is suitable for markets that are trending. Traders use these EMA’s with other indicators to comprehend the trend. It is particularly important for traders and trending, fast-moving markets.EMA is an important indicator for analyzing trends in commodities. It is known that EMA’s are prone to recency bias. However, there is still a conflict between the traders; more emphasis should be given on old data, or emphasis should be given on new data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Exponential Moving Average Formula. Here we discuss calculating the Exponential Moving Average along with practical examples. We also provide an Exponential Moving Average, a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –