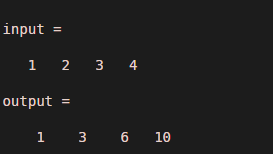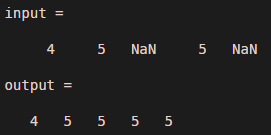Introduction to Cumsum MATLAB
Cumsum stands for the cumulative sum of elements. It gives the overall addition of elements trough an array or set of elements. It is used for a range of numbers or sets of random numbers. The output of the cumsum is completely dependent on the nature of input elements. If input numbers are in vector form them it gives output in vector form only. If input numbers are in matrix form then it gives output in matrix form. And if the input is in a multidimensional form then it gives output in a multidimensional matrix. There are three properties of cumsum such as dim, direction, and nanfflag, and cummax is used to eliminate Nan Values from the input.
Syntax
- Output = cumsum ( input ) Output variable name = cumsum ( input variable name )
- Output = cummax ( input ) Ouput variable name = cummax ( input variable name)
- Output = cumsum ( input matrix , 2 ) output variable name = cumsum ( multidimensional input , dimension )
- Output = cumsum ( input , reverse ) output variable name ( input, direction ), the direction can be forward or reverse.
Why we use Cumsum MATLAB?
Cumsum is a very effective command in Matlab, which is used to do the cumulative sum of given elements or numbers. It is easy to do the addition of limited elements but if the data is big and elements are complex then cumsum plays an important role. it is mostly used in statistics. It outperforms in statistical operation along with mean, average, variance, etc.
Examples to Implement Cumsum MATLAB
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Let us consider one simple example of a vector. The vector is initialized as variable input. Here the input is a range of values from 1 to 4. As the input is in the form of vector then the output will also be in the form of vector only. In output value of output (1) is input (1), the value of output (2) is the addition of input (1) and input (2) and value of output (3) is the addition of input (1), input (2) and input (3), similarly, the value of output (4) is the addition of input (1), input (2), input (3) and input (4). Matlab program of example 1 is given below.
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
input = 1 : 4
output = cumsum (input)
Output:
Example #2
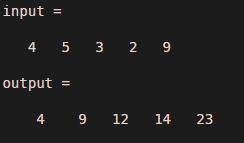
In this example, we have considered some random values in vector ‘input’ which are 4, 5, 3, 2, and 9 . in previous example input values are linear but these values are nonlinear still cumsum performs the same operation. as input is in the form of vector then the output will also be vector. Matlab program for example 2 is given below.
Code:
clc ;
clear all ;
input=[4 5 3 2 9]
output = cumsum (input)
Output:
Example #3
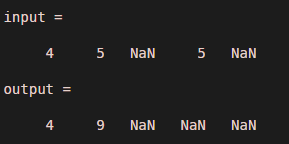
Let us consider one vector with NaN values .suppose input vector is 4, 5, Nan, 5 and Nan, that means there are total five elements present in the input, so it will show addition with Nan is Nan only which is logically wrong .therefore we need to ignore all the Nan values. To ignore Nan values there are two ways one is by using command ‘omitnan’ and second is by using command ‘cummax’. Example 3 shows both the implementations in Matlab.
Code – without ignoring Nan values
clc ;
clear all ;
input = [ 4 5 NaN 5 NaN ]
output = cumsum (input)
Output:
Code – Ignoring Nan values
clc ;
clear all ;
input = [ 4 5 NaN 5 NaN ]
output = cummax (input)
Output:
Example #4
Now let us consider input is in the form of matrix .let input is two by two matrix, then obviously output will be in the form of matrix only that is multidimensional data. In such cases we need to give one more parameter which is a dimension that is 1 or 2, if the dimension is 1 then matrix addition will be column-wise( illustrated in example 4 (a)) and if a dimension is 2 then matrix addition will be row-wise( illustrated in example 4 (b)). If we don’t give any dimension along with input then addition will be column-wise only. ( illustrated in example 4(c))
Code #1
clc ;
clear all ;
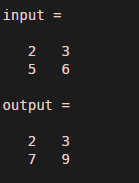
input = [2 3 ; 5 6]
output = cumsum(input,1)
Output:
Code #2
clc ;
clear all ;
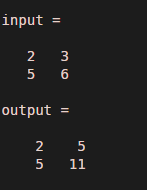
input = [ 2 3 ; 5 6 ]
output = cumsum ( input, 2 )
Output:
Code #3
clc ;
clear all ;
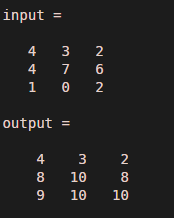
input = [ 4 3 2 ; 4 7 6 ; 1 0 2 ]
output = cumsum ( input,1 )
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen cumsum command with its features like cummax, dimensions, and direction. Cumsum command accepts all types of input, there is no limitation in accessing input it accepts single values, arrays, vectors, multidimensional values, and Nan values.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Cumsum MATLAB. Here we discuss the inroduction to Cumsum MATLAB, syntax, how does it work with examples to implement. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –