Introduction to Eval Function MATLAB
The following article provides an outline for Eval Function MATLAB. MATLAB is a programming environment which is interactive and is used in scientific computing. It is extensively used in a lot of technical fields where problem solving, data analysis, algorithm development and experimentation is required. Software which are discipline specific are extensively written using MATLAB.
What is Eval Command?
Eval command offered by MATLAB is amongst the most flexible and powerful commands in MATLAB. Eval (short form for evaluate) is used to evaluate MATLAB expressions. For all the commands that we can execute using MATLAB prompt, we can make use of ‘eval command’ to execute these commands using M-file. Please remember that MATLAB suggests the use of MATLAB language constructs and functions rather than using eval command as the code can become difficult to understand and debug if we use eval command.
Syntax:
[out1, out2, ..., out N] = eval (exp)
Description:
- ‘eval command’ will evaluate the output for expression passed in the argument.
- We can concatenate sub strings & variables using parenthesis to construct an expression.
- If we want to use a catch expression in case of an error, we can use the syntax:
eval (exp, catch_expr)
Examples of Eval Function MATLAB
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
In this example, we will save data to new files which will be incrementally numbered.
- Declare name and extension of the files to be created.
- Use a ‘for loop’ for creating new files and use eval command to evaluate the expression.
Code:
newFile = ‘learnEval’;
[Declaring the name of our files]fileExtension = ‘.dat’;
[Declaring the extension of our files]for files = 1 : 5
[‘for loop’ to create 5 new files]filename = [newFile, int2str (files), fileExtension];
eval ([‘save ‘, filename , ‘ files’])
end
[In the above code, ‘eval command’ is used to ‘save’ the newly created files with the names as defined by input variable ‘filename’]Input:
newFile = 'learnEval';
fileExtension = '.dat';
for files = 1 : 5
filename = [newFile, int2str(files), fileExtension];
eval (['save ', filename , ' files'])
end
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained 5 new files using ‘eval command’, with the names and extensions as passed by us.
Example #2
In this example, we will generate a sequence of 4 matrices ‘eval1’, ‘eval2’, ‘eval3’ and ‘eval4’ using ‘for loop’ and ‘eval command’.
- Use a ‘for loop’ to declare names of our matrices and use ‘magic’ command to create matrices.
- Use eval command to evaluate the above expression.
Code:
for n = 1:4
[‘for loop’ to create 4 matrices]learnEval = [‘eval’, int2str (n),’ = magic (n)’];
eval (learnEval)
end
[In the above code, ‘eval command’ is used to evaluate the ‘learnEval’ expression and create 4 matrices of dimensions 1×1, 2×2, 3×3 and 4×4]Input:
for n = 1:4
learnEval = ['eval', int2str(n),' = magic (n)'];
eval (learnEval)
end
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained 4 matrices using ‘eval command’, with the names and dimensions as expected by us.
Example #3
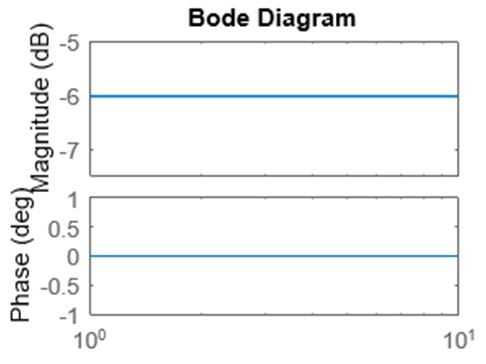
In this example, we will create a bode diagram using numerator & denominator passed by us.
- Ask for numerator.
- Ask for denominator.
- Pass the above 2 inputs and the command to create bode diagram inside ‘eval command’.
Code:
numInput = input (‘Please enter numerator: ‘);
[Asking for the numerator]denInput = input (‘Please enter denominator: ‘);
[Asking for the denominator]eval ([‘bode (‘ , mat2str (numInput), ‘,’ , mat2str (denInput) , ‘) ‘])
[In the above code, ‘eval command’ is used to create a bode diagram using 2 inputs entered by us]Input:
numInput = input ('Please enter numerator: ');
denInput = input ('Please enter denominator: ');
eval (['bode(' , mat2str(numInput), ',' , mat2str(denInput) , ') '])
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained a bode diagram using ‘eval command’.
Example #4
In this example, we will execute size function for a 3 D array using ‘eval command’
Code:
A = ones (3);
[Initializing the input array]A (:, :, 2) = A’;
[Array1, Array2, Array3] = eval (‘size (A)’) [Defining the output variables] [In the above code, ‘eval command’ is used to execute the size function for the input array]Input:
A = ones (3);
A (:, :, 2) = A';
[Array1, Array2, Array3] = eval ('size (A)')
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained the size of each dimension of the array using ‘size function’ as a command inside ‘eval’.
Conclusion
‘Eval Command’ can be used in MATLAB to evaluate an expression passed as an argument inside the parenthesis. Along with the expression, the input variables are also passed to get the desired output. Please remember that in its latest versions, MATLAB recommends language constructs and functions as better option than using Eval command.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Eval Function MATLAB. Here we discuss what is eval command? along with programming examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –